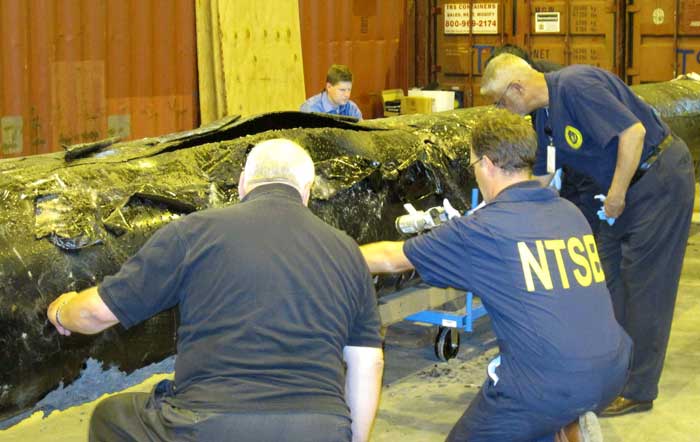
The costs for Enbridge to clean up the 2010 Marshall, Michigan oil spill now far exceeds the maximum estimate that the Joint Review Panel gave for a major spill on the Northern Gateway Pipeline and also exceeds the amount of money the JRP ordered Enbridge to set aside to deal with a spill. Enbridge’s cleanup costs have also now edged past the higher liability amount requested by the Haisla Nation.
According to the US firm Enbridge Energy Partners’ filing with the United States Securities and Exchange Commission, as of September 30, 2013, the cost of cleanup was $1.035 billion US, not including possible additional fines and penalties that might be imposed by US authorities in the future.
In its decision, the Joint Review Panel estimated the cost a major oil spill from the Northern Gateway project would be about $693 million. As part of the 209 conditions, the JRP ordered Enbridge to set aside “financial assurances” totaling $950 million.
Note all costs in this article are for a pipeline breach. The Joint Review Panel had different estimates for a tanker spill and the liability rules for marine traffic are different from pipelines.
In its filing for the third quarter of 2013, with the SEC, Enbridge Energy Partners say that the cost up until September 2013 had “exceed[ed] the limits of our insurance coverage.” The same filing says that Enbridge is in a legal dispute with one its insurers.
In its SEC filing, Enbridge says:
Lakehead Line 6B Crude Oil Release
We continue to perform necessary remediation, restoration and monitoring of the areas affected by the Line 6B crude oil release. All the initiatives we are undertaking in the monitoring and restoration phase are intended to restore the crude oil release area to the satisfaction of the appropriate regulatory authorities.
As of September 30, 2013, our total cost estimate for the Line 6B crude oil release is $1,035.0 million, which is an increase of $215.0 million as compared to December 31, 2012. This total estimate is before insurance recoveries and excluding additional fines and penalties which may be imposed by federal, state and local governmental agencies, other than the Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration, or PHMSA, civil penalty of $3.7 million, we paid during the third quarter of 2012. On March 14, 2013, we received an order from the EPA, or the Environmental Protection Agency, which we refer to as the Order, that defined the scope which requires additional containment and active recovery of submerged oil relating to the Line 6B crude oil release. We submitted our initial proposed work plan required by the EPA on April 4, 2013, and we resubmitted the workplan on April 23, 2013. The EPA approved the Submerged Oil Recovery and Assessment workplan, or SORA, with modifications on May 8, 2013. We incorporated the modification and submitted an approved SORA on May 13, 2013. The Order states that the work must be completed by December 31, 2013.The $175.0 million increase in the total cost estimate during the three month period ending March 31, 2013, was attributable to additional work required by the Order. The $40.0 million increase during the three month period ending June 30, 2013 was attributable to further refinement and definition of the additional dredging scope per the Order and associated environmental, permitting, waste removal and other related costs. The actual costs incurred may differ from the foregoing estimate as we complete the work plan with the EPA related to the Order and work with other regulatory agencies to assure that our work plan complies with their requirements. Any such incremental costs will not be recovered under our insurance policies as our costs for the incident at September 30, 2013 exceeded the limits of our insurance coverage.
According to the SEC filing, the breakdown of costs include $2.6 million paid to owners of homes adversely impacted by the spill.
Despite the efforts we have made to ensure the reasonableness of our estimates, changes to the recorded amounts associated with this release are possible as more reliable information becomes available. We continue to have the potential of incurring additional costs in connection with this crude oil release due to variations in any or all of the categories described above, including modified or revised requirements from regulatory agencies in addition to fines and penalties as well as expenditures associated with litigation and settlement of claims.
The material components underlying our total estimated loss for the cleanup, remediation and restoration associated with the Line 6B crude oil release include the following:
(in millions)Response Personnel & Equipment $454
Environmental Consultants $193
Professional, regulatory and other $388
Total $ 1,035
For the nine month periods ended September 30, 2013 and 2012, we made payments of $62.3 million and $120.9 million, respectively, for costs associated with the Line 6B crude oil release. For the nine month period ended September 30, 2013, we recognized a $2.6 million impairment for homes purchased due to the Line 6B crude oil release which is included in the “Environmental costs, net of recoveries” on our consolidated statements of income. As of September 30, 2013 and December 31, 2012, we had a remaining estimated liability of $265.9 million and $115.8 million, respectively.
As for insurance, Enbridge Energy Partners say:
The claims for the crude oil release for Line 6B are covered by the insurance policy that expired on April 30, 2011, which had an aggregate limit of $650.0 million for pollution liability. Based on our remediation spending through September 30, 2013, we have exceeded the limits of coverage under this insurance policy. During the third quarter 2013, we received $42.0 million of insurance recoveries for a claim we filed in connection with the Line 6B crude oil release and recognized as a reduction to environmental cost in the second quarter of 2013. We recognized $170.0 million of insurance recoveries as reductions to “Environmental costs, net of recoveries” in our consolidated statements of income for the three and nine month periods ended September 30, 2012 for the Line 6B crude oil release. As of September 30, 2013, we have recorded total insurance recoveries of $547.0 million for the Line 6B crude oil release, out of the $650.0 million aggregate limit. We expect to record receivables for additional amounts we claim for recovery pursuant to our insurance policies during the period that we deem realization of the claim for recovery to be probable.
In March 2013, we and Enbridge filed a lawsuit against the insurers of our remaining $145.0 million coverage, as one particular insurer is disputing our recovery eligibility for costs related to our claim on the Line 6B crude oil release and the other remaining insurers assert that their payment is predicated on the outcome of our recovery with that insurer. We received a partial recovery payment of $42.0 million from the other remaining insurers and have since amended our lawsuit, such that it now includes only one insurer. While we believe that our claims for the remaining $103.0 million are covered under the policy, there can be no assurance that we will prevail in this lawsuit.
The Joint Review, Enbridge and Michigan
The Joint Review Panel based its finding on the Marshall, Michigan spill on the figure of $767 million from the summer of 2012 –again showing the limitations of the JRP’s evidentiary deadlines since the costs are now much higher.
The JRP quoted Enbridge as saying:
Northern Gateway considered the high costs of the Marshall, Michigan spill, which were at least $252,000 per cubic metre ($40,000 per barrel), to be an outlier or a rare event because the spill occurred in a densely populated area, because the pipeline’s response time was abnormally long, and because there was the prospect of potentially lengthy legal proceedings.
Enbridge assured the JRP that the corporate culture and management changes and equipment upgrades since the Marshall, Michigan spill lowered that chances of a similar event.
The company based its models for the JRP on much smaller spills, including one spill at Lake Wabamun, Alberta from a train not a pipeline (Vol. 2 p 357)
Enbridge’s risk assessment did not “generate an estimate of economic losses caused
by a spill.”
The JRP says Northern Gateway relied on its analysis of literature, and spill events experienced by Enbridge and other liquid hydrocarbon carriers in Alberta and British Columbia. After assessing all of this information, Northern Gateway regarded the high costs of a cleanup as “conservative”–meaning the company expects costs to be lower than its estimates in evidence before the JRP.
In Northern Gateway’s view the most costly pipeline spill incident would be a full-bore oil pipeline rupture, with an estimated cost of $200 million, and an extremely low probability of occurrence.
Haisla evidence
In their evidence, the Haisla (and other First Nations and intervenors) were doubtful about Northern Gateway’s assurances. The Haisla asked that Enbridge have a minimum of $1 billion in liability, an amount Enbridge has now exceeded in Michigan.
Haisla Nation estimated the cost of damage to ecosystem services because of a terrestrial oil spill from Northern Gateway’s pipeline would be in the range of $12,000 to $610 million for a 30-year period.
The Haisla’s cost estimates were based on values for environmental goods and services and probabilities of spills that were independent of Northern Gateway’s parameters for estimating oil spill costs. In contrast to Northern Gateway’s estimated spill frequency and costs, the Haisla predicted that spills would occur more often and placed a higher value on damages to environmental goods and services.
Haisla Nation argued that Northern Gateway overestimated its ability to detect and respond to a spill. In the Haisla’s view this resulted in the cost of a spill and the requisite financial assurances being understated. Haisla cited several factors, including: remote location, limited access, challenging terrain, seasonal conditions, and river flow conditions that would cause the cost of cleaning up a spill in the Kitimat River valley to be significantly greater than the costs associated with Enbridge’s Marshall, Michigan spill.
For these reasons, Haisla proposed that Northern Gateway should be required to obtain a minimum of $1 billion of liability coverage through insurance and financial assurances. Haisla said that Northern Gateway should file annually the report from an independent third party assessing the financial assurances plan. (Vol 2 p359)
In response Northern Gateway said:
Northern Gateway said that Haisla’s findings were based on a number of fundamental methodological flaws and a lack of probability analysis to support the high frequency of occurrence of oil spill events. Northern Gateway argued that Haisla’s estimates of ecosystem service values were inflated because they were based on values from unrelated studies. In Northern Gateway’s view, Haisla relied on high passive use values that were not justified.
JRP ruling
As it has in most of its decision, the JRP accepted Northern Gateway’s evidence, including its explanation of the Marshall, Michigan spill and then went on to base its spill cost estimates not on a pipeline breach but on the 2005 railway spill at Lake Wabumum, near White Sands, Alberta.
The Panel accepts that the cleanup costs for the Marshall, Michigan spill were orders of magnitude higher because of the extended response time. In this application, the Panel accepts Northern Gateway’s commitment to complete the shutdown in no more than 13 minutes after detection. For this reason the Panel did not use the Marshall spill costs in its calculations. The spill volume and the resulting costs are directly dependent on the Northern Gateway’s control room staff and the pipeline control system fully closing the adjacent block valves no longer than 13 minutes from the detection of an alarm event, as well as the amount of oil which would drain out of the pipeline after valve closure due to elevation differences.
The Panel decided on a total unit cost of $138,376 per cubic metre ($22,000 per barrel). This is midway between the unit cost of $88,058 per cubic metre ($14,000) per barrel proposed by Northern Gateway and the unit cost of $188,694 per cubic metre ($30,000 per barrel) for the Lake Wabamun spill. It is about one-half of the Marshall spill’s unit cost. Giving weight to the Lake Wabamun costs recognizes actual costs experienced in a Canadian spill and the greater costs of spills in high consequence areas. In these areas, individuals, populations, property, and the environment would have a high sensitivity to hydrocarbon spills. The deleterious effects of the spill would increase with the spill volume, the extent of the spill, and the difficulty in accessing the spill area for cleanup and remediation.
Using these spill volume and unit cost values in the calculation below, the Panel estimated the total cost of a large spill could be $700 million. Total cost of a spill = 31,500 barrels x $22,000 per barrel = $693 million, or $700 million when rounded up.
(p362)
The Panel based the financial assurances requirements for Northern Gateway on a spill with a total estimated cost of $700 million and directs Northern Gateway to develop a financial assurances plan with a total coverage of $950 million that would include the following components:
i. Ready cash of $100 million to cover the initial costs of a spill;
ii. Core coverage of $600 million that is made up of stand-alone, third party liability insurance and other appropriate financial assurance instruments, and
iii. Financial backstopping via parental, other third party guarantees, or no fault insurance of at least $250 million to cover costs that exceed the payout of components i. and ii.
The financial backstopping would be available to fill the gap if the spill volumes or unit costs were under-estimated or if the payout from the core coverage would be less than 100 per cent.
The Panel noted that:
The evidence indicates that there is some probability that a large oil spill may occur at some time over the life of the project. In these circumstances the Panel must take a careful and precautionary approach because of the high consequences of a large spill. The Panel has decided that Northern Gateway must arrange and maintain sufficient financial assurances to cover potential risks and liabilities related to large oil spills during the operating life of the project.
Northern Gateway committed to investing $500 million in additional facilities and mitigation measures such as thicker wall pipe, more block valves, more in-line inspections, and complementary leak detection systems. This initiative should enhance the safety and reliability of the system and help reduce and mitigate the effects of a spill, but it would not eliminate the risk or costs of spills. This initiative is not a direct substitute for third party liability insurance and does not eliminate the need for liability insurance or any other form of financial assurance to cover the cost of a spill. (p 361)
So the JRP decision comes down to this, if you accept Northern Gateway’s position that pipeline spills are rare and mostly small, then the company has the financial resources to cover the damage. If, however, Northern Gateway is wrong and the costs of a pipeline cleanup exceed the $950 million required by the Joint Review Panel, as has happened in Michigan, then those JRP conditions are already obsolete.
(Northwest Coast Energy News encourages all readers to read the complete JRP report and SEC filing since space and readability does not permit fully quoting from the report)