When the Russian container ship Simushir lost power in heavy weather west of Haida Gwaii last Thursday and driven by westerly winds came dangerously close to the rocky coast, Canada and British Columbia had to scramble to get vessels to the ship and try to tow it out of danger to Prince Rupert.
Like all other issues on the west coast, the debate is raging.

“Peter Lantin, president of the Haida Nation, told the media at the time, “It was luck.” On Tuesday, Lantin issued another statement, saying. ““Unfortunately, I don’t think anyone considers 20 hours a world class response time. The fact of the matter is that the federal government has little interest in protecting the west coast. From all indications their policy is to calculate an oil spill as an acceptable loss, based on a business model, not on the reality that coastal British Columbians live every day.”
It appears that the Simushir operation was lucky. The normal westerly winds that could have driven the ship onto the rocks of Haida Gwaii changed to southeasterly, keeping the Simushir off shore.
The American heavy duty tug Barbara Foss just happened to be available. The Barbara Foss was towing a cargo barge between Prince Rupert and Whittier, Alaska. The barge was left in Prince Rupert and the tug headed out off the coast of Haida Gwaii a trip that took about 48 hours. (There are also heavy duty Smit tugs at Prince Rupert which joined the operation on Hecate Strait to escort the Simushir into port. There are now reports that the Simushir‘s owners chose to hire the Barbara Foss rather than Smit)

It took the first Canadian Coast Guard vessel, the Gordon Reid, about 14 hours to reach the Simushir (according to Coast Guard officials the original report of 20 hours was wrong). The Gordon Reid did manage to get lines on the Simushir and pull the ship away from the coast, only have the tow lines part (break) three times. So the three Coast Guard vessels, two from Canada, the Gordon Reid and the Sir Wilfred Laurier and the US Coast Guard cutter Spar had to wait for the Barbara Foss to arrive.
Jonathan Whitworth, CEO of Seaspan, speaking to Mark Hume of The Globe and Mail, “it was just bad luck” that none of the tugs that regularly work up and down the west coast were available at the time.
Whitworth told The Globe and Mail that there are about 80 boats between Alaska and Vancouver that could have towed the Simushir to safety. He said that the fact there were no tugs in the immediate vicinity as a “fluke.”
“We certainly have large tugs operating in Haida Gwaii on log barges, for example. So it will be a 6,000-horsepower tug that would [typically] be in that area. It just so happened that over the weekend our two biggest tugs which transit that area were down south,” Whitworth told The Globe and Mail.
Whitworth said that permanently stationing tugs at Haida Gwaii would be both be unnecessary and too expensive.“If there had been a tug stationed in Haida Gwaii then it could have responded possibly quicker. But who’s going to pay for that? Surprisingly from a tug owner it’s not going to be [my view] that there should be a tug every 50 metres up the coast.”
Effective response
In a news release, Rear Admiral Dan Abel, commanding the US Coast Guard 17th District, Alaska said.
“The trusted partnership we have with our Canadian counterparts continues to be a vital component to protecting lives at sea and mitigating potential maritime emergencies. We are pleased this case ended with a positive outcome; preparing for the worst case scenario is the first step in an effective prevention and response plan.”
The question now being asked up and down the BC coast has the provincial or federal governments really have an effective prevention and response plan? If the BC coast had trouble handling a container ship in trouble, how is it ever going to handle a Very Large Crude Carrier loaded with diluted bitumen?
According to the US Coast Guard, although the Simushir was adrift off the coast of Haida Gwaii, the incident triggered Alaska’s emergency response plan. “Coast Guard Sector Juneau deployed six members, including the sector’s commander, to Ketchikan to establish the foundation for a unified command and to exercise their sub area contingency plan with state and local partners.”
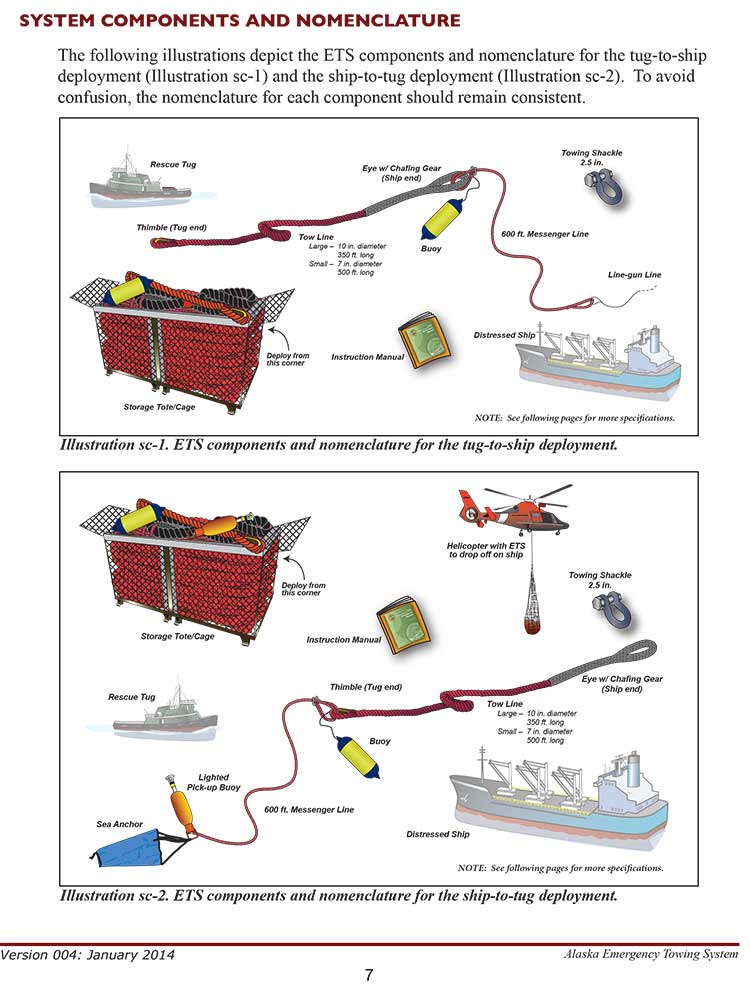
Key to Alaska’s response, is a system ready to go soon after a distress call is received. The Emergency Towing System (ETS) has prepackaged equipment that can be transferred to a disabled vessel either by helicopter or tug, depending on the size and position of the vessel in distress.

The United States Coast Guard deployed two of its Emergency Towing Systems last week to support the Simushir operation, one on a C-130 Hercules dispatched to Sandspit, the second on board the cutter Spar.
While the Alaska ETS systems were not used in the Simushir incident, how Alaska came up with the system is a lesson for British Columbia, for that state-wide program was started by the tiny municipality of Unalaska after a ship quite similar to the Simushir lost power and came within 15 minutes of running aground in Unalaska Bay.
Now just seven years later those Emergency Towing System packages are pre-positioned up and down the Alaska coast, while although Enbridge proposed the Northern Gateway in 2005, here in Canada both the provincial and federal governments make paper promises about a “world class” response system but so far nothing has happened.
Salica Frigo

The Salica Frigo incident in March 2007 was similar to the Simushir incident and like the Simushir, there was luck involved.
According to an Associated Press report at the time, quoting 2005 figures, Dutch Harbor and Unalaska was, for the 17th straight year, the United States leading fishing port for seafood landings in poundage. Commercial fishermen offloaded 887.6 million pounds of fish and shellfish in 2005. The value of its catch, $166.1 million, was second to New Bedford, Mass.
About three years earlier, another ship, the 225 metre (738-foot) Selandang Ayu experienced engine problems, shut off its engines, drifted and ran aground Dec. 9, 2004, in Skan Bay on Unalaska Island’s west side.
Six crewmen died when a US Coast Guard helicopter trying to rescue them crashed. The Selandang Ayu broke in two and spilled an estimated 321,000 gallons of fuel oil, contaminating 54 kilometres (34 miles) of coastline. AP reported that at the time of the Salica Frigo incident in 2007, the cleanup for the Selandang Ayu was more than $100 million.
The Salica Frigo was 135 metre (443 foot) Spanish-flagged ship, the same size as the Simushir.
On Thursday, March 8, 2007, the Salica Frigo was partially loaded with seafood and tied up at dock in Captain’s Bay in Dutch Harbor, Alaska Winds were from the north, from 30 to 40 knots gusting to 60 to 70 knots. The winds began to drive the Salica Frigo away from the dock and the local marine pilot, Capt. Stephen Moreno, consulting with the captain, ordered the ship to sea to ride out the winds. “He really didn’t have enough ground tackle to safely anchor,” Moreno told the AP.
The AP report says Moreno guided the Salica Frigo out to sea, plotted a safe course and then the pilot returned to port. At about, 3 am on March 9, the engine failed. It was not until an hour later, at 4 am, according to KIAL News the Salica Frigo’s captain called the marine pilots and the Coast Guard. North winds were blowing the ship back toward the harbor.
“If it had been from the south, he would have blown offshore,” Moreno told the AP.
The powerless ship drifted for more than three and a half hours toward the shore. Two tugboats came to the ship’s aid but could not establish lines to the stricken vessel.
Moreno and Coast Guard officials estimate the Salica Frigo was just 15 minutes from grounding when crew members were able to restart the engine at 6:43 a.m.
Emergency Towing System
Just weeks later, the Mayor of Unalaska, Shirley Marquardt created and convened a “Disabled Vessel Workgroup” that was tasked with developing a “an emergency towing capability for disabled vessels in the Aleutians using locally available tugboats and an emergency towing system.”
For a demonstration project from July 20 to August 1, 2007, Unalaska had put together and purchased a system suitable for vessels up to 50,000 dead weight tons (DWT) while the state, the the Alaska Department of Environmental Conservation was planning to purchase a system capable of towing vessel greater than 50,000 DWT.
In a news release (pdf) at the time of the exercise, the Alaska Department of Environmental Conservation, said
In the last decade, several distressed or stricken vessels in the Aleutian Islands have adversely impacted the community of Unalaska. In a few cases, these incidents were the cause of environmental and economic repercussions.
In each situation, the vessel was a large tramper or cargo type ship, generally carrying fuel in bottom tanks, thus posing a significant pollution risk. Roughly 67% of port calls to Unalaska/Dutch Harbor in 2004 were either container ships or tramper/reefer vessels.
“These accidents can be devastating to Alaska’s environment and communities. Our goal is to enhance the ability of local assets to respond to distressed vessels in need of assistance due to engine failure,rudder failure, or any other failure which compromises the safe navigation of a vessel,” said DEC Commissioner Larry Hartig.
Tugs not always ready

The other point in the 2007 ADEC news release is a note that tugs are not always equipped for operations such the one involving the Simushir
Generally tug boats (primary responders in this area) have some capability of retrieving vessels but they are not dedicated to this service and therefore the equipment aboard is not representative of equipment needs in this highly specialized situation. The recommended emergency towing system
will enhance local assets with the ability to respond to an emergency with all the proper equipment necessary to retrieve a distressed vessel.The Unalaska resident tugs Gyrfalcon and James Dunlap are the most consistent local assets in the Unalaska region, but there are many other tugs in the area at any one time and thus this system is intended to be universally deployable.
The demonstration project, a partnership between the town, the state, the Coast Guard and the private sector was successful.

In 2014, the Alaska Emergency Towing System project official website says
An Emergency Towing System (ETS) is a pre-staged package of equipment that may be deployed in the event a disabled vessel requires assistance in accessing a place of refuge. A manual that instructs responders on the operations of system as well as procedures for deployment accompanies the system. The system is designed to use vessels of opportunity to assist disabled vessels that are in Alaskan waters. It consists of a lightweight high performance towline, a messenger line used in deploying the towline, a lighted buoy, and chafing gear. These components may be configured to deploy to a disabled ship from the stern of a tugboat or airdropped to the ship’s deck via helicopter.
In December 2010, Unalaska’s plan worked, the town’s ETS system was deployed to assist the disable cargo vessel Golden Seas. “This equipment, along with the availability of an appropriate sized towing vessel helped avert a possible grounding.” the ETS website says.
Since 2007, the Alaska Department of Environmental Conservation has purchased and stored 10 inch Emergency Towing Systems at the USCG Air Station in Kodiak and Sitka, the Navy Supervisor of Salvage warehouse at Fort Richardson, and the Emergency Response warehouse in Adak, Alaska.

The Emergency Towing System can be deployed by helicopter or by tug. A helicopter can lower the tote or cage containing the towing gear onto the deck of the distressed ship. If the tote or cage is carried to the scene by a tug the crew the usual procedure is to use a helicopter to deploy the tote/cage to the distressed vessel or the tug crew. Depending on the circumstances, and although it is not part of the regular system, the tug crew can also line-gun projectile across the deck of the distressed ship so the crew can pull a “messenger line” attached to the tow line on board.
And as for Canada, Gail Shea, Minister of Fisheries and Oceans, answering questions in the Commons Monday about the Simushir incident did nothing more than speak off a prepared script, answering two questions from Nathan Cullen, NDP MP for Skeena Bulkley Valley and from Joyce Murray, Liberal MP from Vancouver Quadra, she said future operations were the responsibility of the private sector,
The Russian ship lost power outside Canadian waters in very rough weather. The private sector provides towing service to the marine industry.
We are grateful that the Canadian Coast Guard was able to keep the situation under control in very difficult conditions until the tug arrived from Prince Rupert.
Whitworth told the Globe that with increased tanker traffic whether LNG or bitumen, the number of tugs on the coast will increase, a point also made by supporters of the various projects.
But without a real commitment from the government for marine safety on the west coast, it is clear, even with the prospect of Very Large Crude Carriers with bitumen or Liquefied Natural Gas tankers plying the coast, the Harper Government considers marine safety nothing more than a case of a paper ship upon a paper ocean.
With such indifference, it is likely that local communities up and down the British Columbia coast will have to follow the example of the small town of Unalaska, population 4,376 in 2010 and create the northwest coast’s own emergency system.
