Chevron is sticking with the Kitimat LNG project but won’t make a Final Investment Decision until it has signed sales and purchase agreements for between 60 and 70 per cent of the natural gas, Chevron’s vice-chairman and executive vice-president of upstream operations, George Kirkland told investment analysts in a conference call Friday.
Kirkland said that decision will happen “irrespective of what happens with Apache,” which has decided to completely exit the project.
 “We need to get partnership resolved and Apache has to move through the issues s and we need to get a new partner in. That needs to happen. That’s quite obvious,” Kirkland added.
“We need to get partnership resolved and Apache has to move through the issues s and we need to get a new partner in. That needs to happen. That’s quite obvious,” Kirkland added.
Other factors, Kirkland told the call, are final test results from the Liard and Horn River natural gas play in northeast British Columbia and finalization of the “pipeline corridor.”
Kitimat-Liard-Horn package
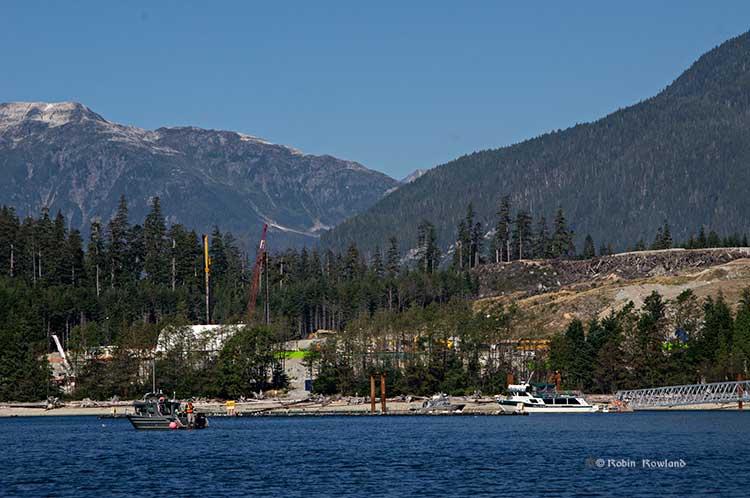
Although the residents of Kitimat are focused on the LNG terminal at Bish Cove, remarks both by Kirkland today and by Apache CEO Steve Farris Thursday, it appears that energy industry views Kitimat LNG as part of a “package” (a term used by both) that includes the Liard and Horn River gas fields and the connecting Pacific Trails Pipeline.
Kirkland also said Chevron has no interest in any further investment beyond the 50 per cent it already holds. “We have 50 per cent of the interest in Kitimat-Liard-Horn River assets. That’s right in the middle of the sweet spot where we like to be where we’re committing people to run the projects and operations. We don’t want more than 50 per cent but we do have available some small amount of working interest that we would provide to a LNG buyer.
“There’s always been a plan for us and Apache to have some working interest that could be sold down to buyers, so they would be part of the development and they would be in the value chain. That has not changed.”
Kitimat LNG’s rival project LNG Canada, run by Shell, has buyer partners in KoGas, Mitsubishi and PetroChina.

Final Investment Decision
One analyst asked Kirkland if the Final Investment Decision would come at the end of 2014, as previously announced, or in 2015. Instead, Kirkland said, “We will reach FID shortly after having 60 to 70 per cent gas committed to an SPA- a sales and purchase agreement. That is the critical decision maker and for both timing and the investment decision, irrespective of what happens with Apache. We’re driven, once again, by having a sales contract or sales contracts that gives us 60 to 70 per cent of the gas committed at an economic price.”
On the Kitimat terminal, Kirkland said, “We’ve got work going on, FEED [Front End Engineering and Design] work on the plant itself.
“We have to understand cost and schedule on that plant… We’re not spending huge money but it is a lot of money in terms of hundreds of millions of dollars. Now that is critical for us to have all that so we can deal knowledgeably with buyers. We have to understand cost. We have to understand resource, so we can deal with the particulars of pricing.
“We are not going to do a project unless it’s economic. We’ve always told you we’re not going to build that project unless we have 60 per cent of the gas sold. If you understand the project it makes sense.”
“I am not concerned if Apache leaves,” Kirkland said. “I think we could easily step in and be the operator of the upstream. I am confident there. Apache has been very good to work with in the early stages of the assessment of Liard.
“I think we’re in good shape but we need clarity, we need to get closure on the partnership and as I mentioned we have to do the work where we deal with buyers and understand costs and understand economics. We are very value driven, we are not going to go FID until we understand the economics of that sale.”
Confident on assets
Kirkland said that the company is confident about the assets in the Liard and Horn River regions but is waiting for final results from some test wells in the Liard.
“We can check off our confidence level on the Horn River. Resources are already high. We’ve already done that appraisal. So the focus on the resource sector is on the Liard, with some appraisal there and getting some production work. The wells where we need to get some production data will be complete by the end of the year. So that’s a really important step forward.”
Kirkland also hinted at the potential problems with the Pacific Trails Pipeline, where there is still a dispute with the Wet’suwet’en First Nation. “We’re going to focus on the pipeline and the end of the pipeline corridor. That’s important and we’re putting some money into that to finalize the pipeline routing, get all our clearances and then we’ve got work going on.”

Overall Kirkland was enthusiastic about other liquified natural gas projects in Australia and elsewhere in the world. Chevron Corporation reported earnings of $5.7 billion for the second quarter 2014, compared with $5.4 billion in the 2013 second quarter. Sales and other operating revenues in the second quarter 2014 were $56 billion, compared to $55 billion in the year-ago period.
Company CEO John Watson said a news release, “In Australia, our Gorgon and Wheatstone LNG projects continue to reach important interim milestones. Gorgon remains on track for expected start-up in mid-2015. We are also advancing the development of our liquids-rich, unconventional properties in the United States, Canada and Argentina.”

 China is probably the largest long
China is probably the largest long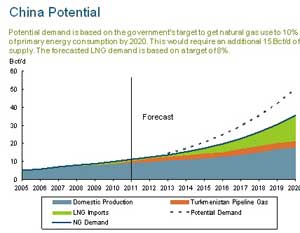 Dave Thorn, Encana vice president of
Dave Thorn, Encana vice president of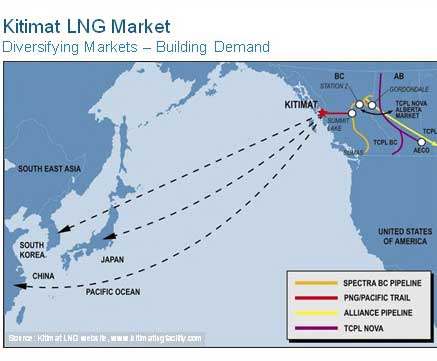 The Kitimat project is currently
The Kitimat project is currently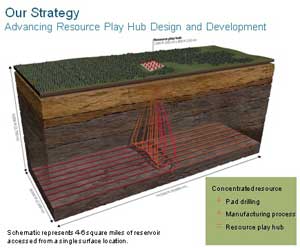 Encana says it has developed a “hub”
Encana says it has developed a “hub”