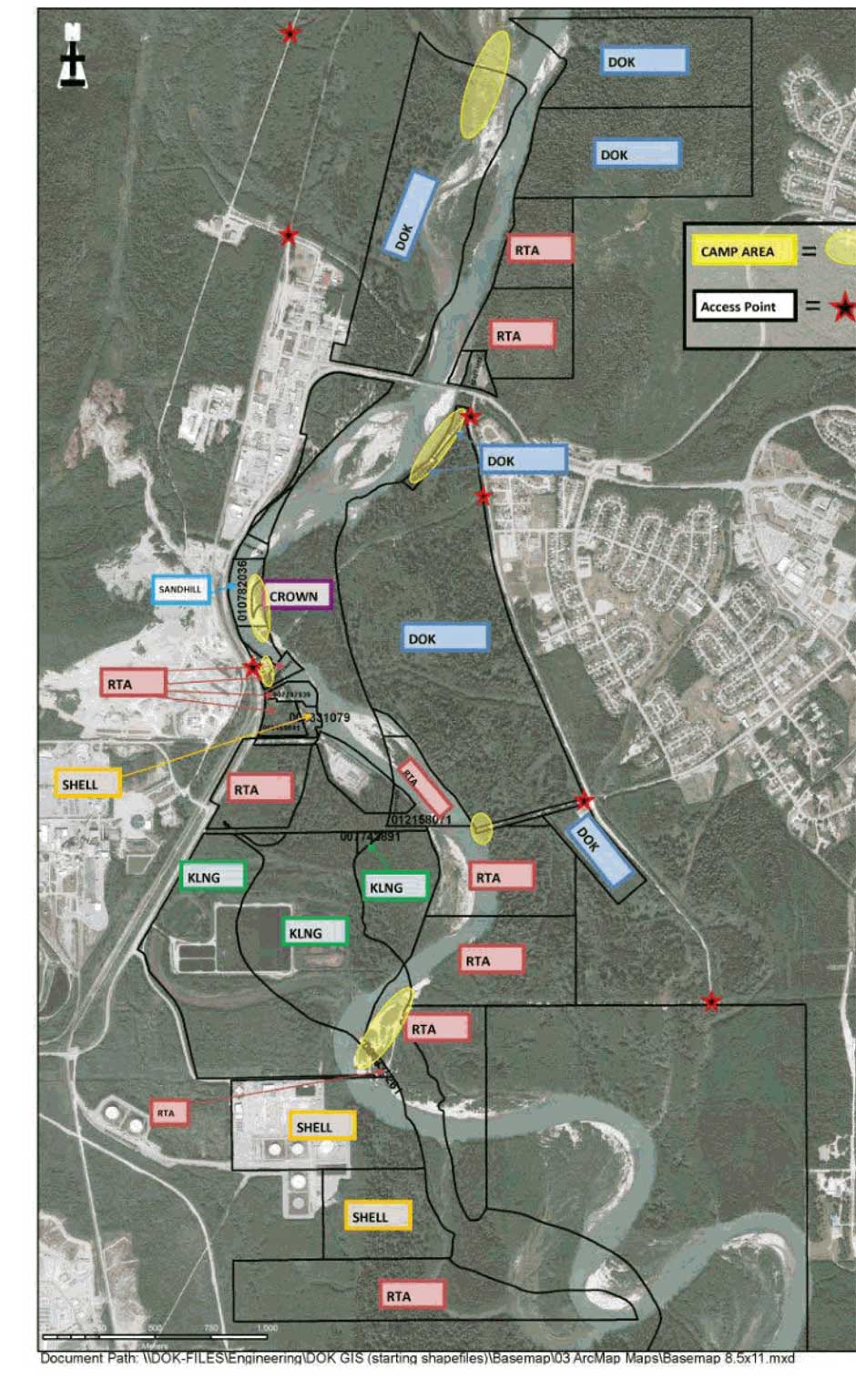
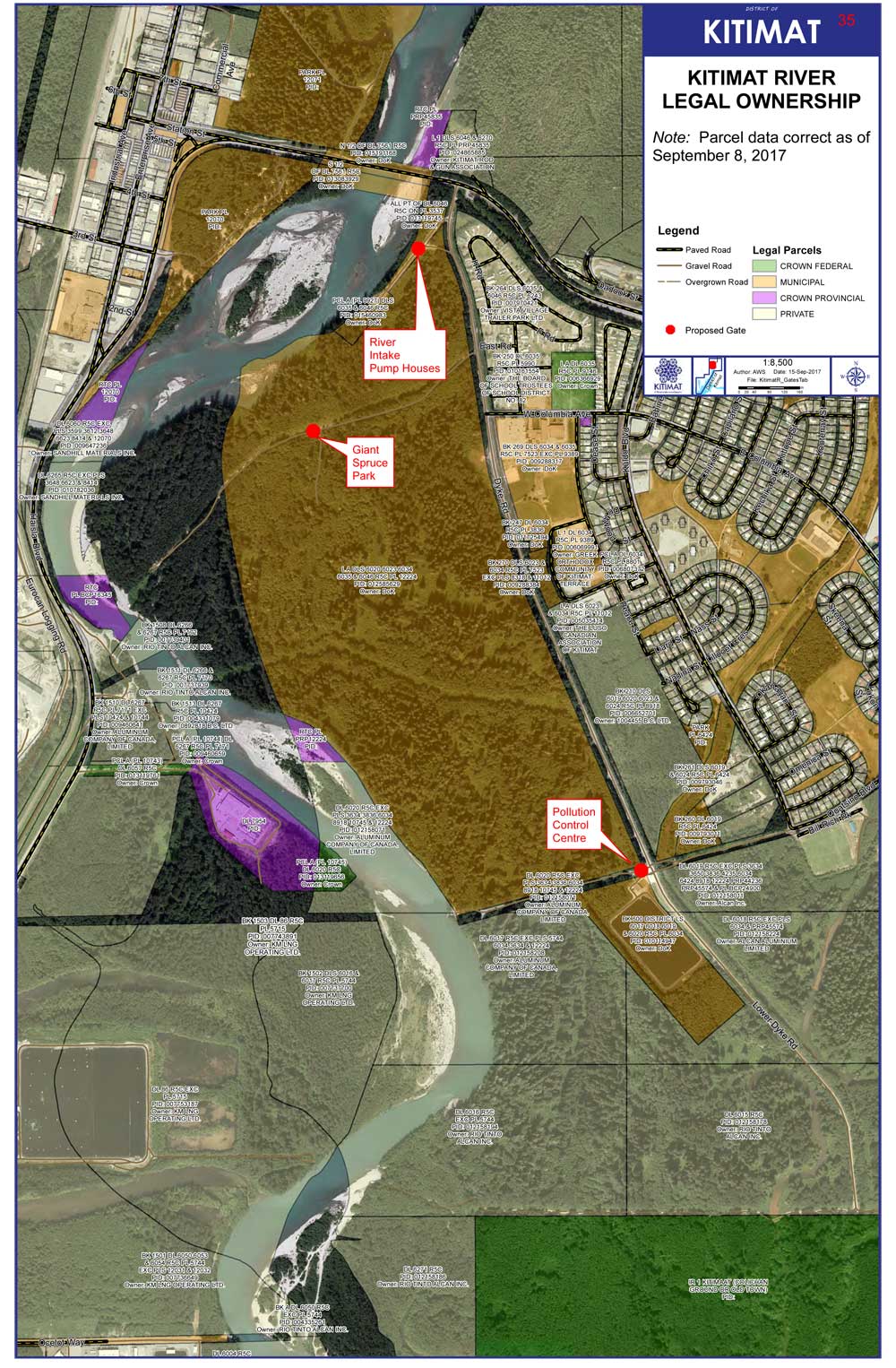
THE RIVERBANK PAPERS: After the flash flood on September 11, 2017, Northwest Coast Energy News filed Freedom of Information/Access to Information requests with a number of provincial and federal agencies who have jurisdiction over the Kitimat river and riverbank camping.
The first response to the FOI request is from the Ministry of Forest, Lands and Natural Resource Operations & Rural Development.
A preliminary assessment by the British Columbia Ministry of Forest, Lands and Natural Resource Operations & Rural Development indicates that the District of Kitimat can regulate access to camping on the Kitimat River bank because although the shoreline is on Crown Land, the camping area is within the boundaries of the District.
One of the possible policies that the District staff is considering is allowing only “day access” to the riverbank.
An email on October 11, from Liz Williamson, a senior policy analyst in the ministry’s Land Tenure Branch to Gwen Sewell, the District’s Director of Planning and Community Development, reads:
Permission does not apply to Crown Land within a municipality—as a result even in the absence of zoning/bylaws, any camping that does occur is technically in non-compliance with the permission and therefore could be subject to enforcement action under the Land Act.
Williamson notes that the province likely will have to be involved.
Ultimately that does rely on provincial resources and it looks like DOK would want a greater role in the use and ability to locally enforce the use as you have mentioned zoning and associated bylaws would likely be a course of action you could consider.
Williamson went on to write:
I’m waiting to hear back from one of my more experienced colleagues but I am not aware of any specific limitation to DOK creating bylaws to regulate public recreational use of vacant Provincial land within the municipal boundaries, so long as it doesn’t conflict with a government interest.
She added that the laws and regulations are complex and advised the District to get legal advice. Then she added the District should have “upfront discussions with appropriate provincial authority to ensure that the bylaws do not conflict with existing policy/legislation or other agency interests.”
On September 19 the District voted to create a “working group” on riverbank access that is now being put together.
Right after the flash flood both Sewell and District of Kitimat Chief Administrative Officer, Warren Waycheshen, exchanged emails with officials of both the Ministry of Lands and Forests and the Ministry of the Environment asking first if the province would have any objections to a proposed plan to put gates on municipal land to limit access to the riverbank. Council later put the gate plan on hold.
The emails quoted provincial land use permission policy that says
“Crown permission to use land requires the activity must abide by and comply with all applicable, regulations and bylaws.
And
Before any person may rely on the Permission they must ensure that the activity is taking place on unencumbered Crown land. The Crown land must not be within
- A Protected Area includes Ecological Reserves, Parks and Conservancies
- Municipality
In his email to Cam Bentley, Resource Manager for the Skeena Lands district, Waycheshen asked if the province was interested in some form of joint administration of the riverbank and if the ministry was interested in joining the working group.
Sewell sent a similar email to Williamson noting,
Camping has been occupying the banks of the Kitimat River—opposite a municipal campground called Radley Park—for decades….This had been a somewhat divisive local issue (it’s no cost and traditional use, grey water, residual garbage, human waste, blocking river access for day users etc. and there is a new willingness to consider regulation or prohibition of camping following a flash flood that required a dangerous multi-force rescue effort to save 14 campers and resulted in significant property loss (RVs, vehicles and camping equipment). As camping is “unregulated” the first responders had no idea how many people were in danger or where to look for campers.
Sewell went on to say:
Given…municipal authority to regulate land use by zoning, I believe Kitimat Council may use their zoning power to limit all or selected land along the Kitimat River to “day use only.” I am far from certain this will be the course of action Council will choose to pursue. For now, we only want to identify possibilities.
RELATED July 2015
Keremeos mayor wants province to stop campers who are leaving trash, human waste on riverbed:CBC
Williamson replied to Sewell saying that it was good there was no loss of life in the flood. She noted the Keremeos had been going through a similar situation but that village’s problem was that, unlike the District of Kitimat, the camping was outside the municipal boundaries of the village.
KEEP THE RIVERBANK PAPERS INVESTIGATION GOING.
These days filing Freedom of Information and Access to Information requests is much more expensive than it was in the past. It is part of obstruction of freedom of information by all levels of government. One agency wants $900 for their files on the Kitimat River camping issue. That is currently under appeal. Donations (see right hand column) will help the residents of Kitimat know more about what is happening on the camping issue.