Energy LNG Politics
The state of Oregon has filed a motion with the US Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (the American equivalent of the National Energy Board) to block, perhaps temporarily, the Jordan Cove Liquified Natural Gas project at Coos Bay, Oregon.
Experts at the June NEB hearings in Kitimat testified by the Jordan Cove could be Kitimat’s chief rival as an LNG terminal.
Like the plans for Kitimat in the early 2000s, the Jordan Cove facility was originally planned as an import terminal and the FERC eventually did issue a permit for the construction of the import terminal.
In the meantime, the natural gas market changed, with the growth in the hydraulic fracturing to retrieve gas from shale deposits. In September, the company involved, Jordan Cove LP applied to the Department for authorization to export natural gas. At the time the company said it intended to ask the Commission in early 2012 to amend its existing authorization to add export facilities.
On Dec. 2, 2011, the Oregon Dept. Of Justice filed a motion with the FERC to revoke the approval of the LNG terminal in Coos Bay and reopen the record so the state can submit evidence that a revised terminal proposal is not in the public interest.
Oregon wants the company to file a new application, arguing that is more appropriate than amending of the import application.
The filing says: “The facts demonstrate a change in core circumstances that goes to the very heart of the case. The heart of this case is whether the Jordan Cove LNG import terminal is in the public interest and the pipeline is required by public convenience and necessity….
Oregon wonders how the “additional imported natural gas supply” would benefit the state and how that would outweigh “the adverse impacts on private landowners and the environment.”
Oregon says that “any benefit that may have existed when the import Project was proposed, no longer exists to offset the adverse impacts of the Project.”
The filing also argues that if the United States exports natural gas through Oregon that will increase domestic prices. It also argues that there hasn’t been enough consideration about the environmental impact of the liquefaction facility.
“This is the right thing to do, to tell them we don’t accept this bait and switch with Jordan Cove,” said Dan Serres, an organizer with the conservation group Columbia Riverkeeper, told the Oregonian newspaper.
Bob Braddock, project manager for Jordan Cove, told the Oregonian he wasn’t surprised by the filing, claiming that Oregon Attorney General John Kroger has made no secret of his opposition to any LNG terminal since before he took office
Braddock repeated arguments familiar to northwest BC from both the LNG and Enbridge Northern Gateway projects, saying the public interest in the pipeline and export terminal includes jobs, tax revenue and pipeline interconnections that would bring a better gas supply to southern Oregon.
A few days earlier, on Nov. 22, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife filed a letter with the FERC, saying it was not being kept up to date about changes in plans by Jordan Cove for the LNG terminal and so could not fully assess the environmental impact. The letter said the project’s mitigration plan had not been provided in sufficient detail and assurance about theit nature, location, effects and implementation. The Fish and Wildlife Service also noted that the company had not addressed or supplied information on the impact the LNG project might have on the program to help the recovery of the Northern Spotted Owl population. In fact, according to the Fish and Wildlife filing the plans were so inadequate that it wasn’t possible to begin formal consultations with company over environmental impacts.
Opponents of the project note that Oregon will probably have the final say on the project, since the terminal location is on state-owned land and the state must approve the leases.
Oregon motion to FERC to set aside order (pdf)
Fish and Wildlife Jordan Cove letter (pdf)

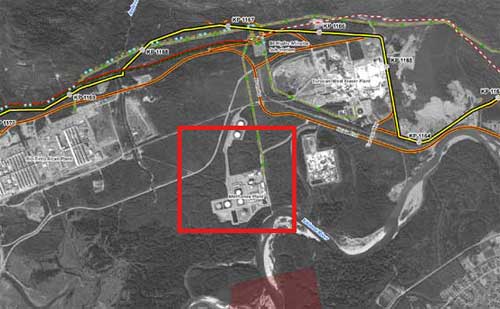 The former Methanex site is seen the red square in this map of the Kitimat service centre prepared by Enbridge as part of its Northern Gateway pipeline proposal and filed with the Joint Review panel. The yellow line is the proposed Enbridge bitumen pipeline. The dark red line is the proposed pipeline that would feed the Kitimat LNG and likely the BC LNG projects, where the red pipeline route has white, that is the Pacific Trails Pipeline. See
The former Methanex site is seen the red square in this map of the Kitimat service centre prepared by Enbridge as part of its Northern Gateway pipeline proposal and filed with the Joint Review panel. The yellow line is the proposed Enbridge bitumen pipeline. The dark red line is the proposed pipeline that would feed the Kitimat LNG and likely the BC LNG projects, where the red pipeline route has white, that is the Pacific Trails Pipeline. See