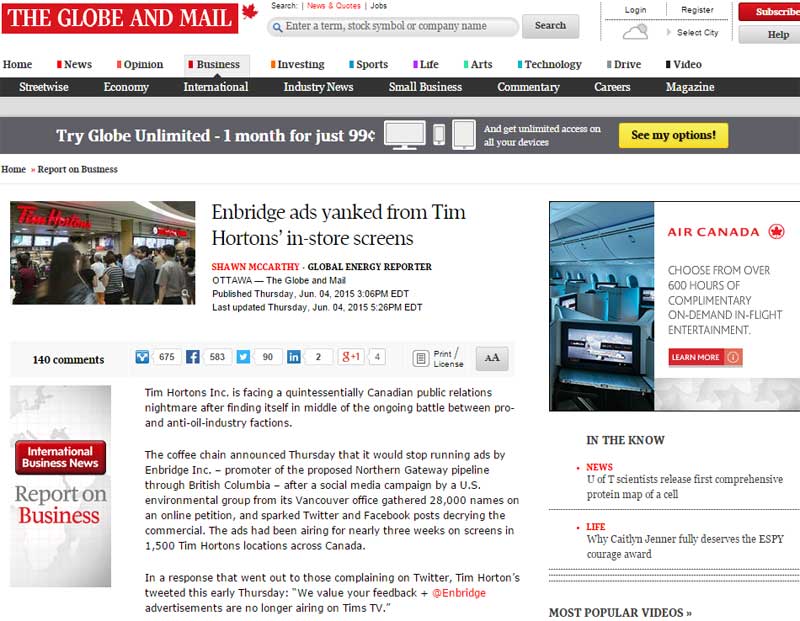
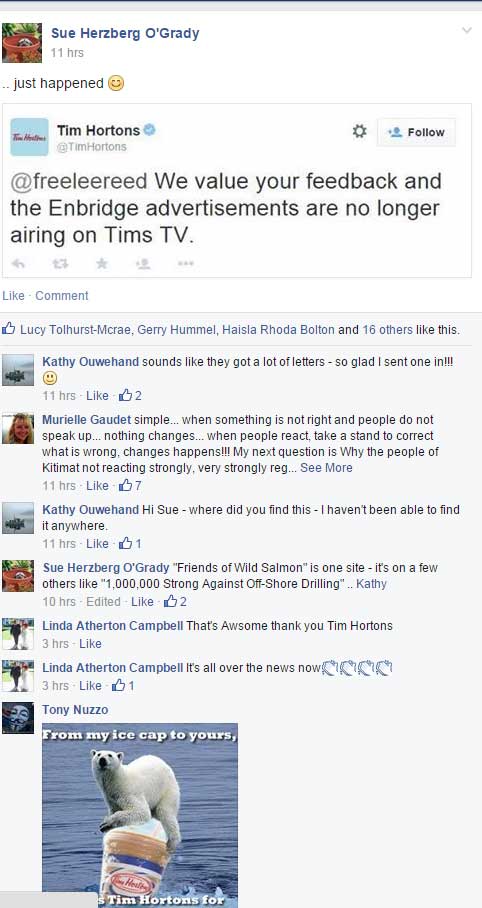
The headline on Thursday’s CBC.ca coverage of the sudden controversy over a boycott in British Columbia of Tim Horton’s over the Enbridge ads sums up everything that’s wrong about media coverage not only of the boycotts, but of northwest energy and environment issues overall.
“Tim Hortons yanks Enbridge ads, sparks Alberta backlash.” The anger at Tim Hortons across northwest British Columbia over those Enbridge ads, the calls for a boycott have been building for more than two weeks but no one in the media noticed despite widespread posts on Facebook and other social media.
As usual, the concerns of the northwest didn’t really become a story until Alberta got involved and the story has become the “Alberta backlash.” Now, there’s a backlash on social media to the Alberta backlash, with northwestern British Columbians tweeting and posting their displeasure, angry at the usual blinkered views of Alberta-centric coverage of energy issues.
Let’s make one thing clear– despite the outraged cries of the usual suspects like Defence Minister Jason Kenney, Conservative MP Michelle Rempel, who represents Calgary Centre-North and Kyle Harrietha, the Liberal candidate for Fort McMurray-Cold Lake that the boycott was aimed at Alberta’s entire energy industry and the province’s views of a manifest destiny as an energy super power, the doughnut boycott was really aimed specifically at Enbridge, and the company’s arrogance and incompetence.
This morning Wildrose party leader Brian Jean has joined the Alberta boycott and is demanding the Enbridge ads be reinstated. “I’ll pick up my Tim’s coffee again when they decide to apologize for taking jabs at our industry, which is so important to Albertans,” Jean is quoted on CBC.ca.
Of course Jean, like most Albertans, isn’t looking at the bigger picture. The question that Jean should really be asking, is the continuing unquestioning support for Enbridge actually harming the rest of the Alberta energy industry by increasing the resistance in northwestern BC to other energy projects? When are Alberta politicians, whether federal or provincial, ever actually going to show even a Timbit of respect for the issues in northwestern British Columbia?
Look at what Enbridge is doing
There is strong support (with some reservations) for the liquified natural gas projects. There is a level of support for pipelines that would carry refined hydrocarbons to the coast, something that the new premier of Alberta, Rachel Notley is seriously considering. But it is so typical of Alberta, the Alberta media and most of the Canadian media, to believe that the boycott was an attack on the entire energy industry.
Ask any executive of an energy company that wants to do business in northwestern British Columbia and they’ll come up with the a joke that is now so old and so often repeated that it’s become a cliché, “We look at what Enbridge is doing and then do the exact opposite.”
The fact is that Enbridge has been dealing with northwestern British Columbia for more than ten years and they still can’t do anything right. Shell, Chevron, Petronas (and before them Apache) and even TransCanada make more efforts to listen to the people, First Nations and non-Aboriginal residents alike, than Enbridge ever has or ever will (despite their claims in their PR campaigns).
While these energy giants may not agree with what they hear, they are respectful and depending on their corporate culture are making genuine efforts to come up with ways to make their projects work. After a decade of blunders, however, Enbridge still hasn’t shown that much respect for anyone here. Those touchy feely ads that appear on television and at Tim Horton’s are just another example of how not to run a public relations campaign.
There are those who oppose any bitumen sands extraction who signed the online petition, but the core of opposition, as always, comes from northwestern BC and the issue is an ill-conceived pipeline.
Enbridge has been successful in one area of its public relations strategy. They’ve convinced Albertans that Enbridge and the Northern Gateway pipeline is an essential part of not only the Alberta economy but Alberta culture. Any attack on Enbridge becomes an attack on Alberta. Hence the unreasoned anger when after Tim Hortons pulled the ads.
The big blame America lie
The other Big Lie we keep hearing from the Harper Government, is that this all orchestrated by American NGOs and activists. Again this shows Alberta-centric contempt for British Columbia. It’s very easy and convenient to keep believing that everyone in northern British Columbia are dumb and stupid and are being led by the ear by those nasty green Americans who have it in for the efforts to make Canada an energy superpower. That idea, promoted by the more conservative Canadian media has always been animal waste. The battle to protect the environment of northwestern British Columbia while at the same time attracting resource projects that have recognized and obtained social licence to operate has always and will always in BC on a case by case, community by community basis.
The only media that so far has managed to get it half right is Jason Kirby writing in MacLean’s who notes that the trouble began on May 18 when Enbridge put up the Tim Hortons ad on their own website. (Did I mention that Enbridge is both incompetent and arrogant?) and it was immediately noticed by those individuals and activists that monitor the Enbridge website.
A morning shock with your morning coffee and Timbits
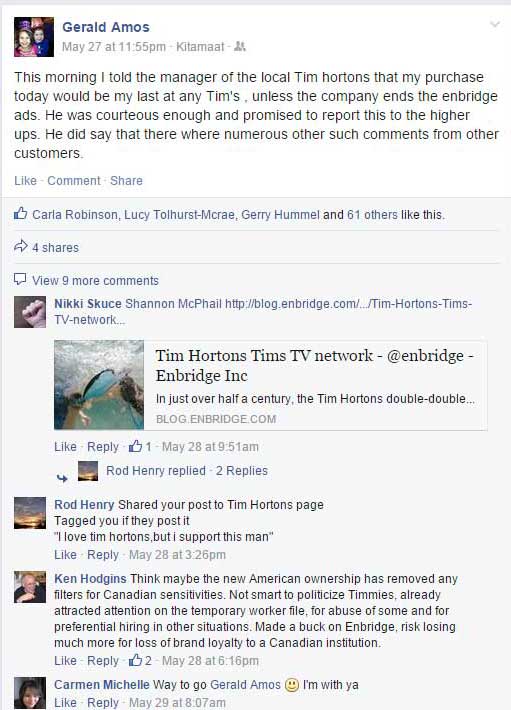
Social media across northwestern British Columbia, mostly Facebook, began spreading the news within hours of the ads appearing in the local Timmys. There were angry posts from individuals who had walked in Tim Hortons and saw the ads.
Why didn’t the media get the story?
So why wasn’t the story covered by the media at least ten days ago?
That’s because in this age of tight budgets, it’s considered easy and economical to try to all of northern BC cover from either Vancouver or Calgary; that means covering from far away both the coast where the pipelines and tankers may or may not operate to the east near the Rockies where the natural gas extraction is on going
If you look at map of northern BC, and the two federal ridings Skeena Bulkley Valley and Prince George–Peace River–Northern Rockies, the population is about 200,000 spread over an area about half the size of Europe. Both ridings in this region are supposedly vital to the future of the Canadian economy, but you wouldn’t know it from most of the media. (The Globe and Mail is an exception, with more ongoing coverage of northern BC than you will find in either The Vancouver Sun or The Province).
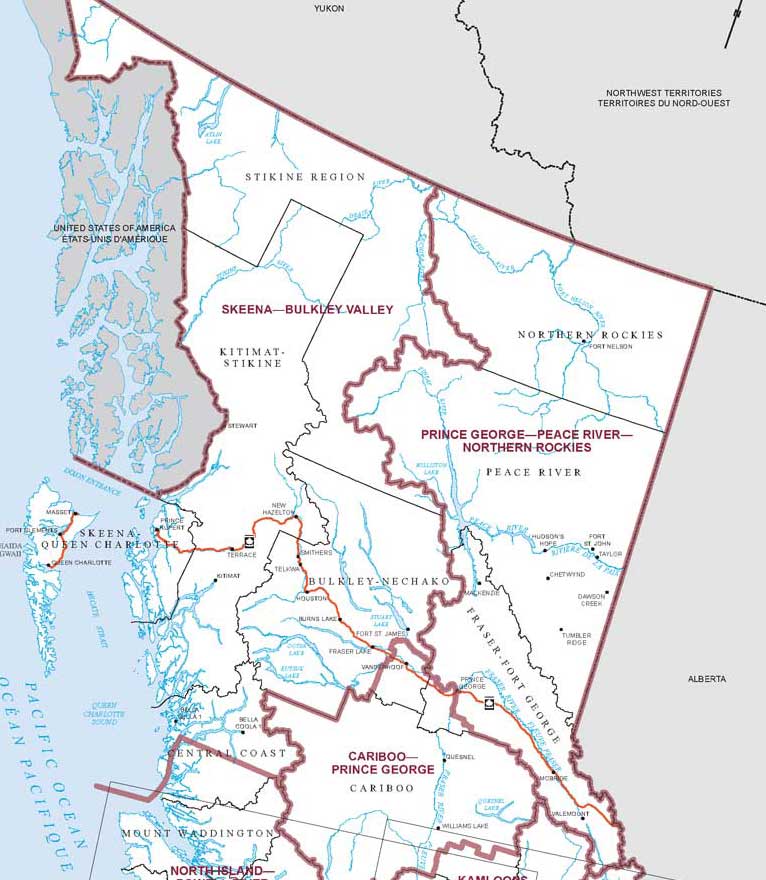
As for CBC, there are just eight radio staff, two in Prince Rupert and six in Prince George to cover all the apparently vital issues across half the province. ( Almost all the staff work mostly for the Daybreak North morning show which dominates the regional rates but it looks like with the latest CBC cutbacks that at least one of those positions will be eliminated). CBC TV and Global cover the region from Vancouver.
At least the Vancouver based media make efforts to cover the north from time to time. The Alberta media, however, especially the Calgary Herald, is hopeless, and so biased against British Columbia and so dismissive of the issues here, that the coverage across Alberta is completely unreliable about 90 per cent of the time—it’s no wonder that the majority of Albertans have no understanding of British Columbia culture and issues.
Then there are the punditi, pontificating from their cubicles in Ottawa and Toronto without a clue, without doing the basic journalism of picking up the phone (or writing an e-mail) to actually find out what’s going on.
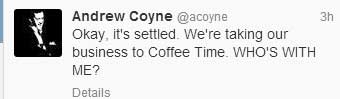
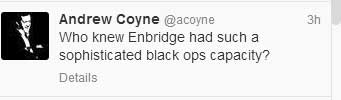
Andrew Coyne, for example, made these rather silly two tongue-in-cheek tweets Thursday night. While Coyne’s tweets do often exhibit a sense of humour, his excellent coverage of the decline of our democratic parliament has to be compared with his blind, unchecked ideological assumptions about the issues of the northwest, which are simplistic, cubicle bound and far off the mark. The same can be said for Jeffrey Simpson in his occasional writing about this region. Neither the view from the Hill, where you can see as far as the Queensway, nor from Bloor Street, where you can see part of the Don Valley, are vantage points to understand what is going in northern British Columbia.
Update: Rex Murphy, writing in the National Post, has now joined the fray, no longer making a secret of his absolute disbelief in climate change and support for Enbridge. However, if you read his column, it is scathing in its contempt for the working men and women of British Columbia who want sustainable environmentally safe resource projects. It appears that to Murphy the only people in this country who actually work for a living in Canada are in Alberta and Newfoundland and no where else. Kitimat has been an industrial town since it was founded in the 1950s, Kitimat rejoiced when former Mayor Joanne Monaghan succeeded in bringing a Timmys to Kitimat and the majority of Kitimat residents voted in the plebiscite against Enbridge. But, of course, all those facts are irrelevant to Murphy and the other conservative pundits who never come within a thousand kilometres of northwestern BC, who believe we can’t think for ourselves and are easily misled by American environmentalists. No wonder journalism is in a death spiral.
Error checks
So let’s look at the specific errors in the media coverage of the Tim Horton’s story.
Both Shawn McCarthy in the Globe and Mail and Kyle Bakyx on CBC.ca seem to accept without question that SumofUs, was the instigator of the petition. Like many issues in northwestern BC, the Lower Mainland or US based activist groups follow the lead of northwestern BC and jump on the bandwagon, not the other way around. Jason Kirby in MacLean’s says the boycott movement began a week ago. Here in Kitimat, it began within hours of the ads appearing in the local Timmys and was picked up on activist social media groups before the SumofUs petition site.
McCarthy repeats the conventional wisdom: “The Conservatives and oil industry supporters have been waging a public relations war with the environmental groups that oppose expansion of the oil sands and construction of new pipelines.”
When is the media ever going to learn that opposition to Enbridge is widespread across most of northern British Columbia, from First Nations to city and regional councils to a plurality of residents? When is the media going to drop the stock phrase “First Nations and environmentalists”? Does anyone remember the vote in Kitimat last April against the Northern Gateway project?
CBC.ca quotes Alan Middleton of York University “Enbridge, of course, is not just pipelines and oilsands; they are a whole range of products including heating people’s homes. Tims should have thought about that.” Again a mistake. I lived in Toronto for many years. A company called Consumers Gas supplied natural gas to homes until it was taken over by Enbridge, so Enbridge does heat the homes in Toronto. But what has that got to do with northwestern British Columbia? Why didn’t CBC.ca call the University of Northern British Columbia? Easier to call York (which by the way is where I got both my BA and MA)
McCarthy quotes Rempel as saying, “One has to wonder whether head office talked to their franchise owners in Alberta before making the decision. I imagine those calls are being made this afternoon – certainly there are a lot of people voicing their displeasure.”
The question that should have been asked whether or not Tim Hortons consulted their franchise owners in British Columbia before ordering them to play the ads. People here were “voicing their displeasure” from the moment the first Kitimatian walked into the local Timmys for an early morning coffee and had to stand in line while being told how wonderful Enbridge is.
Of course, if Albertans force Tim Hortons into reinstating the ads, that will only trigger a bigger boycott in British Columbia. As Maclean’s asks, “what were they thinking?”
Jason Kenney, flying in, flying out
As for Jason Kenney, who is quoted by the CBC as tweeting: “I’m proud to represent thousands of constituents who work for Enbridge & other CDN energy companies,” if Kenney aspires to be Prime Minister one day, he had better start thinking about representing more Canadians than just those employed by the energy industry—a mistake that his boss Stephen Harper keeps making.
Jason Kenney did visit Kitimat for a just a few hours in February 2014 for a tour of the Rio Tinto modernization project and an obligatory and brief meeting with the Haisla First Nation council. If Kenney had actually bothered to stick around a few more hours and talk to the community, everyone from the environmentalists to the industrial development advocates, he might not have been so quick on the trigger in the Twitter wars.
Not one of the major media who covered this story, not The Globe and Mail, not CBC.ca, not MacLean’s, no one else, once bothered to actually call or e-mail someone who lives along the Northern Gateway pipeline route in British Columbia, the area where the boycott movement actually began to ask about Enbridge’s track record in this region. The media still doesn’t get it. This morning’s stories are all about Alberta. As usual, my dear, the media doesn’t give a damn about northwestern British Columbia.
That is why the coverage of the Tim Hortons boycott is a double double failure of the Canadian media.
Where else the media is failing northwestern BC
Full disclosure. Since I took early retirement from CBC in 2010 and returned to Kitimat, I have worked as a freelancer for CBC radio and television, Global News, Canadian Press, The National Post, The Globe and Mail and other media.
However, largely due to budget cuts, freelance opportunities, not only for myself, but others across the region have dried up. The media seems to be concentrating more on the major urban areas where there is larger population base and at least more of the ever shrinking advertising dollar. I am now told more often than I was a couple of years ago that “we don’t have the budget.”
Now this isn’t just a freelancer who would like some more work (although it would be nice). If the media these days actually had environmental beats for reporters the boycott of Tim Hortons in northwest BC would have been flagged within a couple of days, not almost two and half weeks and later only when Alberta got hot under its oily collar.
So as well as the Tim Horton’s boycott here are two major ongoing stories from Kitimat that the media haven’t been covering.
100 day municipal strike
-Kitimat’s municipal workers, Unifor 2300, have been on strike since February 28. Three rounds of mediation have failed, the union has refused binding arbitration, the pool, gym and community meeting halls have been closed since February, the municipal parks and byways are now returning to the wilderness. Only essential services are being maintained (but residents still have to pay their property taxes by July 2, taxes that are skyrocketing due to increased assessments for home values based on LNG projects that haven’t started) By the time most people read this the strike will have been on for 100 days. There is no settlement in sight and both sides, despite a mediator ordered blackout, are fighting a press release war on social media. Can you imagine any other place that had a 100 day municipal workers strike with no coverage in the province’s main media outlets, whether newspaper or television? Local CBC radio has covered the strike, as has the local TV station CFTK. (Update: District of Kitimat says in a news release that the mediator has now approved the DoK news releases.)
Of course, in the bigger picture the media concentrates on business reporting. There haven’t been labour reporters for a generation.
Kitimat air shed hearings
-The environmental hearings on the Rio Tinto Alcan proposal to increase sulphur dioxide emissions in the Kitimat Terrace air shed, after two weeks in Victoria, where there was no media coverage, are now continuing in Kitimat, where again there is little media coverage. CFTK is covering the hearings; otherwise the main coverage comes from the activist group DeSmog, hardly a credible or unbiased source. I made the decision not to cover the hearings either. I can’t afford any longer to sit around for two weeks, unpaid, no matter how vital the hearings are to the community.
So if most Canadians were surprised that there was a boycott of the unofficial national symbol, Tim Hortons, it’s because of that double double media fail and as the media continues to decline, as budgets are cut, as “commodity news” disappears, expect more surprises in the future. Oh by the way Kitimat is vital to the national economy but we can cover it from a cubicle in Toronto.
Final disclosure: I am not a coffee drinker. When I go to Timmy’s I prefer a large steeped tea and an apple fritter.