LNG Partners LLC, of Houston, one of the backers of Douglas Channel Energy, the BC LNG Douglas Channel Project, a partnership between LNG firms and the Haisla Nation, has signed a preliminary deal with Golar LNG for two tankers.
![]() Golar LNG, which describes itself on its website as “one of the world’s largest independent owners and operators of LNG carriers” said in its interim results report to shareholders on November 28:
Golar LNG, which describes itself on its website as “one of the world’s largest independent owners and operators of LNG carriers” said in its interim results report to shareholders on November 28:
On October 10, Golar entered into a 90 day Vessel Charter Option Agreement with LNG Partners LLC (Houston, TX) for the provision of two newbuild LNG carriers under long term contract to deliver LNG production from the Douglas Channel LNG Project in British Columbia (BC), Canada.
The Douglas Channel Project, in which LNG Partners is an equity owner, is a proposed liquefaction facility on the west bank of the Douglas Channel, within the district of Kitimat, BC. In addition to prospectively providing two vessels, the agreement confers certain preferential rights for Golar to participate in the project with LNG Partners LLC by way of infrastructure investment or LNG offtake.
In the same report, Golar LNG reported operating income of $70.2 million for the third quarter of 2012, an increase of 21 per cent from the second quarter.
Golar, which has its headquarters in Hamilton, Bermuda, says that since 2001, it has grown from a fleet of six LNG Carriers focused on LNG transportation, to a fleet of 13 vessels (with 13 newbuilds due from quarter three 2013), dedicated to both LNG transportation and midstream floating solutions.
The latter means that Golar is working on what the industry calls Floating Storage & Regasification Units (FSRU). LNG is transferred to the FSRU either for storage or where the low-temperature liquified natural gas is heated back to a gaseous state.
The FSRU storage tanks are generally made from aluminium.
Golar is also moving into Liquified Natural Gas production vessels, that is floating ships that produce the LNG than taking it from a shore-based plant.
Golar’s report also reflects the weakness in the LNG markets, a factor that is slowing development of the Kitimat LNG projects.
Golar says “a bearish cargo market [for shipping] prevailed in the third quarter with falling prices and weak demand in the Far East. Chartering activity remained thin and lacked direction and consequently, short-term charter rates experienced a correction from rates seen earlier in the year.”
It goes on to say:
Looking to the fourth quarter, weak Far East demand may result in additional vessels being released into the market, however, with limited available modern undedicated vessels a resumption in interest from buyers could very easily pull rates upward again.
As for the world LNG market, Golar says “downward pressure on pricing was experienced primarily due to high inventory levels that persisted East of Suez.”It also says that more LNG projects are coming onstream which could provide potential competition for Kitimat:
New LNG supply will soon be coming to the market with the commissioning of Angola LNG in the Atlantic Basin. Despite delays at the West African project during the third quarter, exports are expected to start early in the New Year. This represents a set-back of about ten months from the original target date for the country’s first LNG project.
In the Far East, ConocoPhillips and Origin Energy announced the sanctioning of a second train at its Australia Pacific LNG project. The project is planning to bring the first train on late in 2015 with the second train following in 2016. Both trains will be sized at 4.5 million tonnes. Additionally, during the quarter Chevron made positive statements about proceeding with a fourth train at its Gorgon LNG project in Barrow Island, Western Australia. There are currently three trains at Gorgon under construction totalling 15.6 million tonnes.
In addition to Angola, given imminent start-up of the project, supply projects under construction in both the Atlantic and Pacific Basin have reached close to 100 million tonnes, with construction officially beginning at Cheniere’s Sabine Pass LNG export facility.
It was the decision by Cheniere to sell LNG to the Far East markets based on North American prices rather than the higher Japanese price that led to a further delay by Apache earlier this year to give the final go-ahead for the Kitimat LNG project.
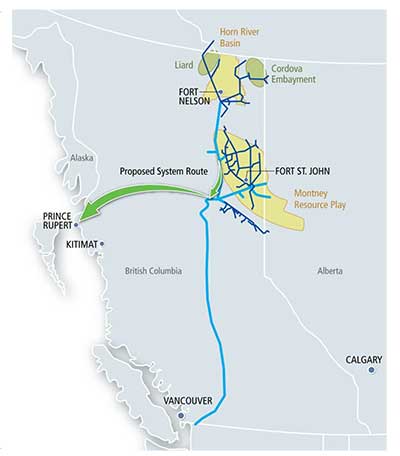


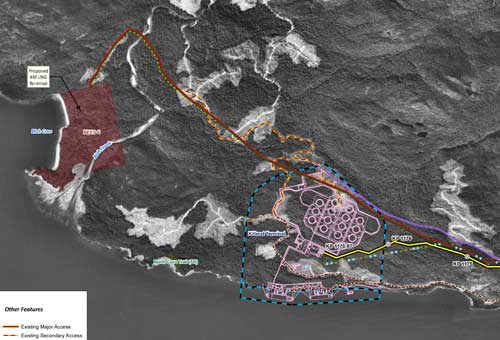
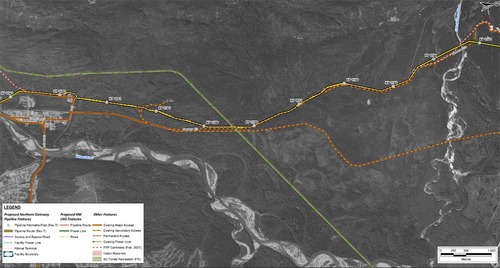 In this map, the Enbridge pipeline is yellow with a black outline, the LNG pipeline is red. Where there are yellow and red alternating squares, that means the two pipelines will follow the same route. Solid orange lines are paved roads,broken orange lines are unpaved roads and the green lines are power lines.
In this map, the Enbridge pipeline is yellow with a black outline, the LNG pipeline is red. Where there are yellow and red alternating squares, that means the two pipelines will follow the same route. Solid orange lines are paved roads,broken orange lines are unpaved roads and the green lines are power lines.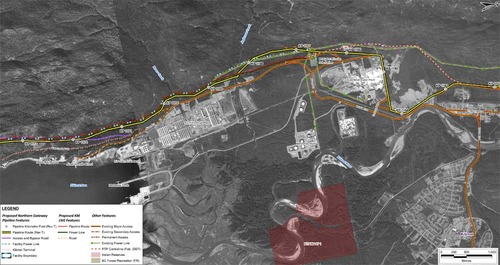 Just before the pipelines reach the service centre, they diverge, the yellow Enbridge pipeline following the road route around the periphery of the service centre, while the gas pipeline at first follows the route of the Pacific Trails Pipeline and then snakes off at the hydro substation. The two pipelines then run parallel just off Haisla Boulevard across from the Rio Tinto Alcan plant. The green line beside the two pipelines marks a hydro line that would be build to power the facilities.
Just before the pipelines reach the service centre, they diverge, the yellow Enbridge pipeline following the road route around the periphery of the service centre, while the gas pipeline at first follows the route of the Pacific Trails Pipeline and then snakes off at the hydro substation. The two pipelines then run parallel just off Haisla Boulevard across from the Rio Tinto Alcan plant. The green line beside the two pipelines marks a hydro line that would be build to power the facilities.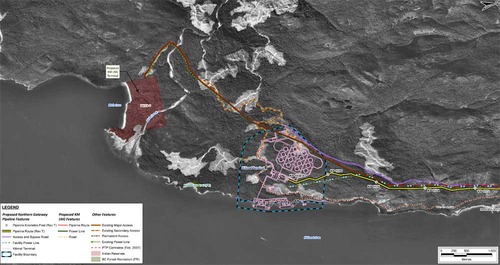 The final map shows the Enbridge pipeline coming into the bitumen/condensate terminal with its large footprint, while the natural gas pipeline continues, crosses Bish Creek and then enters the Bish Cove KM LNG terminal. If the BC LNG terminal is built at North Cove, just west of the proposed Enbridge Northern Gateway facility, a branch pipeline would go from the main gas pipeline down to that facility. (There were indications at the June NEB hearings that negotiations were under way on “sharing” gas “molecules” between the two groups).
The final map shows the Enbridge pipeline coming into the bitumen/condensate terminal with its large footprint, while the natural gas pipeline continues, crosses Bish Creek and then enters the Bish Cove KM LNG terminal. If the BC LNG terminal is built at North Cove, just west of the proposed Enbridge Northern Gateway facility, a branch pipeline would go from the main gas pipeline down to that facility. (There were indications at the June NEB hearings that negotiations were under way on “sharing” gas “molecules” between the two groups).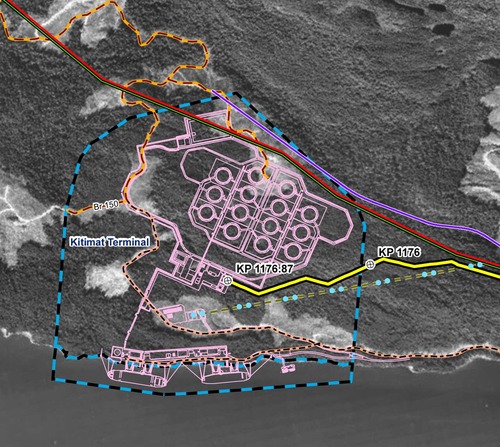 Footprint of the Enbridge Northern Gateway plant.
Footprint of the Enbridge Northern Gateway plant.
