Updated with Enbridge statement
The United States Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration today cited Enbridge for a series of violations in connection with the pipeline rupture and bitumen spill at Mashall, Michigan, in 2010 and is proposing the company be fined a record $3.7 million.
A letter issued today, July 2, 2012, from the PMHSA to Richard Adams, Vice President, U.S. Operations, Enbridge Energy Limited Partnership, lists a series of alleged failures by Enbridge.
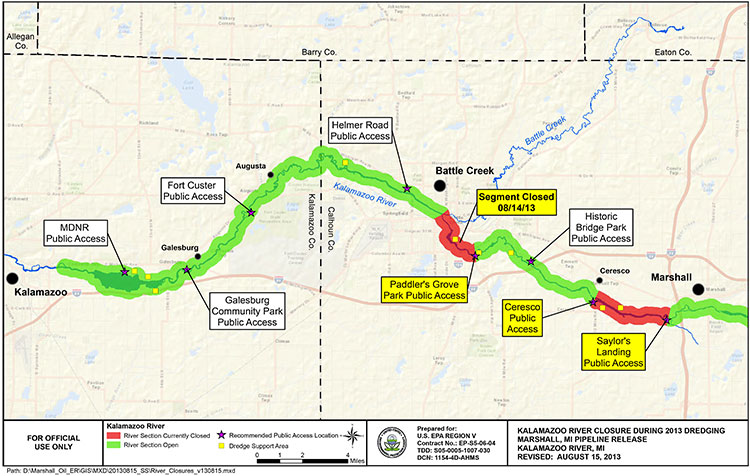
The letter says the investigation began on July 26, 2010, the day after the Enbridge Energy Limited Partnership’s 30-inch diameter Line 6B pipeline ruptured near Marshall, Michigan on July 25, spilling 20,000 barrels of crude and contaminating 38 miles of the Kalamazoo River.
That investigation, the letter says, turned up numerous violations of US regulations including, safety rules, faulty risk analysis, failure to follow proper operation and management procedures and problems with reporting and operator qualification requirements.
The PHMSA alleges that Enbridge violated 24 regulations for pipeline safety and procedures, with civil penalties ranging from $41,200 to $1,000,000 for a total of $3.7 million.
None of the allegations have been proven and Enbridge is free to contest the filings and allegations and ask for a hearing.
In a news release, Enbridge responded:
Enbridge appreciates the hard work and due diligence that PHMSA has put into this investigation,” said Stephen J. Wuori, President, Liquids Pipelines, Enbridge Inc. “Safety has always been core to our operations. Enbridge completed a detailed internal investigation of this incident in the fall of 2010 and has made numerous enhancements to the processes and procedures in our control center since the Line 6B accident, including the training provided to pipeline operators, and has made significant changes in this critical component of our operations. Incident prevention, detection and response have also been enhanced. We will carefully examine the NOPV to determine whether any further adjustments are appropriate.
The letter says the investigation began on July 26, 2010, the day after the Enbridge Enbridge Energy Limited Partnership’s 30-inch diameter Line 6B pipeline ruptured near Marshall, Michigan on July 25, spilling 20,000 barrels of crude and contaminating 38 miles of the Kalamazoo River.
That investigation, the letter says, turned up numerous violations of US regulations including, safety rules, faulty risk analysis, failure to follow proper operation and management procedures and problems with reporting and operator qualification requirements.
The letter also outlines what happened during the spill, as seen through the eyes of PHMSA investigators.
According to the letter, the Enbridge pipeline failed despite a series of In-Line Inspections that the company had performed on the pipeline. Those inspections, the PHMSA investigators say found “multiple corrosion and crack-like anomalies on the pipe joint that failed on July
25, 2010.” It is alleged that Enbridge did not conduct any field examination of the reported anomalies before the accident.
According to the PHMSA, there was actually a crack detection being performed on Line 6B on the day of the failure and the testing equipment was left in the pipeline until the after the line was restarted on September 27, 2010.
The reports says the Michigan pipeline ruptured at 17:58 EDT on July 25, 2010, approximately 0.6 miles downstream of the company’s Marshall pumping station. At the time, Enbridge’s Edmonton Control Center (CCO) was in the process of starting a scheduled 10-hour shutdown of the pipeline.
The PHMSA report says:
as soon as the failure occurred, the CCO received multiple alarms and indications of abnormal operations on Line 6B, but the company did not execute its suspected-leak or emergency procedures. Instead, Enbridge allowed the pipeline to remain idle as part of the Scheduled Shutdown for approximately 10 hours, during which time a new shift came on duty at the CCO, which brought in a new set of controllers, supervisors, and support personnel.
At approximately 04:00, on July 26, 2010, Enbridge initiated the scheduled start-up of Line 6B … Within minutes, the CCO received multiple alarms and indications of abnormal operating conditions, which indicated that the pressure at the Marshall pumping station had not increased as expected and the imbalance between the volume of product injected into the pipeline and the volume of product being delivered from the pipeline exceeded established thresholds. Again, Enbridge did not execute its suspected leak or emergency procedures. Instead, Enbridge continued to pump crude oil into the line while the controller, supervisors, and support personnel evaluated the situation.
After an hour, the Edmonton control centre abandoned the attempted restart and shut down the pipeline. During the time Enbridge was trying to restart the pipeline, an additional 10,460 barrels of crude oil was injected into the pipeline.
The PHMSA report says that the Enbridge control room was monitoring the “lack of typical pressure and flow conditions for this pipeline configuration and alarms.” Control room supervisors contacted managers and the decision was made to restart the pipeline a second time, which began at 0720 on July 26.
Again the Enbridge control “received multiple alarms and indications of abnormal
operating conditions.”
Enbridge continued to pump oil for another 31 minutes sending 5,831 barrels of oil into the pipeline.
By this time supervisors and managers were discussing the possibility of a suspected leak but no one activated Enbridge’s spill procedures. The second restart was halted at 0751 at which time a new shift took over the control room.
Enbridge managers “discussed the two restart attempts, resulting in the Line 6B controller
conducting further investigation into the historical operating information on the line but
taking no action to deal with a spill.”
It was three hours and fifteen minutes after the shift change, at 11:18 on July 26, roughly 17 hours after the failure occurred, that the Enbridge control room received an emergency call from an employee of a local gas company, Consumers Energy, reporting oil in a creek near Marshall, Michigan.
It was at that point that Enbridge closed remotely operated valves on each side of the reported leak, isolating three miles of pipeline on either side of the rupture. It was then that Enbridge activated its emergency procedure and field personnel were sent to the scene. The field personnel confirmed the spill to the Edmonton control room at 11:43.
On July 28, the Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration issued “a Corrective Action Order” to Enbridge requiring the company to take action to protect the public, property, and the environment. “Amongst other things, the Corrective Action Order required a pressure reduction, verification of pipeline integrity, integration of information, and provisions for ensuring ongoing safe operation considering all risk factors.”
The letter then cites Enbridge for the following alleged violations:
Pipeline integrity management in high consequence areas
The letter says that after an integrity assessment of Line 6B, Enbridge failed to obtain, within 180 days, sufficient information about anomalous conditions presenting a potential threat to the integrity of Line 6B. Enbridge conducted a high-resolution integrity assessment of Line 6B on October 13, 2007 and received the “vendor report” on June 4, 2008. The citation says “The 180 day deadline was April 10, 2008. Enbridge did not demonstrate that the 180 day period was impracticable.”
The report says Enbridge implemented pressure restrictions on the pipeline on July 17, 2009, approximately 462 days after the deadline to have sufficient information to identify anomalous conditions. A year later, according to the PHMSA, Enbridge submitted a “Long Term Pressure Reduction Notification” to PHMSA on July 15, 2010. The date of discovery was reported by Enbridge as July 17, 2009 not June 2008.
US regulations require pipeline companies to fix “corrosion anomalies” in pipelines with 180 days. The citation says that starting back as far as 2004, Enbridge “did not schedule remediation of
corrosion anomalies involving the longitudinal weld seam of pipe joint #217720, that is the joint that eventually ruptured causing the spill. The report says Enbridge also did not remediate crack-like anomalies on the same pipe joint… that could impair the integrity of the pipeline” and “Enbridge could not demonstrate that the company attempted or scheduled any remediation of the corrosion or crack anomalies that were identified by the assessments” nor did Enbridge schedule that joint for excavation prior to the rupture.
Risk analysis
The PHMSA alleges that Enbridge failed to consider all relevant risk factors associated with the determination of the amount of product that could be released from a rupture on the pipeline. Enbridge’s risk analysis process also assumed a pipeline rupture of this magnitude would be identified by its leak detection instrumentation within five minutes, and that it would take an additional three minutes to close remotely operated valves on either side of the rupture.
Before the spill, Enbridge had estimated the worst case scenario at the that location would be a release 1,670 barrels initially with another 1938 barrels released during “drain down” for a total of3,608 barrels
The actual failure scenario demonstrates the rupture was not recognized by Enbridge, and the isolation valves were not closed, until approximately 17 hours after it occurred. An additional 16,431 barrels of product was injected into the ruptured pipeline, causing the total spill volume to greatly exceed Enbridge’s worst case discharge scenario for this location.
Evaluation
The PHMSA letter alleges that “Enbridge did not properly consider the results of corrosion and cracking assessments nor did Enbridge integrate the information from these assessments to
properly assure overall pipeline integrity.”
While the investigation revealed that while “Enbridge has a long history of performing
integrity assessments” those assessment results “were evaluated independently and not integrated in a fashion that assures pipeline integrity.”
General Requirements
The PHMSA says US regulations require that whenever an operator discovers any condition that could adversely affect the safe operation of its pipeline system, “it shall correct it within a
reasonable time,” adding that “if the condition is of such a nature that it presents
an immediate hazard to persons or property, the operator may not operate the affected part of the system until it has corrected the unsafe condition.”
The letter says” “Enbridge failed to correct a condition that could affect the safe operation of a
pipeline within a reasonable time following discovery. Enbridge discovered the
condition as a result of …. instrumentation alarms and events that alerted
within seconds and minutes of the rupture…”
Since the alarms would have indicated conditions that could adversely affect the safe operation of the pipeline,” the PHMSA says: “The expected initial corrective action is to notify appropriate company and emergency response personnel to investigate and mitigate the effects of any unsafe conditions. This was not done until approximately 17 hours after discovery of the conditions.”
The letter says Enbridge did not follow established written procedures for responding to,
investigating, and correcting the cause of pressure outside of normal operating
limits during the shutdown and Enbridge did not notify responsible personnel in accordance with
the procedure. It says that Enbridge has not developed a specific written procedure for responding to an Invalid Pressure Alarm, but has instead developed a written procedure for required actions based on alarm severity.
For an S6-Severe Alarm, the procedures require the controller to: (1) Notify the Shift Lead; (2) Advise on site/on-call personnel; (3) Create a F ACMAN (Enbridge term for Facility Management record-keeping system used to documents abnormal operating conditions).
The PHMSA says “Enbridge failed to take any of these required actions.”
It goes on to allege that Enbridge did not follow established written procedures for responding to,
investigating, and correcting the cause of pressure in the pipeline that were outside of normal operating limits and goes on to say that Enbridge has not developed a specific written procedure for responding to a Low Suction Pressure Alarm.
As in the previous case, Enbridge’s procedures were based on “alarm severity.”
For an S4-Warning Alarm, the procedures require (1) Discretionary controller response to alarm dependent on operating conditions, (2) Notify the Shift Lead if unsure of response, (3) If multiple S4 alarms are active for a related issue, the response and severity may be raised, ( 4) FACMAN creation may be required, (5) Advise on-site/on-call personnel if required.
Again the PHMSA alleges: “ Enbridge did not take any of the above actions, or any
other actions, in response to this alarm. The fact the Marshall suction pressure
abruptly dropped to 0 psig, which was unexpected and abnormal, dictates followup
investigative actions in accordance with the procedure, in order to determine
the reason/source of the alarm.”
The report says that Enbridge did not follow established written procedures for responding to, investigating, and correcting the cause of an unintended shutdown at the Marshall Unit and Enbridge also did not notify responsible personnel in accordance with the procedure.
Emergencies
The PHMSA says Enbridge did not take necessary action to minimize the volume of hazardous
liquid released in the event of a failure or notify police during an emergency, even though that was required by Enbridge’s own emergency notification procedures, saying that the shift lead in the Edmonton control room should have initiated the procedures at 18:03, on July 25, when an alarm went off.
Enbridge policy on leak “triggers” that is “unexplained abnormal operating conditions or events that indicate a leak” requires that a number of procedure be started once a leak trigger is detected. The PHMA says neither the suspected leak or confirmed leaks procedures were executed by the Edmonton control room nor were managers, field personnel and local police notified.
Public Awareness
The PHMSA letter says that Enbridge did not evaluate the effectiveness of its public awareness program in accordance with the written procedures. The company’s plan calls on the public awareness manager to “informally assess the effectiveness of public awareness efforts” each year, but the PHMSA says “Enbridge could not demonstrate this was being performed.”
The investigation identified a number of instances where actions taken by members of the PAP target audience were not in accordance with the program message (e.g. not associating the odour with that of a possible crude oil release, not contacting Enbridge’s Emergency Number in response to the odour complaints, and entry into the spill area by untrained individuals).
The release resulted in a number of local residents being displaced, contamination of approximately 38 miles of the Kalamazoo River, and contamination of affected fish and wildlife.
Accident reporting
The PHMSA also alleges that Enbridge failed to properly report the incident to the proper authorities, in this case the US Department of Transportation. It says Enbridge failed to accurately report the time of failure and other significant facts relevant to the extent of damages associated with a pipeline rupture which occurred at 17:58, on July 25, 2010. According to the PHMSA, Enbridge incorrectly reported the time the accident was discovered as 09:45 July 26 and also reported the material had not reached the Kalamazoo River yet, and that the release was secured.
According to the letter, investigative interviews show that the Edmonton control room personnel were aware that there were abnormal conditions on the pipeline, that “the rupture had likely occurred when the pipeline was shutdown, the night before” that “the release was not secured, as oil was moving down the Kalamazoo River. The impacts to people, property, and the environment were immediately obvious when emergency response actions were initiated.” The letter says that Enbridge did not file follow up reports to augment the initial report to Department of Transportation nor did it “currently available accident information” to the DOT within 30 days.
A report filed by Enbridge on August 25, 2010, again misreported the time of the spill, now calling it “11:41 on July 26, 2010, when it had been clear within hours of discovery that the failure date and time was approximately 17:58 on July 25, 2010.” It goes on to say that Enbridge report “also did not indicate the number of general public evacuated, even though daily EPA Pollution Reports indicated the number of residences that were evacuated, and Enbridge paid for alternative lodging for these evacuees as necessary.” It also alleges that some of the technical details in that August report on pipeline pressure were inaccurate and goes on to say that some subsequent reports filed by Enbridge were inaccurate although “the correct information has been known by the operator for some time.”
One example was that a witness told investigators on December 5, 2011 indicated that Enbridge determined the total costs of damages associated with the Line 6B rupture were currently $720
million but the value reported in a report filed on February 22, 2011 report was $550 million. The PHMSA says: “It is unknown at what point the $720 million value was determined by Enbridge, but the reported value was not updated until March 6, 2012, approximately 3 months after the interview.”
Employee qualifications
The PHMSA report alleges that Enbridge allowed an “unqualified individual to perform covered tasks (operating a pipeline) without direct observation by a qualified individual.” It says a previously qualified controller, who had been off duty for an extended period of time, was operating the pipeline console, and a qualified controller was assigned to oversee the operations.
According to the investigation “the qualified pipeline controller, even though seated adjacent to the un-qualified pipeline controller, was performing other tasks, and not directing and observing line operations, as required by the written procedures.” The report says that after multiple alarms went off “the unqualified pipeline controller did not respond to the alarms in full accordance with the operator’s written procedures, and the qualified pipeline controller’s oversight of the operations was insufficient to ensure that the required actions were taken.
In its news release, Enbridge added:
Enbridge has worked closely and cooperatively with all federal and state agencies, including PHMSA and the National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) throughout the investigation of the Line 6B accident, and is now reviewing the NOPV in detail. Enbridge will not comment specifically on the contents of the NOPV until it completes that analysis.
On June 18, 2012, Lorraine Little, Enbridge senior manager of US public affairs, liquids operations and projects, appeared before District of Kitimat Council. At that time, Little outlined how the company was working on clean up operations. She also said Enbridge had improved its operations and emergency response since the Michigan incident but would not go into detail, due to ongoing investigations and litigation in the United States.
.
PHMSA notice of possible violation to Enbridge Energy
 Enbridge says it has “completed substantially all of the EPA order, “with the exception of required dredging in and around Morrow Lake and its delta.”
Enbridge says it has “completed substantially all of the EPA order, “with the exception of required dredging in and around Morrow Lake and its delta.”