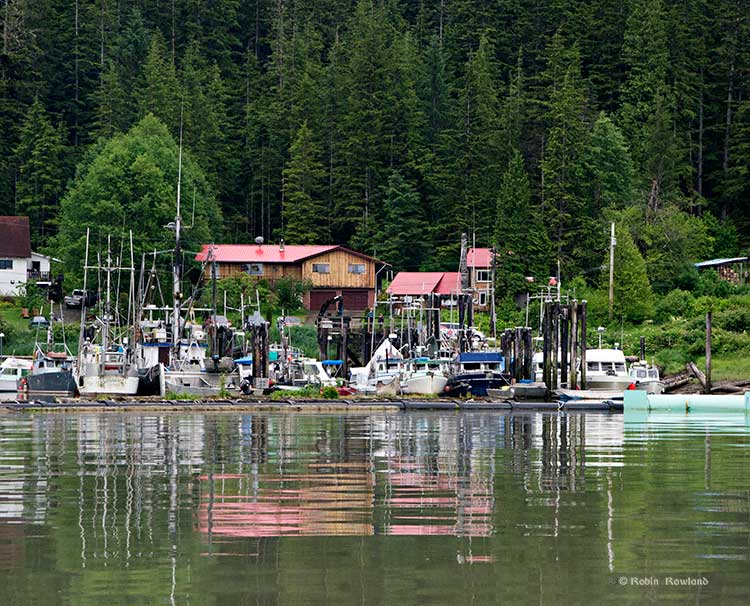
In its extensive document filed with the Northern Gateway Joint Review panel, the Haisla Nation emphasize their opposition to the project.
In its extensive document filed with the Northern Gateway Joint Review panel, the Haisla Nation emphasize their opposition to the project.
However, the Haisla are anticipating that the project will be approved and therefore submitted a lengthy series of conditions for that project, should it be imposed on the northwest by the federal government.
Nevertheless, if the project were to be approved AFTER the Crown meaningfully consulted and accommodated the Haisla Nation with respect to the impacts of the proposed project on its aboriginal title and rights, and if that consultation were meaningful yet did not result in changes to the proposed project, the following conditions would, at a minimum, have to be attached to the project.
1. Conditions Precedent: The following conditions precedent should be met prior to any field investigations, pre-construction activities or construction activities as well as during and subsequent to such investigations or activities. These conditions are necessary to ensure that potential effects of the project can be avoided or mitigated to reduce the likelihood of habitat damage or destruction:
Comprehensive seasonal water quality monitoring throughout the Kitimat River watershed, Kitimat Arm and Douglas Channel that account for seasonal variations in flow, tidal cycles, snowmelt, rainfall, etc.
Parameters for measurement would be have to be agreed upon by the
Haisla Nation prior to certification of the project;
Comprehensive seasonal fisheries surveys of fish habitat utilization throughout the Kitimat River watershed, Kitimat Arm and Douglas Channel that account for where species and life stages are at different times of the year and accurately define sensitive habitats;
Comprehensive seasonal wildlife and bird surveys of habitat utilization throughout the Kitimat River watershed, Kitimat Arm and Douglas Channel that account for where species and life stages are at different times of the year and accurately define sensitive habitats;
Comprehensive seasonal vegetation surveys of habitat utilization throughout the Kitimat River watershed, Kitimat Arm and Douglas Channel that accounts for the distribution of species and life stages at different times of the year and accurately define sensitive habitats;
Development of comprehensive spill response capability based on a realistic assessment of spill containment, spill response and spill capacity requirements throughout the Kitimat River Valley, Kitmat Arm and Douglas Channel. The Haisla Nation’s past experience has shown that relying onpromises is not good enough. This spill response capability must be demonstrated prior to project approval;
Verification that the proposed project would result in real benefits, economic or otherwise, that would flow to the Haisla Nation, to other First Nations, and to British Columbia.
Whenever any field investigations or activities are proposed, the proposal or permit application would have to include the following environmental protections:
Soil and erosion control plans;
Surface water management and treatment plans;
Groundwater monitoring plans;
Control and storage plans for fuels, lubricants and other potential contaminants;
Equipment deployment, access and use plans;
Habitat reclamation of disturbed or cleared areas.
Prior to any pre-construction or construction activities the following detailed studies would have to be undertaken and provided to the Haisla Nation for review and approval, to ensure that the best design and construction approaches are being used, so that potential effects of the project can be avoided or mitigated to reduce the likelihood of habitat damage or destruction:
Detailed analysis of terrain stability and slide potential throughout the pipeline corridor and at the storage tank and terminal site;
Detailed engineering design to mitigate seismic risk and local weather extremes;
.Development of pipeline integrity specifications and procedures including
best practices for leak detection;
Development of storage tank integrity specifications and maintenance and monitoring procedures;
Assessment of spill containment, spill response and spill capacity requirements throughout the Kitimat River watershed, Kitimat Arm and Douglas Channel;
.Development of detailed tanker acceptance program specifications and
procedures;
Development of detailed tanker and tug traffic management specifications and procedures;
Development of detailed port management specifications and procedures including operating limits for tanker operation, movement and docking.
2. Ongoing Consultation: A commitment to ongoing consultation with and accommodation of the Haisla Nation on all of the activities set out above.
3. Ongoing process for variance, waiver or discharge of conditions: A commitment to ongoing meaningful involvement of the Haisla Nation by the National Energy Board prior to any decision on any changes to or sign off on conditions and commitments to any certificate that is issued.
4. Third Party Oversight of Construction: A requirement that NorthernGateway fund a third party oversight committee, which should include a Haisla Nation representative, to monitor certificate compliance during construction of the marine terminal and the pipeline. This committee would have the ability to monitor and inspect construction and should be provided with copies of allcompliance documents submitted by Northern Gateway to the National Energy Board.
5. Operational Conditions: A number of operational conditions should beincorporated into the certificate, including but not limited to:
The requirement to monitor terrain along the pipeline so that breaches based on earth movements can be anticipated and prevented;
The requirement to implement automatic pipeline shutdown whenever a leak detection alarm occurs;
Conditions on the disposal of any contamination that must be removed as a result of an accident or malfunction resulting in a spill that will minimize additional habitat destruction and maximize the potential for regeneration of habitat and resources damaged by the spill;
Parameters for terminal and tanker operations (including standards for tankers allowed to transport cargo; tanker inspection requirements and schedules; escort tug specifications, standards, maintenance and inspection; pilotage protocols and procedures; environmental conditions and operating limits; etc.) as well as other parameters set out in and reliedon for the TERMPOL review to become conditions of any certificate issued by the National Energy Board, with a provision that the Haisla Nation’s approval of any changes to these conditions is required.
Answering the questions from Enbridge Northern Gateway, the Haisla also outline a long series of concerns.
1. Physical and Jurisdictional Impacts
1.1 Construction
The Haisla Nation is concerned about the direct physical and jurisdictional impacts that the construction of the proposed project will have. These concerns are set out for each of the marine terminal, the pipeline, and tanker traffic, below:
Marine Terminal:
a. The proposed marine terminal will require the alienation of 220-275
hectares (554-680 acres) of land from Haisla Nation Territory, land
to which the Haisla Nation claims aboriginal title.
b. The terminal will require the additional alienation of land for
ancillary infrastructure and development, including:
i. road upgrades,
ii. perimeter access roads and roads within the terminal area,
iii. a potential public bypass road,
iv. an impoundment reservoir,
v. a disposal site for excess cut material outside the terminal
area,
vi. a new 10km long transmission powerline, and
vii. a 100-m waterlot with a 150-m “safety zone”.
c. The terminal proposes to use Haisla Nation aboriginal title land,
including foreshore and waters, in a way that is inconsistent with
Haisla Nation stewardship of its lands, waters and resources and
with the Haisla Nation’s own aspirations for the use of this land.
Since aboriginal title is a constitutionally protected right to use the
aboriginal title land for the purposes the Haisla Nation sees fit, this
adverse use would fundamentally infringe the aboriginal title of the
Haisla Nation.
d. The terminal will require the destruction and removal of
documented culturally modified trees, some with modifications
dating back to 1754. These culturally modified trees are living
monuments to the history of the Haisla people.
e. The terminal will expose two Haisla Nation cultural heritage sites to
increased risk of vandalism and chemical weathering.
f. The terminal will result in the direct loss of 4.85 hectares (11.98
acres) of freshwater fish habitat (harmful alteration, disruption or
destruction (HADD) under the Fisheries Act).
g. The terminal will require dredging, underwater blasting, and
placement of piles and berthing foundations, resulting in an as yet
un-quantified loss of intertidal and subtidal marine habitat.
Pipeline:
a. The proposed pipeline construction right-of-way will require the
alienation of 9,200 hectares (22,734 acres) of Haisla Nation
Territory – land to which the Haisla Nation claims aboriginal title –
and will put this land to a use that is inconsistent with Haisla Nation
stewardship of its lands, waters and resources and with the Haisla
Nation’s own aspirations for the use of this land.
b. The pipeline will require 127 watercourse crossings in Haisla Nation
Territory. Seven of these are categorized as high risk, 5 as
medium high risk, and 7 are medium or medium low risk for harmful
alternation, disruption or destruction (HADD) of fish habitat. This
risk is just from pipeline construction and does not address the
issue of spills.
c. The pipeline is estimated to result in temporary or permanent
destruction of freshwater fish habitat of 3.1 hectares (7.68 acres) in
Haisla Nation Territory.
d. The pipeline will require the clearing of land and vegetation and the
destruction of wetlands. The extent of this is yet to be quantified.
Tanker Traffic:
a. Although Northern Gateway has not made any submission on this
point, it is clear that having adequate spill response capability at
Kitimat will require additional infrastructure upgrades in and around
Kitimat, as well as potential spill response equipment cache sites.
None of this has been considered or addressed in Northern
Gateway’s application material – as such the material is
incomplete.
b. The construction for this additional infrastructure could result
impacts to ecosystems, plants, wildlife and fish, and in additional
HADD or fish mortality from accidents.
All of the land alienations required for the proposed project would profoundly
infringe Haisla Nation aboriginal title which is, in effect, a constitutionally
protected ownership right. The proposed project would use Haisla Nation
aboriginal title land in a way that is inconsistent with Haisla Nation stewardship of
its lands, waters and resources and with the Haisla Nation’s own aspirations for
the use of this land. Since aboriginal title is a constitutionally protected right to
use the aboriginal title land for the purposes the Haisla Nation sees fit, this
adverse use would fundamentally infringe the aboriginal title of the Haisla Nation.
The Haisla Nation is also concerned about the socio-economic and health
impacts of the proposed project. Northern Gateway has yet to file its Human
Health and Ecological Risk Assessment. Further, the socio-economic impact
analysis submitted as part of the application provides only a limited assessment
of the potential impacts of the project on the Haisla Nation at a socio-economic
level.
Haisla Nation society and economy must be understood within the cultural
context of a people who have lived off the lands, waters and resources of their
Territory since long before European arrival. To limit a socio-economic impact
assessment to direct impacts and to ignore consequential impacts flowing from
those impacts fails to capture the potential impacts of the proposed project on the
Haisla Nation at a socio-economic level.
1.2 Operation
The proposed marine terminal, pipeline corridor and shipping lanes will be
located in highly sensitive habitats for fish, wildlife and plants. Any accident of
malfunction at the wrong time in the wrong place can be devastating ecologically.
The Haisla Nation has identified the following concerns relating to physical
impacts from the operation of the proposed project:
Marine Terminal:
a. Intertidal and subtidal marine habitat impacts as a result of marine
vessels.
b. The likelihood of spills from the marine terminal as a result of operational
mistakes or geohazards.
c. The effects and consequences of a spill from the marine terminal. This
includes impacts on the terrestrial and intertidal and subtidal marine
environment and fish, marine mammals, birds, and other wildlife, as well
as impacts on Haisla Nation culture and cultural heritage that could result
from such impacts.
d. Response to a spill from the marine terminal, including concerns about
spill response knowledge, planning and capability, as well as impacts
flowing from response measures themselves.
Pipeline:
a. The likelihood of spills from the pipeline as a result of pipeline failure,
resulting from inherent pipeline integrity issues or external risks to pipeline
integrity, such as geohazards.
b. The effects and consequences of a spill from the pipelines. This includes
impacts on the terrestrial environment and freshwater environment, and
on plants, fish, birds, and other wildlife, as well as impacts on Haisla
Nation culture and cultural heritage that could result from such impacts.
c. Response to a spill from the pipelines, including concerns about spill
response knowledge, planning and capability, as well as impacts flowing
from response measures themselves.
Tanker Traffic:
a. Increased vessel traffic in waters used by Haisla Nation members for
commercial fishing and for traditional fishing, hunting and food gathering.
b. The likelihood of spills, including condensate, diluted bitumen, synthetic
crude, and bunker C fuel and other service fuels, from the tankers at sea
and at the marine terminal.
c. The effects and consequences of a spill. This includes impacts on the
marine environment and fish, marine mammals, birds, and other wildlife,
as well as impacts on Haisla Nation culture and cultural heritage that could
result from such impacts.
d. Response to a spill, including concerns about spill response knowledge,
planning and capability, as well as impacts flowing from response
measures themselves.
e. Potential releases of bilge water, with concerns about oily product and
foreign organisms.
These issues are important. They go to the very heart of Haisla Nation culture.
They go to the Haisla Nation relationship with the lands, waters, and resources of
its Territory. A major spill from the pipeline at the marine terminal or from a
tanker threatens to sever us from or damage our lifestyle built on harvesting and
gathering seafood and resources throughout our Territory.
Northern Gateway proposes a pipeline across numerous tributaries to the Kitimat
River. A spill into these watercourses is likely to eventually occur. The evidence
before the Panel shows that pipeline leaks or spills occur with depressing
regularity.
One of Enbridge’s own experiences, when it dumped 3,785,400 liters of diluted
bitumen into the Kalamazoo River, shows that the concern of a spill is real and
not hypothetical. A thorough understanding of this incident is critical to the
current environmental assessment since diluted bitumen is what Northern
Gateway proposes to transport. However, nothing was provided in the application
materials to address the scope of impact, the level of effort required for cleanup
and the prolonged effort required to restore the river. An analysis of this incident
would provide a basis for determining what should be in place to maintain
pipeline integrity as well as what should be in place locally to respond to any spill.
The Kalamazoo spill was aggravated by an inability to detect the spill, by an
inability to respond quickly and effectively, and by an inability to predict the fate
of the diluted bitumen in the environment. As a result, the Kalamazoo River has
suffered significant environmental damage. The long-term cumulative
environmental damage from this spill is yet to be determined.
Further, the Haisla Nation is also concerned about health impacts of the
proposed project and awaits the Human Health and Ecological Risk Assessment
which Northern Gateway has promised to provide.
1.3 Decommissioning
Northern Gateway has not provided information on decommissioning that is detailed enough to allow the Haisla Nation to set out all its concerns about the potential impacts from decommissioning at this point in time. This is not good enough. The Haisla Nation needs to know how Northern Gateway proposes to undertake decommissioning, what the impacts will be, and that there will be financial security in place to ensure this is done properly.
2. Lack of Consultation
Broadly, the Haisla Nation has concerns about all three physical aspects of the
proposed project – the pipeline, the marine terminal and tanker traffic – during all
three phases of the project – construction, operation and decommissioning.
These concerns have not been captured or addressed by Northern Gateway’s
proposed mitigation. The Haisla Nation acknowledges that a number of these
concerns can only be addressed through meaningful consultation with the
Crown. The Haisla Nation has therefore repeatedly asked federal decision-
makers to commit to the joint development of a meaningful consultation process
with the Haisla Nation. The federal Crown decision-makers have made it very
clear that they have no intention of meeting with the Haisla Nation until the Joint
Review Panel’s review of the proposed project is complete.
The federal Crown has also stated that it is relying on consultation by NorthernGateway to the extent possible. The federal Crown has failed to provide anyclarity, however, about what procedural aspects of consultation it has delegated to Northern Gateway. Northern Gateway has not consulted with the Haisla Nation and has not advised the Haisla Nation that Canada has delegated any aspects of the consultation process.
The Haisla Nation asserts aboriginal title to its Territory. Since the essence of
aboriginal title is the right of the aboriginal title holder to use land according to its
own discretion, Haisla Nation aboriginal title entails a constitutionally protected
ability of the Haisla Nation to make decisions concerning land and resource use
within Haisla Nation Territory. Any government decision concerning lands,
waters, and resource use within Haisla Nation Territory that conflicts with a
Haisla lands, waters or resources use decision is only valid to the extent that the
government can justify this infringement of Haisla Nation aboriginal title.
The Supreme Court of Canada has established that infringements of aboriginal
title can only be justified if there has been, in the case of relatively minor
infringements, consultation with the First Nation. Most infringements will require
something much deeper than consultation if the infringement is to be justified.
The Supreme Court has noted that in certain circumstances the consent of the
aboriginal nation may be required. Further, compensation will ordinarily be
required if an infringement of aboriginal title is to be justified [Delgamuukw].
The Haisla Nation has a chosen use for the proposed terminal site. This land
was selected in the Haisla Nation’s treaty land offer submitted to British Columbia
and Canada in 2005, as part of the BC Treaty Negotiation process, as lands
earmarked for Haisla Nation economic development.
The Haisla Nation has had discussions with the provincial Crown seeking to
acquire these lands for economic development purposes for a liquefied natural
gas project. The Haisla Nation has had discussions with potential partners about
locating a liquefied natural gas facility on the site that Northern Gateway
proposes to acquire for the marine terminal. The Haisla Nation sees these lands
as appropriate for a liquefied natural gas project as such a project is not nearly
as detrimental to the environment as a diluted bitumen export project. This use,
therefore, is far more compatible with Haisla Nation stewardship of its lands,
waters and resources.
By proposing to use Haisla Nation aboriginal title land in a manner that is
inconsistent with Haisla Nation stewardship of its lands, waters and resources,
and that interferes with the Haisla Nation’s own proposed reasonable economic
development aspirations for the land, the proposed project would result in a
fundamental breach of the Haisla Nation’s constitutionally protected aboriginal
title.
Similarly, Haisla Nation aboriginal rights are constitutionally protected rights to
engage in certain activities (e.g. hunting, fishing, gathering) within Haisla Nation
Territory. Government decisions that infringe Haisla Nation aboriginal rights will
be illegal unless the Crown can meet the stringent test for justifying an
infringement.
Main story Haisla Nation confirms it opposes Northern Gateway, demands Ottawa veto Enbridge pipeline; First Nation also outlines “minimum conditions” if Ottawa approves the project
Haisla Nation Response to NGP Information Request (pdf)