Staff of the Northern Gateway Joint Review panel explain the hearing process to residents of Kitimat at Riverlodge Recreation Centre, June 16, 2011. (Robin Rowland/Northwest Coast Energy News)
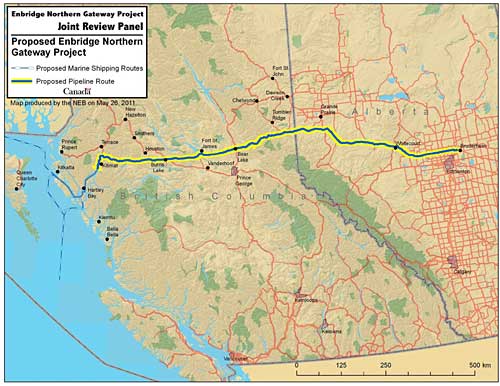
It will take more than year for the Enbridge Northern Gateway Joint Review Panel to complete hearings and taking evidence before it even begins to consider a decision whether or not to approve the controversial pipeline proposal.
Even then, the worries of the residents of northwest of British Columbia will be only one factor in the panel’s decision.
The Joint Review panel information town hall reached Kitimat on the afternoon of Thursday, June 16. One of the information sheets handed out at the town hall explained the Joint Review Panel this way:
In deciding if the Project is in the public interest, the Panel will consider whether Canadians would be better or worse off if the Project was approved. The public interest includes all Canadians and refers to a balance of economic, environmental and social considerations that change as society’s values and preferences evolve over time.
(Emphasis in original)
Here is a summary of how the process will work:
This summer, those who wish to formally participate in the hearing process must register with the panel.
For those who wish full intervenor status, the deadline to apply is July 14, 2011.
For those who wish to make oral statements in the community round of hearings, the deadline to apply is October 6, 2011.
Those formal intervenors who wish to request information from Northern Gateway have two deadlines. August 25, 2011 is the deadline for the first round, after which Northern Gateway must respond by October 6. The intervenors then can ask Northern Gateway a second set of questions, with a deadline of November 3, 2011. Northern Gateway must respond by November 24, 2011.
The deadline for intervenors to file written evidence with the panel is December 22, 2011.
Community hearings
On January 10, 2012, the Joint Panel will begin the “community hearings” phase where anyone who met the registration deadline, either as an intervenor or a community participant, can make a presentation to the panel.
These community hearings will be held across northern BC and Alberta, along the route of the pipeline and down the coast, with, sources say, a significant session slated for Kitimat.
The community hearings are expected to take several weeks.
Those who made oral comments to the panel then have until March 13, 2012 to file follow up letters.
Final hearings
The community hearings are then followed by another round of filing by the intervenors and government participants.
On June 16, 2012 the Joint Review Panel will then open the more formal “final hearings” at a location to be determined.
Around the same time, the Joint Review Panel must prepare an environmental assessment report that will be submitted to the Minister of the Environment.
Again, according to the handout material, there is a caveat in the panel’s mandate
The significance of any negative environmental and socio-economic effect is only determined after considering the actions that are proposed to prevent or reduce the effects. (Emphasis in the original)
In other words, as those who have attended Enbridge’s briefing sessions know, the company has outlined a whole series of safety measures, for example, adding navigation aides to Douglas Channel and parts of the coast.
If the environmental movement wishes to challenge the voluminous reports, likely costing millions of dollars that Enbridge has already filed as part of its application to the Joint Review Panel, the environmental concerns will have to be backed up with solid and expensive expert evidence.
Once the Minister of the Environment has the environmental assessment, the government then responds:
The government response will set out whether the Government of Canada agrees or disagrees with the conclusions and recommendations made the Panel by the panel regarding the potential environmental and socio-economic affects of the Project. The Governor-in-Council [ the federal cabinet] must approve the government response. This approved response will be made available to the public.
The decision
After it hears the government response on the environment, the panel makes its decision, whether or not the project can proceed.
The Panel will issue its Reason for Decision which will include a decision whether or not the Project is in the Canadian public interest.
If the Panel decides the Project can proceed, its Reasons for Decision will include conditions that Northern Gateway must meet before, during and after the construction of the Project.
If the Panel decides that the Project should proceed, the Panel will send its decision to the Governor in Council who can either accept or reject the decision but cannot modify it.
The Governor in Council means the federal cabinet, so the final decision will rest with Prime Minister Stephen Harper.