Biofuel Environment
A study of west coast forests in California, Oregon and Washington concludes that biofuel from forests could increase carbon dioxide emissions by at least 14 per cent.
Oregon State University calls the study “the largest and most comprehensive yet done on the effect of biofuel” from the US west coast.
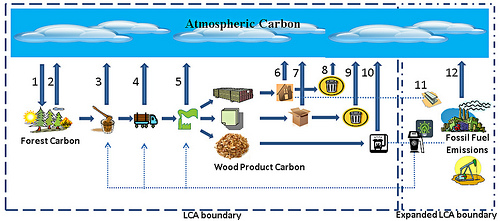
A diagram from the Oregon State University shows how using biofuels would increase the carbon emissions by releasing more forest carbon, including the processing and transportation of biofuel. (Oregon State University)
The study, published Sunday in Nature Climate Change, contradicts previous findings that suggest biofuel could be either carbon neutral or reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
It is uncertain whether the conclusions of the study could apply to northwestern British Columbia, due to different ecological conditions, including pine beetle devastation and the effects of climate change.
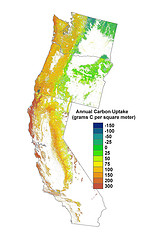 For four years, the Oregon State study examined 80 forest types in 19 ecological regions in the three states, ranging from temperate rainforests to semi-arid woodlands. It included both private and public lands and different forest management practices.
For four years, the Oregon State study examined 80 forest types in 19 ecological regions in the three states, ranging from temperate rainforests to semi-arid woodlands. It included both private and public lands and different forest management practices.
Tara Hudiberg, a PhD candidate at Oregon State and lead author, said in an e-mail interview, “We applied thinning scenarios which would remove whole trees and use the merchantable portion for wood products and the rest for bio-energy use (tops, branches, smaller trees of less then five inch DBH (diameter at breast height ).
“On the [US] West Coast, we found that projected forest biomass removal and use for bio-energy in any form will release more carbon dioxide to the atmosphere than current forest management practices.
“Most people assume that wood bio-energy will be carbon-neutral, because the forest re-grows and there’s also the chance of protecting forests from carbon emissions due to wildfire,” Hudiburg said. “However, our research showed that the emissions from these activities proved to be more than the savings.”
The only exception was if forests in high fire-risk zones become weakened due to insect outbreaks or drought, which impairs their growth and carbon sequestration as well as increasing the potential for large forest fires (a situation prevalent through much of British Columbia due to the devastation caused by the pine beetle.) The study says in that situation, it is possible that some thinning for bio-energy production might result in lower emissions in such cases.
“Until now there have been a lot of misconceptions about impacts of forest thinning, fire prevention and bio-fuels production as it relates to carbon emissions from forests,” said Beverly Law, a professor in the OSU Department of Forest Ecosystems and Society and co-author of this study.
(Oregon State University)
“If our ultimate goal is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, producing bio-energy from forests will be counterproductive,” Law said. “Some of these forest management practices may also have negative impacts on soils, biodiversity and habitat. These issues have not been thought out very fully.”
The study examined thousands of forest plots with detailed data and observations, considering 27 parameters, including the role of forest fire, emissions savings from bio-energy use, wood product substitution, insect infestations, forest thinning, energy and processes needed to produce bio-fuels, and many others.
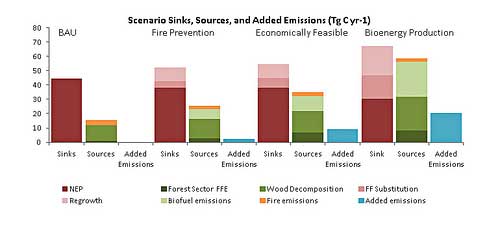
It looked at four basic scenarios: “business as usual”; forest management primarily for fire prevention purposes; additional levels of harvest to prevent fire but also make such operations more economically feasible; and significant bio-energy production while contributing to fire reduction.
Compared to “business as usual” or current forest management approaches, all of the other approaches increased carbon emissions, the study found. Under the most optimal levels of efficiency, management just for fire prevention increased it two percent; for better economic return, six percent; and for higher bio-energy production, 14 percent.
“We looked at CHP (combined heat and power from combustion) and cellulosic ethanol and we accounted for all sources of Carbon emissions from harvest to use,” Hudiberg said.
She added, “We don’t believe that an optimal efficiency of production is actually possible in real-world conditions. With levels of efficiency that are more realistic, we project that the use of these forests for high bio-energy production would increase carbon emissions 17 percent from their current level.”
About 98 percent of the forests in the three western US states are now estimated to be a carbon sink, meaning that even with existing management approaches the forests sequester more carbon than they release to the atmosphere. Forests capture a large portion of the carbon emitted worldwide, and
some of this carbon is stored in pools such as wood and soil that can
last hundreds to thousands of years, the scientists said.
The study suggests that increases in harvest volume on the US West Coast, for any reason, will instead result in average increases in emissions above current levels.
“Energy policy implemented without full carbon accounting and an understanding of the underlying processes risks increasing rather than decreasing emissions,” they conclude.
When asked about British Columbia, Hudiberg noted: “We are not aware of anything in particular, but we do know that BC forests may (or already are) be more susceptible to climate change impacts and insect outbreaks. So initially, it may be a more suitable region for bio-energy but the same analysis we did here would have to be done [in BC] to know for sure. She cautions, “The study conclusions are based on the regional conditions and current regional carbon uptake with current management practices For other areas, the current conditions need to be assessed before deciding if bio-energy will increase or decrease carbon emissions.”
Biofuel in northwestern BC
Biofuels are seen as a growth industry in northwestern British Columbia, with a number of companies are starting to work on various forms of biofuel investments including large corporations as well as medium and small business.
- In Kitimat, Pytrade has proposed a biomass plant that would use pyrolysis to convert wood waste into liquid bio-fuels and also generate heat that can be used by green houses used to train people in horticulture in conjunction with North West Community College. Pytrade also plans to make money by selling carbon offsets for every tonne of C02 not emitted into the atmosphere they will make money by selling credits. An application by company for a provincial a one million dollar Innovative Clean Energy (ICE) grant has been approved.
- General Biofuels Canada is planning a 500,000 metric tonne per year wood pellet facility in Terrace. This project would use hemlock fibre from “non-saw grade fibre” from area forest licence holders.
- Toronto-based CORE BioFuel Inc. Wants to build a plant, likely in Houston, (and perhaps more plants) to turn forest waste fibre into gasoline. Each plant would cost $100 million and require 220,000 tons of fibre a year to produce 67 million litres of gas.
As well as the College of Forestry at Oregon State University, the study involved institutions in Germany and France. It was supported by the US Dept. Of Energy.


