The long awaited Kitimat air shed study, released by the province Friday, July 17, 2014, says “that with proper management, Kitimat’s ai rshed can safely accommodate new industrial growth” without major affects on either human health or the environment.
Link to news release : Study shows Kitimat airshed can handle new industrial development
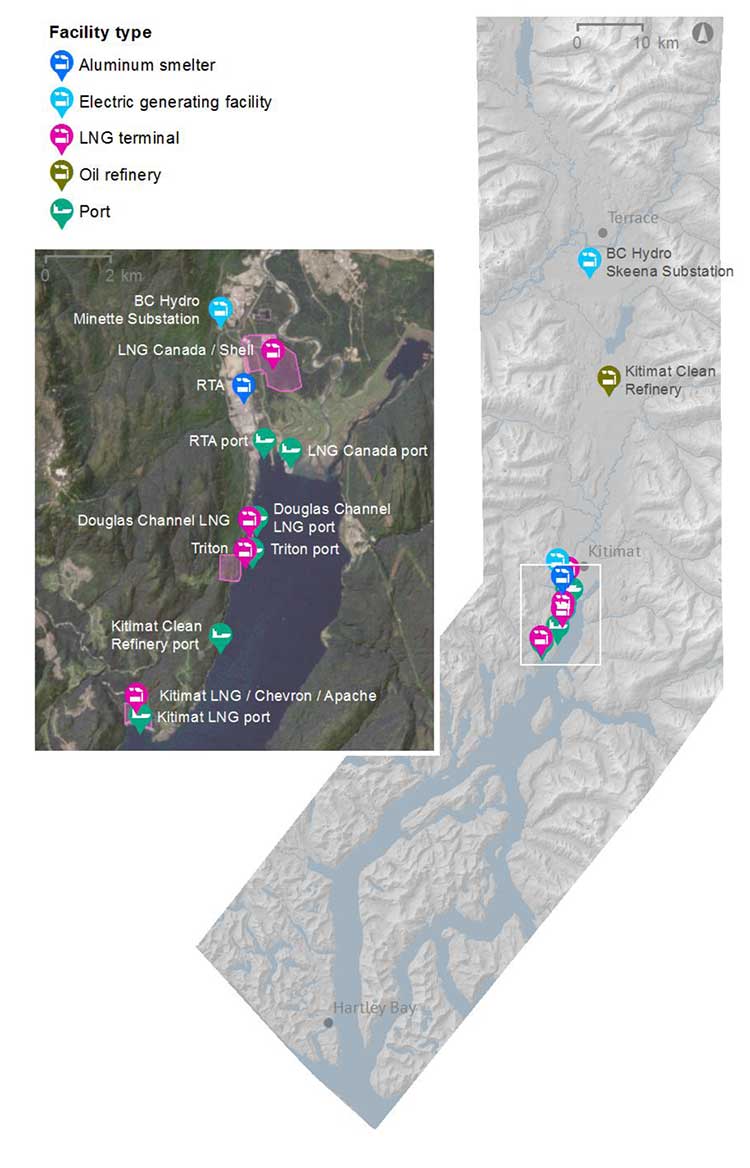
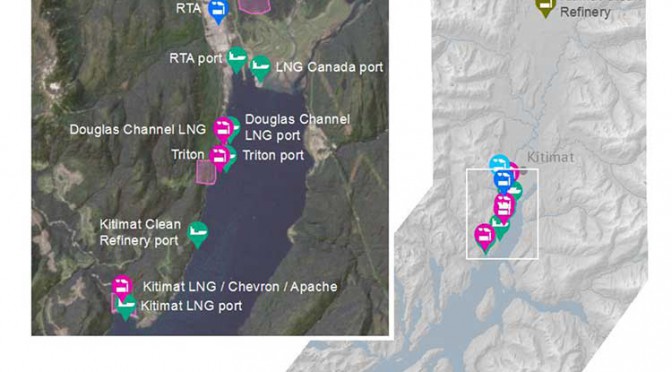
The Kitimat Airshed Assessment looked at the cumulative effects of industrial air emissions, primarily sulphur and nitrogen oxides, and their potential impacts on both human health and the environment from
- Rio Tinto Alcan’s existing aluminium smelter and its planned modernization
- David Blacks proposed “Kitimat Clean” oil refinery at Onion flats
- Four proposed LNG facilities; Shell-led LNG Canada, Chevron lead Kitimat LNG, the floating Douglas Channel LNG at the old log dump and a second floating LNG project called Triton.
- BC Hydro gas turbine powered electrical generation facilities in Kitimat and near Terrace
- Predicted increased to marine shipping in Douglas Channel.
The study was divided into two zones.
Health results were first examined for Kitimat townsite, the Kitimat Industrial Service Centre and Kitamaat Village.
The wider study included Gitga’at Old Town, Hartley Bay (Kulkayu), Kitimat-Stikine, Kitselas, Kitsumkaylum, Kshish, and Terrace.
Enbridge missing
There was one big factor missing from the study, it does not include the Enbridge Northern Gateway project, although the consultants who did the study do cite a couple of the air quality studies that Enbridge filed with the Northern Gateway Joint Review Panel. That despite the fact the Joint Review Panel under Condition 82 required that Enbridge file with the NEB for approval, at least four months prior to commencing construction, “an Air Quality Emissions Management and Soil Monitoring Plan for the Kitimat Terminal.”
The JRP report acknowledged that emissions from the Enbridge terminal would be minimal but would contribute to the cumulative effect of pollutant emissions from other industries and required Enbridge to consult with the District of Kitimat, the environment ministries and other industries in planning for emissions.
The map from the airshed study also shows that the possible marine terminal for David Black’s proposed Kitimat Clean refinery project is at or close to where the proposed Enbridge Northern Gateway terminal would be.
Health and environment
The study looked at proposed emission levels and the effect of emissions elsewhere in the world and then compared those studies with the Kitimat Valley. It found that the risk of sulphur dioxide was “directly related to proximity to industrial area”–largely the Kitimat Service Centre area–and that there would be a minor increase in respiratory incidents of 0.5 per cent to 2 per cent, with a slight increase of nitrogen dioxide but those were within existing guidelines.
As for environmental impact, the study says nitrogen dioxide impacts will be low. There wil be “some increased risk of soil impacts” from sulphur dioxide. The study says there will be “no negative impacts to vegetation across all scenarios” but did find “potential for acidification” of seven small lakes. Lakelese Lake is not one of those affected.
The study also doesn’t include particulate matter and although it does consider climate change, did not take into consideration possible increase of green house gases in the Kitimat Valley.
The consultants, Esssa Technologies of Vancouver, based its findings on an earlier study by Rio Tinto Alcan on emissions from the Kitimat Modernization Project and worked on those findings by adding new industries and a greater area to the models they used.
The province and industry says they will continue to monitor air, water, soil and vegetation “to ensure these values are protected.”
The higher levels of sulphur dioxide emissions from the Rio Tinto Alcan Kitimat Mondernization Project will be allowed to continue under the current permit. Environment Minister Mary Polack told reporters that will only change if the current court challenge to the sulphur dioxide levels are successful.
| What Northern Gateway Joint Review said about emissions in the air shed | |
| Among the 209 conditions imposed on the Enbridge Northern Gateway project is No. 82, an Air Quality Emissions Management and Soil Monitoring Plan.
Northern Gateway must file with the NEB for approval, at least 4 months prior to commencing construction, an Air Quality Emissions Management and Soil Monitoring Plan for the Kitimat Terminal…
One of the things that the Joint Review Panel noted in requiring Enbridge Northern Gateway to have an updated plan and to collaborate with Kitimat and other industries is that levels of acceptable sulphur doixide in the atmosphere are changing and much of Northern Gateway’s modelling was based on standards that were becoming obsolete. In the Joint Review Panel report, section 8.7, the JRP said:
The provincial air shed report considered only two contaminants, sulphur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide. Northern Gateway said there would be minimal atmospheric emissions from the construction and operation of the pipeline. The focus was on the Kitimat marine terminal.
Northern Gateway said there “no exceedances of hazardous air pollutant guidelines were predicted as a result of the project itself” but there could be a cumulative effect with other industries in the Kitimat waterfront. The Joint Review Panel ruled:
|
Related
Kitimat air shed study raises more questions than it actually answers


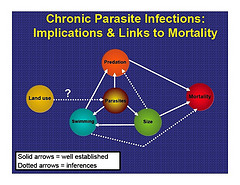 The study, which took place on the West Fork Smith River concluded that heavy loads of parasites can affect salmon growth, weight, size, immune function, saltwater adaptation, swimming stamina, activity level, ability to migrate and other issues. Parasites drain energy from the fish as they grow and develop.
The study, which took place on the West Fork Smith River concluded that heavy loads of parasites can affect salmon growth, weight, size, immune function, saltwater adaptation, swimming stamina, activity level, ability to migrate and other issues. Parasites drain energy from the fish as they grow and develop.