What is it about the islands in Douglas Channel? First, Enbridge gets in to a lot of hot water, so to speak, for erasing the islands in Douglas Channel in an animation promoting the Northern Gateway Pipeline. See for example The Vancouver Sun on back on Aug. 16, 2012, when it picked up a story from the Times Colonist – Enbridge map sinks islands, angers critics. The controversial video segment showed Douglas Channel wide open for navigation, rather than marked with about one thousand square kilometres of mountainous islands.  This map, created by the Leadnow.ca and Sumofus.org websites was widely used by the media to show the difference. Enbridge later amended its video with a disclaimer that it is “broadly representational.” A video by Shortt and Epic Productions “This is Not An Enbridge animation” showing the beauty of northwestern BC quickly went viral.
This map, created by the Leadnow.ca and Sumofus.org websites was widely used by the media to show the difference. Enbridge later amended its video with a disclaimer that it is “broadly representational.” A video by Shortt and Epic Productions “This is Not An Enbridge animation” showing the beauty of northwestern BC quickly went viral.
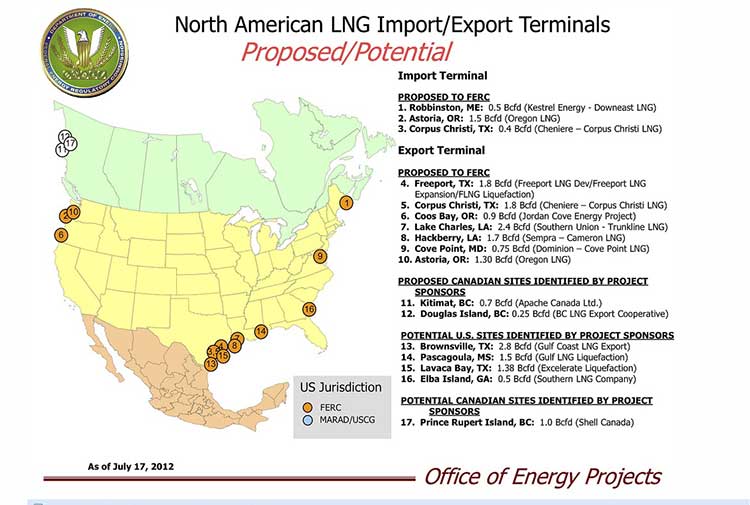
As this was happening, the United States government Federal Energy Regulatory Commission issued a map that shows Liquified Natural Gas import and export terminals across North America, a map that adds an island to the Channel–“Douglas Island.”
In fact, the map manages to get a lot about Canadian LNG projects wrong. It locates the BC LNG project on the non-existent Douglas Island. The company’s name Douglas Channel Energy Partnership actually gives the proper location this way
south of the Moon Bay Marina, within the District of Kitimat and the asserted traditional territory of the Haisla Nation. The site is approximately 10 km southwest of Kitimat and 7 km north of Bees Cove Indian Reserve 6 (Bish Cove)
The small cove where BCLNG will put its barges to create the LNG is often locally called North Cove.
The FERC map also misplaces the Shell LNG project, now known as LNGCanada, in Prince Rupert, even though Shell confirmed the Kitimat location on May 15, 2012. It also calls it Prince Rupert Island, although the town of Prince Rupert is actually located on Kaien Island.
The map does apparently get the KM LNG project somewhat correct, attributing it to Apache Canada, but leaving off Apache’s partners, Encana and EOG.
The map recently also appeared on the website of Oregon Public Broadcasting in an article Five Keys To The Pacific Northwest’s Natural Gas Export Debate by reporter Amelia Templeton, which outlines the growing controversy over the plans to export US LNG through Coos Bay, Oregon via the Jordan Cove Project.
It appears that in Oregon, the Coos Bay LNG project is becoming as controversial as the Northern Gateway project is in Canada.
The issues outlined by Templeton include the threat of expropriation (called “eminent domain” in the US and also a key issue in the debate over the Keystone XL pipeline on the plains). There are arguments on jobs versus the environment, especially the perceived threat to wild rivers and salmon spawning grounds. Finally one issue that is lower on the agenda in northwestern BC but a big worry in Oregon, the potential for a devastating earthquake along the Cascadia fault.
During the NEB hearings on the KM LNG (Apache/EOG/Encana) project in June, 2011, many of the “expert” witnesses urged that that first Kitimat project go ahead quickly because of perceived competition from Oregon.
Unlike in Oregon, LNG projects are generally perceived positively in the northwest and all three are going ahead, although not as quickly as originally planned due to market volatility among prime potential customers in Asia.
 Jordan Cove project manager Robert Braddock told the industry newsletter, Platt’s Gas, that he is “not afraid of competition from the north, where Kitimat LNG is planning an export terminal in British Columbia. ‘We actually presume that Kitimat would be built,” Braddock said. “We assume that we would be built number two and we think there is plenty of room for two such facilities on the West Coast.’
Jordan Cove project manager Robert Braddock told the industry newsletter, Platt’s Gas, that he is “not afraid of competition from the north, where Kitimat LNG is planning an export terminal in British Columbia. ‘We actually presume that Kitimat would be built,” Braddock said. “We assume that we would be built number two and we think there is plenty of room for two such facilities on the West Coast.’ Similar to plans to take shale gas from the Horn River Formation in northeastern BC, Jordan Cove would tap into the
Similar to plans to take shale gas from the Horn River Formation in northeastern BC, Jordan Cove would tap into the