Energy
 China is probably the largest long
China is probably the largest long
term customer for liquified natural gas that will be shipped through
the port of Kitimat, executives from Encana, one of the three
partners in the KM LNG project said in an investor conference call
Tuesday, Oct. 4, 2011.
India could also be big customer for
LNG shipped from the Horn River in northeastern BC through Kitimat,
Encana said.
Although Japan will be increasing its
purchases of liquified natural gas in the coming years, the immediate
situation with Japan is less certain. While the March 2011
earthquake and tsunami knocked out the Fukishima nuclear plant and
prompted Japan to scale back other nuclear plants and increase LNG
purchases, Encana says the country has still not come up with any
definite policies
 Dave Thorn, Encana vice president of
Dave Thorn, Encana vice president of
Canadian marketing, who also oversees the Encana’s role in the
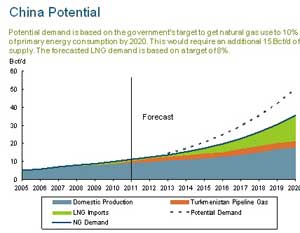
Kitimat project, said that China’s overseas imports now account for
eight per cent of its purchases of natural gas. That is expected to
rise to 10 per cent in the next few years. Thorn said there is a big
gap between current LNG contracts and what Encana says is long term
demand from China. He speculated that there could be increasing
demand from China during the 20 years or so the Kitimat LNG project
is exporting LNG. ( As well as projected population and
manufacturing growth, even in a weak economy, China is now heavily
dependent on coal, but is also investing in “green” projects
which means there could eventually be a switch from coal to natural
gas).
The fact that one giant Chinese
customer, PetroChina, pulled out of a deal with Encana earlier this
year doesn’t seem to be a setback. Thorn said that there is strong
interest from at least six unnamed major customers for LNG to be
shipped through Kitimat. “The expression of interest ranged from
simply LNG supply to existing or planned regasification facilities
through to participation all along the value chain from shipping,
equity interest in the Kitimat facility as well as upstream
participation,” Thorn said.
 The Kitimat project is currently
The Kitimat project is currently
undergoing a front end engineering evaluation by KBR. There is a
similar study under way on the Pacific Trails Pipeline that could
carry the natural gas to the terminal. Both studies are expected to
be complete by the end of 2011. Encana expects the National Energy
Board to approve KM LNG’s application for an export licence in
December. Encana and its partners, Apache Corporation and EOG
Resources, expect to make a final investment decision in January
2012.
If all goes as planned the Kitimat
terminal would be shipping 700 million cubic feet of natural gas a
day to Asia when the terminal begins operations in 2015. Encana and
its partners are already optimistic, talking about plans to double
capacity to to 1.5 billion cubic feet a day in the coming years.
What’s driving much of this is the
high price of natural gas in Asia, which is pegged to the price of
oil, compared to North America where natural gas prices are
determined by the marketplace. With shale gas increasingly abundant
the price on this continent has been dropping and that has affected
the bottom lines and stock prices of Encana and other natural gas
producers. Encana is also bolstering its bottom line by tapping
“liquid-rich reserves” (oil and natural gas) that may be found
in the areas where they are currently pumping natural gas.
The Horn River Basin area in
northeastern BC was a surprise discovery by an Encana crew in 2003,
said Kevin Smith, Encana Vice President of New Ventures. The company
then began to quietly acquire assets, either by buying land or by
leasing in the region. “The Horn River resource base is enormous,
highly accessible and will certainly play a large role in North
American and even global gas supply in the years to come,” Smith
told the conference call.
During the June NEB hearings in
Kitimat, witnesses described the Horn River formation as special but
were reluctant to go into detail. Smith said the shale in the Horn River
is “all the attributes for high productivity,” including large
reserves and “overpressured system” which helps extraction. “It
keeps getting better and better.”
As well as going west to Asia, natural
gas from Encana’s Horn River assets will go east to Alberta to fuel
bitumen sands production which Smith said will require an additional
1.3 billion cubic feet a day by 2020, This is likely to be
controversial with the environmental groups and bitumen sands
opponents who have always taken issue with the idea that clean
natural gas would be burned to help get crude of the dirtier bitumen
sands.
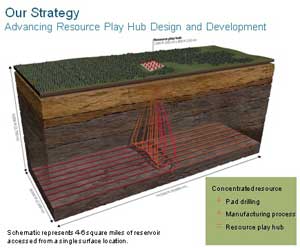 Encana says it has developed a “hub”
Encana says it has developed a “hub”
system in the Horn River where a central well site can use horizontal
drilling to tap areas where once many wells would have been needed.
“Fracking” or fracturing shale gas
requires large amounts of water. As was pointed out in the June
hearings in Kitimat, Encana has tapped an ancient, underground alt
water reservoir called Debolt which allows it to reuse the water from
the formation and minimizing use of local fresh water.
British Columbia is helping the shale
gas industry with favourable royalties in the northeast including
royalty credits for building infrastructure in the region.
Encana, however, is under pressure
from inflation. It faces rising costs from steel, labour and all
kinds of services. While it supplies the bitumen sands with natural
gas, it is also in competition with the Fort MacMurray area for
supplies and labour.
Related links
Dow Jones (via Fox) Encana Eyes Asia As Key Market For B.C. Natural Gas
CP (via Canadian Business) Encana says costs of labour, steel, services rising in energy sector
 China is probably the largest long
China is probably the largest long Dave Thorn, Encana vice president of
Dave Thorn, Encana vice president of The Kitimat project is currently
The Kitimat project is currently Encana says it has developed a “hub”
Encana says it has developed a “hub”