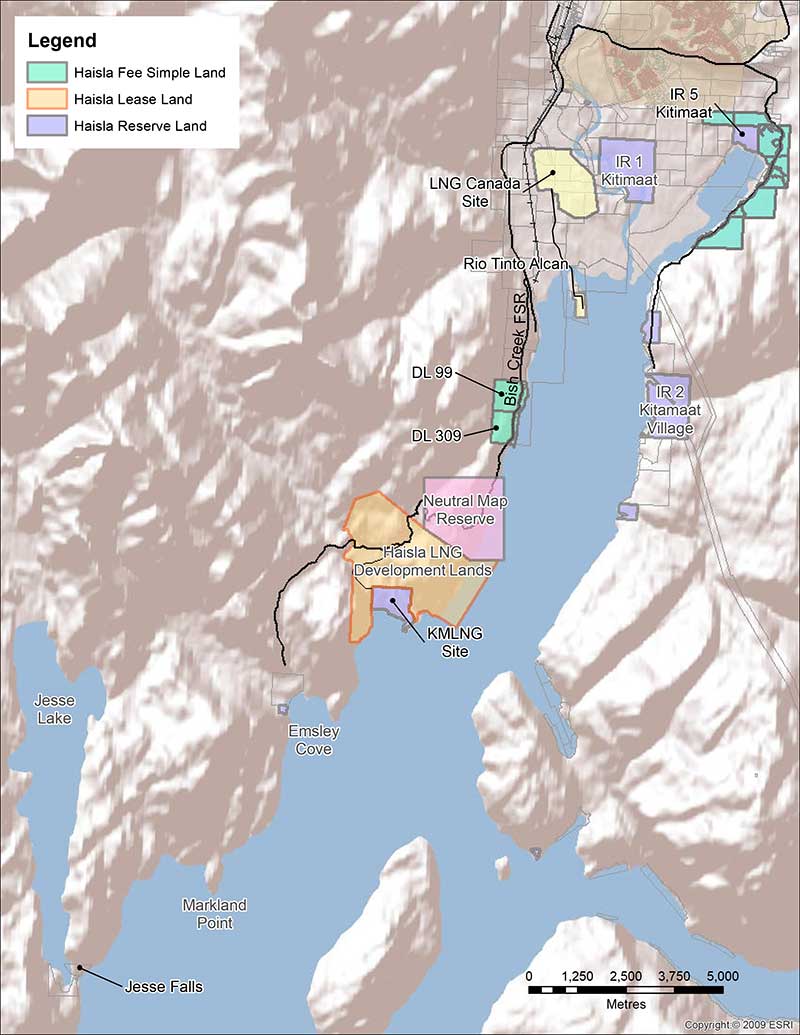
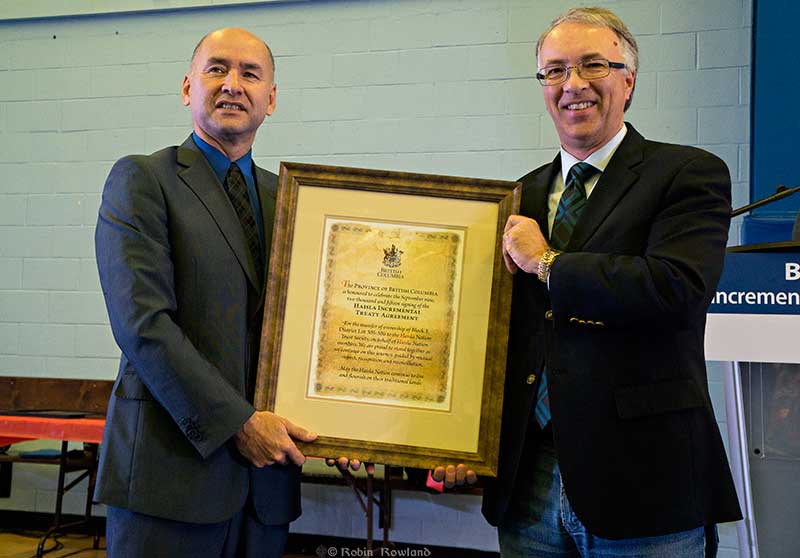
The Haisla Nation celebrated the signing of an incremental treaty agreement with the British Columbia government Tuesday at the Haisla Recreation Centre in Kitamaat Village. The treaty will see the return of Haisla lands on the shore of Douglas Channel of Lots 305 and 306 south of the Kitamaat Village, designated Indian Reserve #2 and Indian Reserve #3, also known as the Walsh Reserve, thus connecting the two reserves.
In a news release, the BC Ministry of Aboriginal Relations and Reconciliation said that under the agreement, approximately 120 hectares of Crown land will be transferred to the Haisla Nation.
The land lies in the heart of the Haisla Nation territory and will support the community’s goal of expanding housing, commercial and public space for its members, and opening new business opportunities.
The release went on to say, “The agreement continues the productive relationship between the Haisla Nation and B.C., which is furthering economic development opportunities and improving social conditions.”

It took decades for the land to be returned to the Haisla.
At the ceremony, Allan Donovan, the Haisla’s lawyer said, “We are here to celebrate the achievement of something that should have happened when the Haisla reserves were set aside in 1889. At that point, the reseve commissioner noted the Haisla reserves were the smallest and least desirable in the whole nation.

“But he left it at that, but in the years and decades afterward, the Haisla sought to extend their reserve holdings and their lands and have done so with an increasing degree of success.
“The actual negotiations to see the lands returned actually started over 60 years ago with limited success. But the Haisla are always persistent when it comes to issues of land, when it comes to issues of justice.
“In the 25 years since then there have been a number of attempts over the years This time with Haisla leadership and cooperation from the government of British Columbia, that dream has become a reality. The land has been returned to the rightful owners, joining up these two reserves.
Building goodwill
The ministry said the British Columbia introduced incremental treaty agreements “to help speed up the treaty process by building goodwill among parties and bringing the benefits of treaty faster to First Nations. These agreements also provide increased certainty on the land base and with natural resource development.”
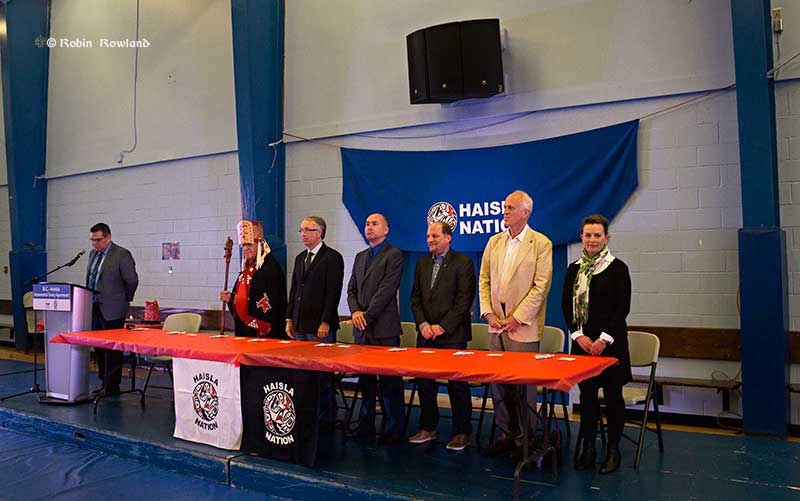
At the ceremony, John Rustad, the Minister of Aboriginal Relations and Reconciliation said that so far the province has signed 18 incremental treaty agreements with various BC First Nations.
“This is a relationship building step between the Haisla Nation and the province, to lay foundations for things we can continue to do in the future,” Rustad said, “Over the past number of years now the Haisla and the province have made great strides and have a very good relationship (at least I believe a very good relationship, … As we move forward in developing our relationship.”

Rustad noted that representatives of the Shell-led LNG Canada project, Chevron and AltaGas were at the Recreation Centre to witness the ceremony.
“It’s about embracing those opportunities and ways to find a balance between environment and economics. No one has been better than the Haisla in being able to do that, working with the companies working with the province, working with their neighbors to create opportunity.
“It is through hard work and through partnerships that is truly a path forward toward building a prosperous future.
“We are very proud as a province to be working with the Haisla as a partner,” Rustad said. “We have our difference, we have things we may not agree on but I also believe very strongly that as we work together the steps to ensure prosperity for all of British Columbia but also especially for the prosperity of the Haisla nation This agreement between the Haisla and the province is an example of some of the things we can do right and we can try to correct the situations that have existed for such a long period of time, to find a way to build a prosperous future.”
Stop dwelling on the past
Ellis Ross, the Haisla elected Chief Counsellor told the Haisla and their guests. “It’s time to stop dwelling on the past and start building the future. All the pieces are there Everybody wants to help us get to a better place. Our partners from LNG Canada are here.Chevron is here. It’s everyone working together for the future, to bring the pieces of the puzzle to ensure our future generations.
“We don’t have to beg to be part of the BC agenda. We should be equal particpants.in everything in our territory. That’s what we should be focused on Stop getting distracted with the minor little differences, where infighting stopped us from the promises that have been promsed us for the past forty or fifty years.”
He said the Haisla started working with the Christy Clark government in 2009.
“We both took different approaches to our relationship We both agreed there is a common goal to be achieved if we just put aside our differences. I am not sure how many people know this but the provincial government actually helped us acquire the hospital lands (the site of the old “pink lady” hospital across from the City Centre mall)
“In terms of the water lot that the Haisla own, we’re the only First Nation in Canada that owns water lots and that ‘s because of the provinical government support for us.”

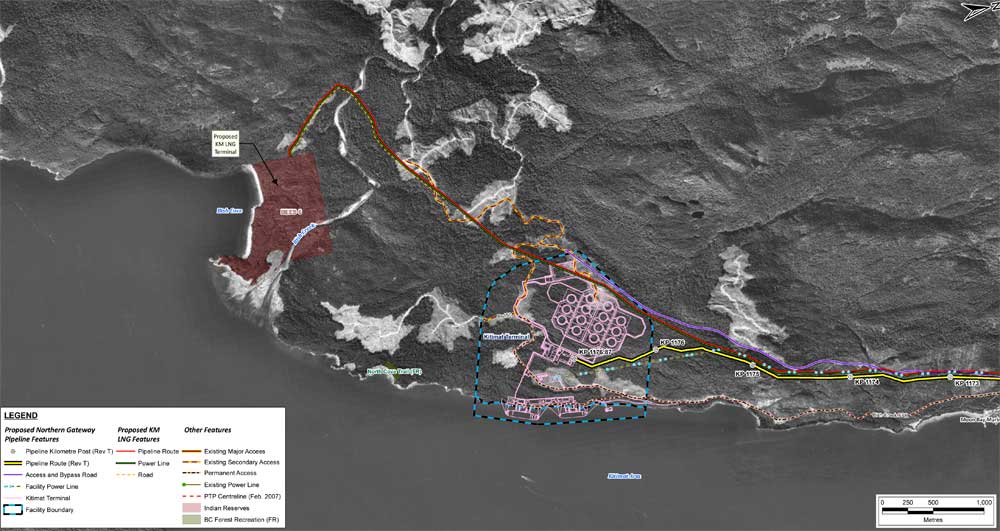
He also thanked the province for helping the Haisla lease land with an option to purchase near Bish Cove (Beese in traditional Haisla terminology) and worked with the federal government so that the Minette Bay lands could also be added to the reserve lands. He said Haisla staff consult on a regular basis with provincial officials.
“Our staff are working on permits for the benefit of the Haisla as well as everybody else. I think the Haisla are a working definition of what reconciliation actually means and it matters to the average Haisla citizen…
“There are different definitions out there about what reconciliation means. Everyone has a different definition Right how BC and the Haisla are proving that reconciliation is possible without getting into politics.
“It’s agreements like this what we’re talking about today that truly set the stage for the future of the Haisla people.
“We’re not going to be around in a hundred years but in a hundred years the future if Haislas are still talking about the same issues they talked about 50 years ago, we as leaders failed today.
“This is only one of the many agreements that we sign with the provincial govt and with LNG Canada and with Chevron and everybody else that’s willing to sit down and work out some sort of agreement with us.
“In fifty, a hundred years I am sure our descendants won’t be talking about poverty, they won’t be talking about unemployment, they wont be talking about extra land so we can build more houses. they’ll be talking about issues we can’t even understand yet but they won’t be dealing with the issues we’re trying to deal with today.
“What is the next agreement? The only thing that makes this possible is two parties sitting down and saying ‘let’s get an agreement for the betterment of all.’”

–
Quick Facts:
- Haisla Nation has approximately 1,840 members, with 700 people living in Kitamaat Village, at the head of Douglas Channel, about 10 kilometres south of Kitimat.
- The incremental treaty agreement provides for the early transfer land to Haisla Nation, ahead of a final agreement with the Haisla.
- The Province and Haisla Nation have collaborated on a number of initiatives, including facilitating negotiations for the Haisla to purchase former District of Kitimat hospital lands; the purchase of MK Bay Marina; and transfer of foreshore lots in the Douglas Channel
- In 2012, Haisla Nation and the Province signed the Haisla Framework Agreement allowing for the purchase or lease of approximately 800 hectares of land adjacent to Indian Reserve No. 6, intended for LNG development. The framework agreement also commits the parties to land-use planning around the Douglas Channel, helping to create certainty and allowing other projects in the area to proceed.
- Haisla is a member of the First Nations Limited Partnership, a group 16 First Nations with pipeline benefits agreements with the Province for the Pacific Trail Pipeline. Haisla and the Province also have a forestry revenue sharing agreement and a reconciliation agreement.
- Haisla Nation is a member of Marine Planning Partnership for the North Pacific Coast, which provides recommendations on stewardship and sustainable economic development of the coastal marine environment.
- Over the past decade, the Haisla Nation has engaged in 17 joint ventures with industries seeking to support economic activity for the region
(Source Ministry of Aboriginal Relations and Reconciliation)