LNG Canada says it wants to be “first out of the gate” in the competitive race to send BC’s liquified natural gas to Asian markets.
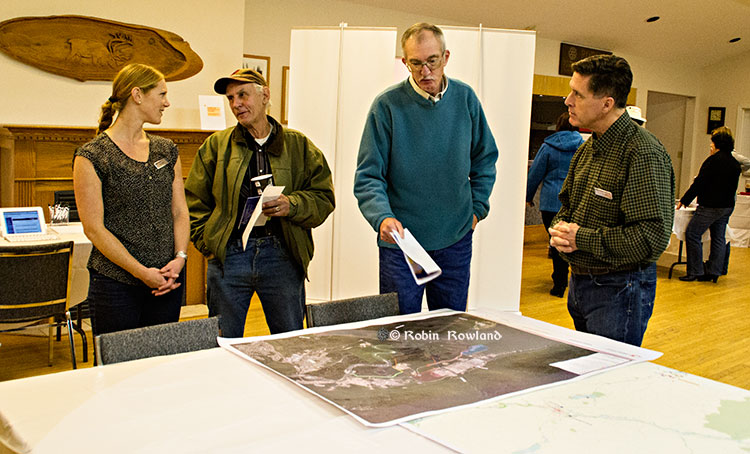
The company held a well attended open house at the Kitimat Rod and Gun on November 27, with the usual array of posters and experts, to mark the beginning of the environmental assessment process for what is formally called the “LNG Canada Export Terminal Project.:
The LNG Canada Export Project is a partnership of Shell,Canada Energy, Diamond LNG Canada, an (“affiliate” of Mitsubishi), Korea Gas Corporation and Phoenix Energy (an “affiliate” of PetroChina) filed a draft application for an Environmental Assessment Certificate with the BC Environmental Assessment Office and Canadian Environmental Assessment Agency on November 8. The 30-day public comment period on the draft Application Information Requirements started on November 13, 2013 and end on December 13, 2013.
The extensive documentation can be downloaded in PDF format from the BCEAO site. The documents can also be viewed at the Kitimat and Terrace Public Libraries and the LNG Canada office in Kitimat at the old Methanex site.
“What we want to be able to do is actually to provide information in a way that we can provide a lot of conversation with the community, so we can really have a dialogue, to give them a place where they know than go to get answers. We do believe that we can be the best project in British Columbia, the only way we can do that is if we have the support of the community,” LNG Canada’s Susannah Pierce told reporters.
“We would like to be first out of the gate. This is a competitive industry and we’re not just competing in terms of providing Canadian gas to the Asian markets, we’re competing with everyone else for the opportunity to deliver product to market.”
The application says that the all-important Financial Investment Decision will likely be “made mid-decade followed by 4-5 years of construction with commissioning of the first phase to follow.”
The first phase would have a first phase of about 12 million tonnes a year of LNG, with another MTPA (million tonnes per anum) in “one or two subsequent phases.”
Federal, provincial and municipal governments or agencies, First Nations and the general public have the ability to comment on the proposal.
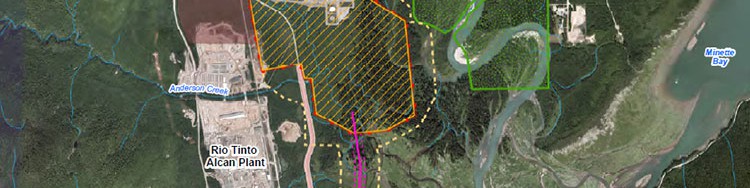
An aerial photo map included in the application shows the footprint of the proposed LNG Canada operation. Although the LNG Canada project is based at the old Methanex plant, the map shows that the LNG plant will take up a much larger area than the original. The old Methanex access road would be widened parallel to the Rio Tinto Alcan smelter and a Cyrogenic Pipeline would cross the Kitimat River estuary to the marine terminal.
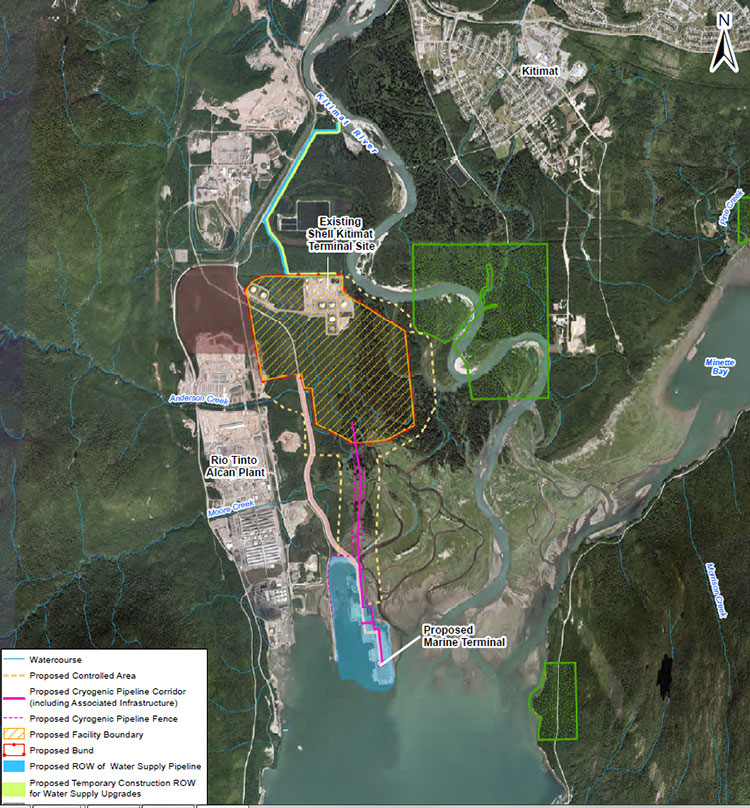
The scope of the project includes one possibly controversial item: “Onsite power generation,” where natural gas would be used to power the cooling equipment to turn the gas into LNG.
The assessment will also look the natural gas receiving and production facility; “a marine terminal able to accomodate two LNG carriers each with capacity up to 265,000 cubic metres (approximately 122,000 DWT) and a materials offloading area; supporting infrastructure and the construction facilities.
The environmental assessment will examine air quality, green house gas management, the acoustic environment (the noise created by the project), soil, vegetation, wildlife, freshwater, esturine fish and habitat, marine resources including fish and fish habitat and marine mammals, water and ground water quality.
The economic and social assessment includes infrastructure, land use, “visual quality,” odour, marine transportation and use, community health and well being, archaeological heritage and human health.

The assessment process will also “assess potential cumulative economic, health, social and heritage effects from the Project…interacting cumulatively with similar effects of past, present and future projects activities. The current table of projects to be considered for cumulative effects include the Rio Tinto Alcan Aluminum Smelter and Modernization Project, the Kitimat LNG and Douglas LNG terminals, the possible Enbridge Northern Gateway porject, the new use for the old Methanex and Cenovus operations, the operations at the Sand Hill, the former Moon Bay and current MK Bay Marinas.
Projects further away include LNG and other projects and associated pipelines at Prince Rupert, including expansion of the current ports and the redevelopment of Watson Island. Cruise ship and BC ferry operations will be only considered where they impact the shipping routes. Any forestry operations will also only be considered where they impact the project.
Updated to fix typos, including spelling of Feldhoff