Environment Fishery
A study at the University of Oregon suggests that parasites in fish, including a threatened species of Oregon coho salmon, may have a greater impact on fish health than previously believed. Chronic parasite infection could be increasing the mortality in salmon and other fish species, leading to another factor in declining stocks.
Mike Kent, a University of Oregon microbiologist, who is the main author of the study says: “We’ve known for a long time that salmon and other fish are affected by parasites, so that isn’t new… parasites have been present for decades, they have often been dismissed as a cause of increasing salmon mortality.”
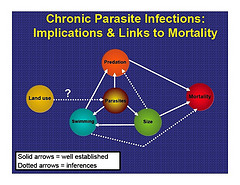 The study, which took place on the West Fork Smith River concluded that heavy loads of parasites can affect salmon growth, weight, size, immune function, saltwater adaptation, swimming stamina, activity level, ability to migrate and other issues. Parasites drain energy from the fish as they grow and develop.
The study, which took place on the West Fork Smith River concluded that heavy loads of parasites can affect salmon growth, weight, size, immune function, saltwater adaptation, swimming stamina, activity level, ability to migrate and other issues. Parasites drain energy from the fish as they grow and develop.
“But we’re now getting a better appreciation that it’s the overall parasite load that is so important,” Kent says. “The higher levels of mortality only show up with significant increases in the parasite burden.”
(Image courtesy University of Oregon)
Kent says the number of parasites affecting salmon in Oregon rivers has been increasing slowly over the years, due to warmer waters and more nutrients in the water that can be a result of logging, agriculture, inadequate bank protection and other land use changes over many years.
“Salmon can actually tolerate a fairly wide range of temperatures, it’s not just the fact a stream is warmer that’s killing them, in and of itself,” Kent says. “We now believe that some of these forces are leading to heavier parasite loads. This could be important in understanding declining salmon populations.”
Parasites that can infect salmon and other fish have complex life cycles, which could include passing through the intestinal tracts of birds that eat fish, then producing eggs that infect snails. The snails thrive in warmer water where fertilizer runoff provides them nutrients.
The salmon eat the snails, completing the cycle.
The impact of parasites on fish health was much more severe in parts of the West Fork Smith River where water moved more slowly and nearby logging and agricultural practices increased water temperature and nutrient loads. Fish in those areas had parasite infestations about 80 times higher than those higher up in the tributary.
The infections impact the salmon’s ability to survive, especially if juvenile fish are infected, that reduces their ability to survive the winter and also affects swimming ability, meaning the juvenile fish are more vulnerable to predators.
.
“Understanding why certain salmon populations are heavily infected with these parasites, which likely are driven by landscape characteristics, could help in management or recovery planning,” the scientists wrote in their conclusion, “given that our data indicates that severity of these infections are associated with survival.”
The study was done by scientists from OSU and the Oregon Cooperative Fish and Wildlife Research Unit. The corresponding author was Jayde Ferguson, a doctoral student in the OSU Department of Microbiology, and other collaborators included researchers from the OSU Department of Statistics, College of Veterinary Medicine, and Carl Schreck in the Department of Fisheries and Wildlife. The research was supported by the Oregon Department of Fish and Wildlife.The study will be published soon in the journals Aquaculture, Journal of Parasitology, and International Journal of Parasitology.
