The Canadian Environmental Assessment Agency is calling for comments on the proposed LNG project at Prince Rupert.
As part of the strengthened and modernized Canadian Environmental Assessment Act, 2012 (CEAA 2012) put in place to support the government’s Responsible Resource Development Initiative, the Canadian Environmental Assessment Agency must decide whether a federal environmental assessment is required for the proposed Pacific Northwest LNG Project in British Columbia. To assist it in making its decision, the Agency is seeking comments from the public on the project and its potential effects on the environment.
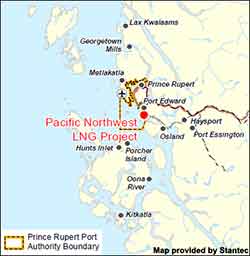
Progress Energy Canada Ltd. is proposing to construct and operate a liquefied natural gas (LNG) facility and marine terminal near Prince Rupert, within the District of Port Edward. The Pacific Northwest LNG facility would be located on Lelu Island. The proposed project would convert natural gas to LNG for export to Pacific Rim markets in Asia.
The agency says written comments must be submitted by March 11, 2013.
The CEAA says it will post its decision on the website if a federal environmental assessment is required.
It goes on to say:
If it is determined that a federal environmental assessment is required, the public will have three more opportunities to comment on this project, consistent with the transparency and public engagement elements of CEAA 2012.
Projects subject to CEAA 2012 are assessed using a science-based approach. If the project is permitted to proceed to the next phase, it will continue to be subject to Canada’s strong environmental laws, rigorous enforcement and follow-up, and increased fines.
 By “CEAA 2012,” the agency is referring to the omnibus bill, best known as C-38, which actually weakened the CEAA’s ability to review projects. “Science-based approach” has become a stock phrase used by the government of Stephen Harper on resource issues, while it weakened environmental review procedures, terminated the jobs of hundreds of scientists and restricted those who are left in the government from speaking to the media or commenting on issue.
By “CEAA 2012,” the agency is referring to the omnibus bill, best known as C-38, which actually weakened the CEAA’s ability to review projects. “Science-based approach” has become a stock phrase used by the government of Stephen Harper on resource issues, while it weakened environmental review procedures, terminated the jobs of hundreds of scientists and restricted those who are left in the government from speaking to the media or commenting on issue.
In December,the CEAA called for similar input for the Coastal GasLink project to Kitimat, with a deadline of January 30. No decision has been announced for that project. which would be built by TransCanada for the Shell LNG Canada project.