Aluminum
Rio Tinto Alcan president primary metals, Jean Simon, announces the go-ahead for the Kitimat Modernization Project at ceremony at the plant in Kitimat, Dec. 1, 2011. (Robin Rowland/Northwest Coast Energy News)
“It’s a go.”
The “go” meant that the Rio Tinto Alcan board had finally approved spending $2.7 billion for the long awaited Kitimat modernization project that would update the 60-year old aluminum smelter, increasing production capacity by 48 per cent to 420,000 tonnes a year.
Rio Tinto Alcan primary metal president Jean Simon made the announcement Thursday, Dec. 1, 2011 to cheers at a theatre (converted from the dining hall) at the new construction camp at the Kitimat smelter.
That money is in addition to expenditures already approved, bringing the total investment in the modernization project to $3.3 billion US.
“This will help us put Kitimat and Canada at the forefront of the 21st century global aluminum industry,” Simon said. “It is a truly transformational project.” He said it was in line with RTA’s long term strategic objective of long life, large scale, low cost assets. The project, Simon said, will take advantage of Rio Tinto Alcan’s competitive advantages: clean self generated hydro power and leading edge technology.
If all goes as expected, the first new metal will be poured in the first of half of 2014.
The new smelter will use a RTA proprietary smelting technology that reduce carbon dioxide emissions by 50 per cent.
The long planned project had been put on hold in 2008 as the world weathered the financial meltdown.
Kitimat mayor Joanne Monaghan said at the ceremony, “This is something our community has been waiting a very long, long time for….Kitimat has suffered through some very had economic times over the last several years and this announcement means we have the certainty that the aluminum business will be here for the next 35 to 50 years… We’ve seen a lot of industry disappear from Kitimat over the past few year and its been hard on our community. In fact, with Methanex leaving, with Eurocan leaving I felt like the mayor of doom. And then, all of a sudden, all of these things are happening. And I feel like the mayor of boom.
“We know the importance of that first initial investment to show that Kitimat is the strategic place to invest. And when RTA began its expansion, and its construction camp, then all of a sudden three LNG plants came on stream. We had a biomass plant ready to come in. So thank you Alcan for starting that whole trend for people coming into our community.”
It is Asia is fueling Kitimat’s new boom, and not just in natural gas, but also in aluminum. When Kitimat was planned and built 60 and more years ago, Asia, China, Japan, Korea were in ruins, devastated by the Second World War. Now it is Asia, and the short great circle route from Kitimat harbour to the market ports, that is one reason that the Kitimat modernization project was approved.
“Most of the aluminum is going into Asia. Korea, Japan and other countries,” Simon said in a post-ceremony news conference. “We’ve been producing here for 60 years and Kitimat has always been recognized as a very solid, reliable and good quality producer of aluminum so our customers from Asia are demanding the metal from Kitimat. So this is good news for them too.”
 Paul Henning, RTA vice president of BC operations, is not only a corporate manager. He was the very entertaining master of ceremonies for the announcement. (Robin Rowland/Northwest Coast Energy News).
Paul Henning, RTA vice president of BC operations, is not only a corporate manager. He was the very entertaining master of ceremonies for the announcement. (Robin Rowland/Northwest Coast Energy News).
Paul Henning, VP BC Operations and strategic projects Western Canada, was asked if Kitimat can handle the demand and possible bottle necks with, as well as Kitimat modernization, three LNG projects, possibly the Enbridge Northern Gateway pipeline and perhaps other projects in the coming couple of years.
“The good news is that we’re first,” Henning said. “The folks who grab the ball usually have a chance. We’re working with those folks. People availability will be the key. I think there’s a lot of common sense going on, these are mega projects. Mega projects need lots of people. I wouldn’t call it coordination, but there is an understanding. They understand our timing, we understand their timing.
“All being equal we’re not competitors. It’s going to be an extended boom for the region. And of course, the projects are stacked, all trying to happen at the same time.
“It’s challenging, just for resources and infrastructure. If they can be spread, it’s a win, win, win. At the end of the day Our business drives what we do in the timing. Their business care drives their timing. At the end of the day, we’re first in.”
Thursday wasn’t the best day to show Kitimat off to the world, with a cold wind driving sleet, snow and rain all at the same time. BC Premier Christy Clark’s plane was turned back from Terrace Kitimat airport and a second aircraft with RTA CEO Jacynthe Cote was redirected to Prince Rupert.

RTA employees and guests watch a slideshow of historic photos of the early days of Kitimat before the official ceremony announcing the go-ahead for the Kitimat modernization project. (Robin Rowland/Northwest Coast Energy News)
As the audience and guests waited for the arrivals that were not to come, there was a slideshow of historic photos on giant LED screens, showing the early days of Kitimat, the construction of the dam, transmission lines, townsite and the potlines.
Then the elaborate ceremony began, with Paul Henning acting as master of ceremonies, introducing the Haisla Spirit of the Kitlope drummers before Simon made the “go” announcement.
It was good community relations that helped the RTA board give the go-head, Simon said.
“We will also honour the landmark Haisla Nation, Rio Tinto Alcan Legacy Agreement and are proud of this partnership to provide opportunities and training and that is resulting in increasing numbers of Haisla Nation members working on the project,” said Simon.
Haisla chief councillor Ellis Ross had been flying up with Christy Clark, so Councillors Henry Amos, Alex Grant and Keith Nyce were at the ceremony on behalf of the Haisla. “On behalf of the Haisla Nation, we offer you a warm welcome to our Traditional Territory. The Haisla Nation has worked very closely with RTA and supported the reality of this important and exciting decision. Together with RTA, our Nation is very proud of the legacy agreement we have reached.” Nyce said.
The Haisla are not only our closest neighbours but our best friends,” Henning said at the news conference. “It hasn’t always been like that. I think leadership from the Haisla, starting with Steve Wilson, transferring to Ellis Ross. Ellis has taken it to another level. The recognition of wanting to engage in the future was the key. We had to recognize and respect that past, to learn how to work together and build for the future.
“It’s actually a cohesive joint approach to economic development and sustainability within the Haisla First Nation and the plant. It actually betters the plant because we have employees that live here, work here, there are 120 Haisla folks who are working within the operation. That to me is sustainability in real time.”
Henning is also confident that the company will successfully negotiate a new contract with the Canadian Auto Workers local. Henning said that 2007 contract was designed to get the company through to first hot metal but then the financial crisis struck.”The good news gives us certainty.”Henning said. “We know what we have to drive for. We’ll get a contract, we’ll get a contract, we always do. Some are prettier than others. The confidence from this is a great start. The union were here today, I am confident that we will get through and get a contract that really fits this program.”
After he took the podium, Michel Lamarre, director of the Kitimat Modernization Project joked. “We often say that when we get married, and it’s raining, the marriage is very strong and I think this is going to be the case for the KMP project.” He said Kitimat management had made a very solid case for a very solid project to the RTA board.
 Michel Lamarre, director of the Kitimat modernization project, talks about the challenges of the next two years until first metal in 2014. (Robin Rowland/Northwest Coast Energy News)
Michel Lamarre, director of the Kitimat modernization project, talks about the challenges of the next two years until first metal in 2014. (Robin Rowland/Northwest Coast Energy News)
“We are building a state of the art facility which will be a jewel. This is something we can all be proud of… The next two years will be very busy and very exciting. Let’s build the project with zero harm, zero harm to the people who are building it and zero harm to the environment.”
The weather was just too nasty for an official ground breaking ceremony at the construction site, so it was moved indoors, with RTA executives and employees, the Haisla representatives and Mayor Monaghan turning the shovels into a ceremonial pile of dirt.
The indoor groundbreaking ceremony marking the approval of the Kitimat modernization project. Left to right Michel Lamarre, director KMP, RTA operations employee Ron Leibach, Brent Hegger, VP major projects, Kitimat mayor Joanne Monaghan, Jean Simon, RTA president primary metals, Paul Henning, VP BC operations and Henry Amos, Councillor, Haisla Nation. (Dwight Magee/RTA)

 Paul Henning, RTA vice president of BC operations, is not only a corporate manager. He was the very entertaining master of ceremonies for the announcement. (Robin Rowland/Northwest Coast Energy News).
Paul Henning, RTA vice president of BC operations, is not only a corporate manager. He was the very entertaining master of ceremonies for the announcement. (Robin Rowland/Northwest Coast Energy News).
 Michel Lamarre, director of the Kitimat modernization project, talks about the challenges of the next two years until first metal in 2014. (Robin Rowland/Northwest Coast Energy News)
Michel Lamarre, director of the Kitimat modernization project, talks about the challenges of the next two years until first metal in 2014. (Robin Rowland/Northwest Coast Energy News)
 The Russian sail training vessel STS Pallada. (Pallada)
The Russian sail training vessel STS Pallada. (Pallada) A map of the tsunami debris field by Nikolai Maximenko and Jan Hafner of IPRC. The line shows the track of the Pallada where the debris was spotted between Sept. 21 and Sept. 28, 2011. The red rhombus (diamond) marks the location where the Japanese boat was found. The red circle denotes maximum debris density spotted by the Pallada. The purple shows the extent of the debris field from the updated university computer model as of Sept. 25. Click for larger image. (IPRC)
A map of the tsunami debris field by Nikolai Maximenko and Jan Hafner of IPRC. The line shows the track of the Pallada where the debris was spotted between Sept. 21 and Sept. 28, 2011. The red rhombus (diamond) marks the location where the Japanese boat was found. The red circle denotes maximum debris density spotted by the Pallada. The purple shows the extent of the debris field from the updated university computer model as of Sept. 25. Click for larger image. (IPRC) The crew of the Pallada hoists on board a Japanese boat, registered in Fukishima prefecture, and presumably washed out to sea during the March 11, 2011 tsunami. (Pallada)
The crew of the Pallada hoists on board a Japanese boat, registered in Fukishima prefecture, and presumably washed out to sea during the March 11, 2011 tsunami. (Pallada)
 China is probably the largest long
China is probably the largest long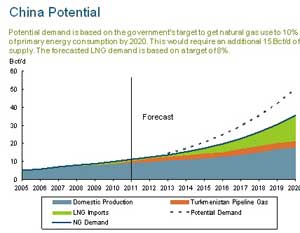 Dave Thorn, Encana vice president of
Dave Thorn, Encana vice president of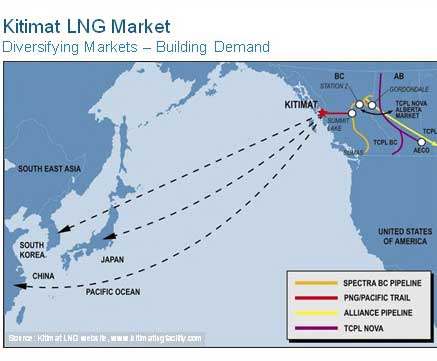 The Kitimat project is currently
The Kitimat project is currently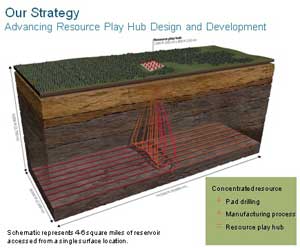 Encana says it has developed a “hub”
Encana says it has developed a “hub”