Energy Environment Politics
 BC Premier Christy Clark meets with the leaders of the Haisla First Nation at Kitamaat Village, Monday, Sept. 19, 2011. (BC government hand out )
BC Premier Christy Clark meets with the leaders of the Haisla First Nation at Kitamaat Village, Monday, Sept. 19, 2011. (BC government hand out )
BC Premier Christy Clark made a flying visit to Kitimat Monday, Sept. 19, 2011, dropping into Kitamaat Village to meet with the leaders of the Haisla First Nation and, as part of the flying, boarded a helicopter to take a look at the KM LNG at under construction at Bish Cove, before flying out again.
It was all part of the premier’s campaign style job strategy which sees Clark touring the province this week and unveiling a complete jobs package on Thursday.
The proposed liquified natural gas terminals at Kitimat are not as controversial in this region as the proposed Enbridge Northern Gateway pipeline. There is general support for the LNG projects, allowing for safety concerns about LNG tankers and environmental problems from the construction of the pipeline.
Clark’s visit to the Kitimat region is controversial here because from all appearances, there was little or no substance. If the visit had in been the early decades of the last century, when politicians traveled by train rather than helicopter, it would have been a “whistle stop,” nothing more.
A BC premier visiting the traditional territory of the Haisla First Nation should, of course, make a courtesy call on the leadership in the village, although it appears the visit was short, routine rather than a truly substantial meeting.
As for the rest of the Kitimat region was concerned, the premier’s short in and out photo op was not aimed at helping the people of Kitimat but appeared to be more spinning her jobs strategy throughout the rest of the province which is less familiar with the history of development in Kitimat.
No one in the local media, the Northern Sentinel, Kitimat Daily nor Northwest Coast Energy News were given any information about timing of the premier’s visit, perhaps because local reporters might ask tougher questions than the BC legislature pool traveling with Clark. The Northern Sentinel only found out about the time of the meeting after one of the numerous calls made by local media was actually returned in time for their reporter to be in the village for the premier’s visit.
As of Sunday, no meeting between the premier and Kitimat Mayor Joanne Monaghan was scheduled. At the last minute, after some political arm twisting, the premier did have a brief ten to fifteen minute meeting with Monaghan and Municipal Manager Ron Poole at the village on Monday. (It should be noted that members of Kitimat council will meet with Clark at the up coming convention of the Union of BC Municipalities).
At 14:55 Monday, Sept. 19, Clark (or her PR team) tweeted.
We’re taking steps to get #kitimat’s liquefied natural gas plant running by 2015. A strong LNG industry means local jobs. #bcpoli
The message was quickly retweeted by Clark supporters. That tweet raised eyebrows, since the process for the KM LNG is already well under way, with construction apparently on schedule for the 2015 date when the first natural gas will flow into a tanker. The licence for KM LNG is in the hands of the federal National Energy Board.
What the tweet meant became clearer once the premier’s office issued a news release
Christy Clark’s “more aggressive approach to the development of the natural gas sector” includes traditional small c conservative elements:
Cutting red tape: accelerate the lengthy permitting processes and improve the decision making required to bring large-scale production facilities from a concept to a reality, and that these commitments will be a greater priority for B.C. on a go forward basis.
Skills training: working with industry partners for some time on the future skills required to support a new LNG industry. The goal is to ensure the post-secondary system is able to deliver the targeted training necessary to grow the oil and gas industry, including LNG.
Attracting investment: by working with industry stakeholders and First Nations to remove the barriers and secure the investment required to establish up to three LNG plants by 2020. As of today, the Province is aware of a handful of LNG proposals.
The only practical element in Clark’s announcement was help for the Haisla First Nation in dealing with multiple developments: (as related in the news release)
The Province’s assistance is timely,” said Haisla Nation Chief Councillor Ellis Ross. “Our own training capacity is limited by resources and capabilities, and these have been exhausted given the projects now underway on our territory and the demands they place on our people for skills and training. Our economic future has never looked better, and this assistance will help us deliver on this promise to our community.”
Michael Smyth of The Province (along with a number of Tweeters) noted that most of Clark’s announcement was recycled.
Those same economic storms have buffeted the government, too, and Clark doesn’t have a lot of money to spend on direct job creation — not if she keeps her promise to balance the budget in 2013.
So, expect many re-announcements of old projects. The proposed Kitimat liquefied natural gas plant Clark trumpeted Monday, for example, was approved three years ago.
She’s also expected to cheerlead the Northwest Transmission Line project this week, another one that’s been in development for years.
Without a lot of money to throw around, Clark will talk about getting government out of the way of private-sector job creation. Deregulation and cutting red tape is less expensive than direct stimulus spending to create jobs.
The environmentalists won’t be happy when she starts fast-tracking permits for mining and other resource extraction, but losing “green” votes is the least of her worries.
Veteran journalist Norm Farrell in his blog “Let’s play political football with Kitimat” gives a list of how often a Kitimat LNG project has been announced going back to an Associated Press report from 1981
The Rim Gas Project, which includes Petro-Canada of Calgary, Westcoast Transmission of Vancouver and Mitsui and Co. Ltd. of Japan, wants to deliver and sell liquefied natural gas to Japan from a plant it will build at Bish Cove, six miles from Kitimat.
And Kitimat Tweeter YWGSourpuss posted:
Kitimat has kinda sorta might been getting an LNG Plant since I was a teenager. Meanwhile, Methanex and Eurocan were culled, dust blows…
and then
I see media wonks waffling about LNG/Kitimat/need for cheap energy. Remember Kemano Completion? Ask Rio Tinto re: hole in the mountain.
On the Opposition side of the question, Vancouver Sun columnist Vaughn Palmer looked at an apparent split in the opposition NDP over the LNG issue Wednesday, noting that the environment critic NDP environment critic Rob Fleming is concerned about the controversial fracking process used to retrieve natural gas from shale:
When you look at where the gas would come from, we’re talking about major shale-gas deposits. There are big concerns there, from an environmental perspective, around water usage and whether it’s sustainable, and water contamination when it’s injected underground to bring the gas to the surface – the fracking process – and a lot of greenhouse gases produced.
Palmer reports that the NDP house leader John Horgan has indicated that he and Opposition leader Adrian Dix support LNG exports.
In Horgan’s estimation, it could be piped to the coast, liquefied and shipped out with minimal risk. “Liquid natural gas doesn’t stick to things. It blows up, or it vents. So the environmental consequence of a catastrophe with an LNG tanker is relatively insignificant,” he told me during an interview on Voice of B.C. on Shaw TV.
“So the risk to our coastline from LNG is insignificant; the benefit to British Columbians is quite significant. And it’s our resource, so we’ll get the royalties for extracting it, we’ll get value added by getting it to an LNG facility, and then we’ll get a better price for it in Asia.
Palmer is concerned about Fleming’s caution not to rush things, stating that
For “you can’t rush these things” is precisely the opposite of what industry analysts are saying about LNG development. The window on the Asian market is closing, and if B.C. doesn’t get moving, the opportunity will be gone. Again.
One wonders where Palmer gets his evidence that window of opportunity for the Asian markets is closing? With the Fukishima meltdown, the market window for LNG is actually expanding, not just in Japan but across East Asia. What some in the energy industry are warning about is Canadian gas being exported through the United States, warnings that were prominent at the NEB hearings in Kitimat last June and is largely industry spin trying to hurry the approval process along.
The controversy over fracking will continue, with the energy industry claiming it is safe and the environmental activists saying it is not. What is apparent about fracking as Pro Pubilica have pointed out in their continuing investigation of the issue, is that use of the process on a wide scale is new and there aren’t enough adequate studies of the process. Inadequate study could mean consequences down the road, we don’t know, so there should be some caution.
The blasting continues at the KM LNG site at Bish Cove as the shoreline rocks are levelled to close to sea level. Meanwhile the political spin pitches just as much hot air and debris into the atmosphere.
Related Links
Vancouver Sun Clark leaves out Island on jobs tour
Northern View: B.C. Jobs Plan’ keys on trade with Asia
 Jordan Cove project manager Robert Braddock told the industry newsletter, Platt’s Gas, that he is “not afraid of competition from the north, where Kitimat LNG is planning an export terminal in British Columbia. ‘We actually presume that Kitimat would be built,” Braddock said. “We assume that we would be built number two and we think there is plenty of room for two such facilities on the West Coast.’
Jordan Cove project manager Robert Braddock told the industry newsletter, Platt’s Gas, that he is “not afraid of competition from the north, where Kitimat LNG is planning an export terminal in British Columbia. ‘We actually presume that Kitimat would be built,” Braddock said. “We assume that we would be built number two and we think there is plenty of room for two such facilities on the West Coast.’ Similar to plans to take shale gas from the Horn River Formation in northeastern BC, Jordan Cove would tap into the
Similar to plans to take shale gas from the Horn River Formation in northeastern BC, Jordan Cove would tap into the
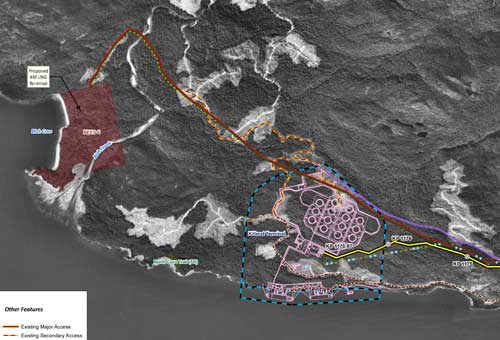
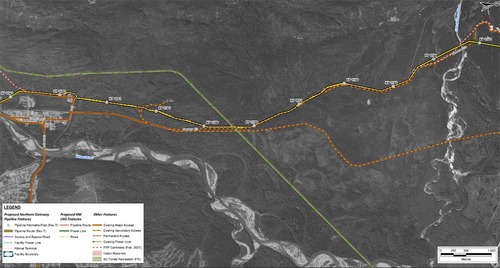 In this map, the Enbridge pipeline is yellow with a black outline, the LNG pipeline is red. Where there are yellow and red alternating squares, that means the two pipelines will follow the same route. Solid orange lines are paved roads,broken orange lines are unpaved roads and the green lines are power lines.
In this map, the Enbridge pipeline is yellow with a black outline, the LNG pipeline is red. Where there are yellow and red alternating squares, that means the two pipelines will follow the same route. Solid orange lines are paved roads,broken orange lines are unpaved roads and the green lines are power lines.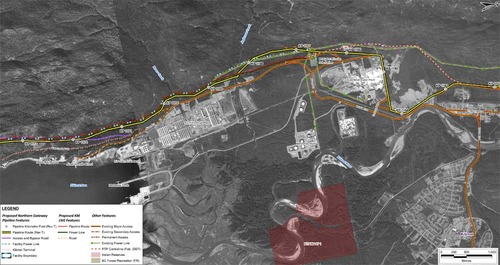 Just before the pipelines reach the service centre, they diverge, the yellow Enbridge pipeline following the road route around the periphery of the service centre, while the gas pipeline at first follows the route of the Pacific Trails Pipeline and then snakes off at the hydro substation. The two pipelines then run parallel just off Haisla Boulevard across from the Rio Tinto Alcan plant. The green line beside the two pipelines marks a hydro line that would be build to power the facilities.
Just before the pipelines reach the service centre, they diverge, the yellow Enbridge pipeline following the road route around the periphery of the service centre, while the gas pipeline at first follows the route of the Pacific Trails Pipeline and then snakes off at the hydro substation. The two pipelines then run parallel just off Haisla Boulevard across from the Rio Tinto Alcan plant. The green line beside the two pipelines marks a hydro line that would be build to power the facilities.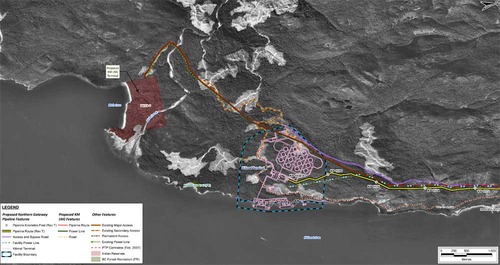 The final map shows the Enbridge pipeline coming into the bitumen/condensate terminal with its large footprint, while the natural gas pipeline continues, crosses Bish Creek and then enters the Bish Cove KM LNG terminal. If the BC LNG terminal is built at North Cove, just west of the proposed Enbridge Northern Gateway facility, a branch pipeline would go from the main gas pipeline down to that facility. (There were indications at the June NEB hearings that negotiations were under way on “sharing” gas “molecules” between the two groups).
The final map shows the Enbridge pipeline coming into the bitumen/condensate terminal with its large footprint, while the natural gas pipeline continues, crosses Bish Creek and then enters the Bish Cove KM LNG terminal. If the BC LNG terminal is built at North Cove, just west of the proposed Enbridge Northern Gateway facility, a branch pipeline would go from the main gas pipeline down to that facility. (There were indications at the June NEB hearings that negotiations were under way on “sharing” gas “molecules” between the two groups).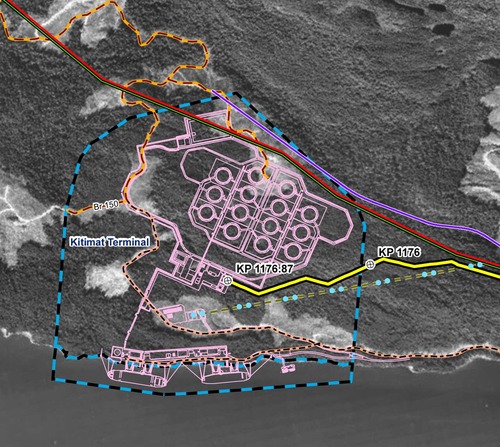 Footprint of the Enbridge Northern Gateway plant.
Footprint of the Enbridge Northern Gateway plant. BC Premier Christy Clark meets with the leaders of the Haisla First Nation at Kitamaat Village, Monday, Sept. 19, 2011. (BC government hand out )
BC Premier Christy Clark meets with the leaders of the Haisla First Nation at Kitamaat Village, Monday, Sept. 19, 2011. (BC government hand out )
 As reported in April by Alberta Oil
As reported in April by Alberta Oil 