A new study suggests that the health of the grizzly bear population is also a strong indicator of the health of Pacific salmon—and perhaps surprisingly, allowing grizzlies to consume more salmon will, in the long term, lead to more, not less, salmon.
The study, led by Taal Levi, of the University of California at Santa Cruz and colleagues from Canada, suggests that allowing some more Pacific salmon to escape the nets of the fishing industry and thus spawn in coastal streams would not not only benefit the natural environment, including grizzly bears, but could also eventually lead to more salmon in the ocean. Thus there would be larger salmon harvests in the long term—a win-win for ecosystems and humans.
The article, “Using Grizzly Bears to Assess Harvest-Ecosystem Tradeoffs in Salmon Fisheries,” was published April 10 in the online, open-access journal PLoS Biology. In the study Levi and his co-authors investigate how increasing “escapement”—the number of salmon that escape fishing nets to enter streams and spawn—can improve the natural environment.
“Salmon are an essential resource that propagates through not only marine but also creek and terrestrial food webs,” said lead author Levi, an environmental studies Ph.D. candidate at UCSC, specializing in conservation biology and wildlife ecology.
Salmon fisheries in the northwest Pacific are generally well managed, Levi said. Managers determine how much salmon to allocate to spawning and how much to harvest. Fish are counted as they enter the coastal streams. However, there is concern that humans are harvesting too many salmon and leaving too little for the ecosystem. To assess this, the team focused on the relationship between grizzly bears and salmon. Taal and his colleagues first used data to find a relationship between how much salmon were available to eighteen grizzly bear populations, and what percentage of their diet was made up of salmon.
The study looked at Bristol Bay, Alaska, the Chilko and Quesnel regions of the Fraser River watershed and Rivers Inlet on the Inside Passage, just northeast of northern Vancouver Island.
The study says adult wild salmon are “critical” to ocean, river and terrestrial ecosystems. As well as humans, salmon are eaten by orcas, salmon sharks, pinnipeds (seals and sea lions). On land, salmon are eaten by black and grizzly bears, eagles and ravens.
Because the grizzly is the “terminal predator” the study says “if there are enough salmon to sustain healthy bear densities, we reason there should be sufficient salmon numbers to sustain populations of earlier salmon-life history predatory such as seabirds, pinnipeds and sharks.”
As is well known in the northwest, the study says “bears are dominant species mediating the flow of salmon-derived nutrients from the ocean to the terrestrial ecosystem. After capturing salmon in estuaries and streams grizzly bears typically move to land to consume each fish, distributing carcass remains to vertebrate and invertebrate scavengers up to several hundred metres from waterways.”
“We asked, is it enough for the ecosystem? What would happen if you increase escapement—the number of fish being released? We found that in most cases, bears, fishers, and ecosystems would mutually benefit,” Levi said.
The problem, the study says, is that fisheries management have a narrow view of their role, what the study calls “single-species management,” concentrating on salmon and not the wider ecosystem. “Currently,” the study says, under single-species management, fisheries commonly intercept more than 50 per cent of in bound salmon that would otherwise be available to bears and the terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems they support.”
The relationship between salmon and bears is basic, Levi said. “Bears are salmon-consuming machines. Give them more salmon and they will consume more—and importantly, they will occur at higher densities. So, letting more salmon spawn and be available to bears helps not only bears but also the ecosystems they nourish when they distribute the uneaten remains of salmon.”
When salmon are plentiful in coastal streams, bears won’t eat as much of an individual fish, preferring the nutrient-rich brains and eggs and casting aside the remainder to feed other animals and fertilize the land. In contrast, when salmon are scarce, bears eat more of a fish. Less discarded salmon enters the surrounding ecosystem to enrich downstream life, and a richer stream life means a better environment for salmon.
In four out of the six study systems, allowing more salmon to spawn will not only help bears and the terrestrial landscape but would also lead to more salmon in the ocean. More salmon in the ocean means larger harvests, which in turn benefits fishers. However, in two of the systems, helping bears would hurt fisheries. In these cases, the researchers estimated the potential financial cost—they looked at two salmon runs on the Fraser River, B.C., and predicted an economic cost of about $500,000 to $700,000 annually. This cost to the human economy could help support locally threatened grizzly bear populations, they argue.
While these fisheries are certified as sustainable by the Marine Stewardship Council (MSC), the researchers suggest that the MSC principle that fisheries have minimal ecosystem impact might not be satisfied if the fishery is contributing to grizzly bear conservation problems.
The researchers believe the same analysis can be used to evaluate fisheries around the world and help managers make more informed decisions to balance economic and ecological outcomes.
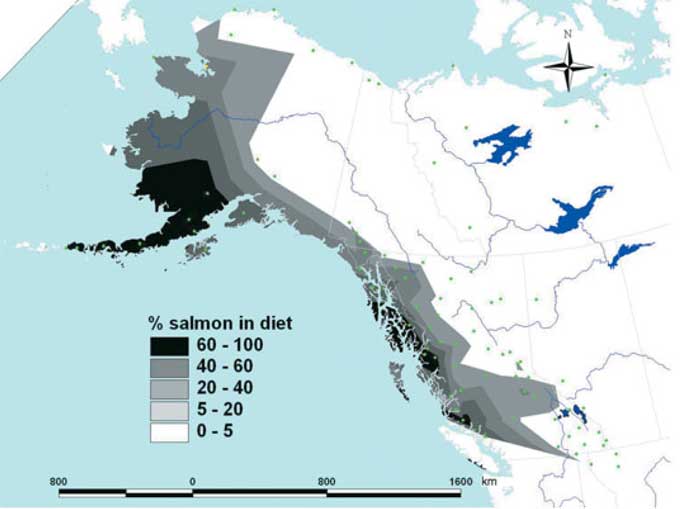
What do grizzlies eat in northwestern BC ?
The current study and previous studies track the grizzly’s diet by studying the nitrogen and carbon istopes in grizzly hair. In one study in the early part of this decade, the BC Ministry of the Environment used guard hairs from “passive hair snags” as well as samples from bears killed by hunters or conservation officers.
The 2005 study says “Guard hairs are grown between late spring and fall, thus integrating the diet over much of the active season of temperate-dwelling bears.” Analysis of the isotopes can show what the bears ate over the season.
The study identified four elements in the grizzly diet across British Columbia, Alaska, Yukon and the Northwest Territories: plants, “marine-derived nutrients” mostly salmon, meat (primarily from ungulates such as moose) and in inland areas, kockanee salmon.
As could be expected, grizzly salmon consumption is highest in coastal areas. Males generally consume more salmon than females, likely because a mother grizzly may avoid taking salmon if there is danger to the cubs from males. The further inland a grizzly is found, salmon is a lesser factor in the bear’s diet. In Arctic regions, grizzlies can feed on arctic char, whales, seals and barren-ground caribou.
So what do local grizzlies eat? (excerpts from the 2005 study, Major components of grizzly bear diet across North America, National Research Council Research Press published March 28, 2006)
North Coast 54.54 N 128.90 W (north and west of Kitimat)
Plants 33 per cent Salmon 67 per cent
Mid Coast 52.50 N 127.40 W (between Bella Bella and Ocean Falls)
Plants 58 per cent Salmon 42 per cent
Upper Skeena Nass 56.80 N 128.80 W
Plants 71 per cent Salmon 5 per cent Meat 13 per cent
Bulkley Lakes 54.10 N 127.10 W
Plants 63 per cent Salmon 6 per cent Meat 16 per cent Kokanee 15 per cent
Cranberry 55.40 N 128.40 W (near Kiwancool)
Plants 30 per cent Salmon 17 per cent Meat 40 per cent Kokanee 13 per cent
Khutzeymateen 54.68 N 129.86 W (near Prince Rupert)
Plants 22 per cent salmon 78 per cent
###
Other authors of the 2010 study are Chris Darimont, UCSC, Misty MacDuffee Raincoast Conservation Foundation, Denny Island, BC; Marc Mangel, Paul Paquet, UCSC and University of Calgary, Christopher Wilmers, USCC
Funding: This work was funded by an NSF GRF and Cota-Robles Fellowship (TL), a NSERC IRDF (CTD), the Wilburforce and McLean Foundations, and Patagonia. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
2005 study by Garth Mowat Aurora Research Crescent Valley BC and Douglas Heard BC Ministry of the Environment, Nelson