This page has been updated at
In the news: Alberta to BC drop dead, the pipeline is going ahead and you don’t get any money
Energy, environment and science in northwest British Columbia
This page has been updated at
In the news: Alberta to BC drop dead, the pipeline is going ahead and you don’t get any money
Today BC Premier Christy Clark’s government outlined a series of “world leading” standards for environmental protection on the ocean and on land, if pipeline projects like the Northern Gateway and the Kinder Morgan expansion are to go ahead.
One has to wonder what Premier Clark told Prime Minister Stephen Harper when she gave him the “heads up” call on the new policy last week?
After all, the BC Liberal’s call for “world leading” standards comes just weeks after the Harper’s government, in Bill C-38, changed environmental assessment into a pro-industry process, gutted the Fisheries Act protection for habitat and severely cut back the Department of Fisheries and Oceans and Environment Canada.
So far, in the province of British Columbia, with both the governing Liberals and opposition New Democrats have been spectacularly unsuccessful in persuading the Harper government to reverse the closure of the Kitsilano Coast Guard station.
In the background paper released along with the news release on the five conditions for pipeline and tanker safety, the BC government is calling for greatly enhanced Coast Guard resources and tanker monitoring as well as payment for oil spill response.
Among the conditions for marine safety enhancement BC is asking:
At Enbridge community briefings in Kitimat last year, the company’s own marine experts said that the 72 hour response time from Vancouver and Victoria for a possible spill in the Douglas Channel was completely inadequate. In its fillings with the Joint Review Panel, Enbridge has proposed setting up and funding its own response stations along the BC coast, although so far, Enbridge has not provided any details on how the response stations would be set up and how they would work.
In 2010, the auditor general reported that Transport Canada and the Canadian Coast Guard have not used a consistent or systematic approach to tanker traffic and spills nor are there formal processes for ensuring that risks are reassessed.
Sheila Fraser found that
In the United States Senate, Canadian Coast Guard response for an oil spill in the Strait of Juan de Fuaca was described as “call the Americans”
For some search and rescue missions the federal government has indicated that it will rely more on the all-volunteer Royal Canadian Marine Search and Rescue service (formerly the Coast Guard Auxiliary) which is already stretched thin in some areas of the Pacific Coast, rather than the full time professionals from the Coast Guard service itself.
On the industry response, BC says
The federal government should review its rules and requirements to ensure industry-funded response funds are sustainable and adequate to fully cover a major response without requiring public money. Currently, the total amount of ship owner insurance and industry funding available for spill response is $1.3 billion. By comparison, the U.S. federal government maintains a spill fund that is forecast to grow to nearly $4 billion by 2016.
Again given the government backs and the Conservative government’s close ties with the energy industry, one has to wonder what if those provisions can be enforced, especially since more and more of the energy industry in Canada is owned off shore, increasingly in China with its sorry environmental record. (Globe and Mail CNOOC’s Nexen bid: A new test for Harper)
If there are to be “world-leading” standards for environmental protection in this country, it has to be paid for. So the question remains, who will pay for it? The federal government is cutting back, Alberta doesn’t want to raise the relatively small royalties it charges the energy industry and Canada is not likely to get a contribution from China.
Who pays to protect the coast and the northern interior going to be a big question for Stephen Harper in the coming months. With the polls showing Adrian Dix and the NDP leading in contention for a provincial election next year, and now with Christy Clark, apparently, demanding higher standards, will Harper open the Ottawa wallet now, will he wait until he faces a much tougher BC premier in Adrian Dix next year, or will he stubbornly hold his course of forcing Canada into his vision of a conservative, limited government nation, with, in the case of an oil spill on land or sea, that will cost the federal treasury billions, even if the energy industry picks up some of the tab?
Auditor General 2010 Report (pdf)
Auditor General 2007 report (pdf)
Here is the background information on the BC provincial government’s policy on pipeline projects, as released July 23, by the government:
BACKGROUNDER 1
World-leading marine spill preparedness and response systems for British Columbia
Protecting the province’s environment is a priority for its citizens and the B.C. government. While B.C. is not the government lead in terms of responding to a marine spill, advocating for world-class protection measures and procedures is a B.C. priority. Guided by an analysis of international marine response plans and procedures, the B.C. government is moving forward with 11 recommendations to the federal government aimed at improving Ottawa’s marine spill management. Chief among those recommendations are:
Encourage the federal government to strengthen requirements for certified marine spill response organizations.
Current response times and planning capacity are less stringent than other jurisdictions like Alaska and Norway. For example, for the types of tankers being proposed for Canada’s west coast, Alaska requires planning for 300,000 barrels. In Canada, response organizations are only required to maintain response plans for spills up to approximately 70,000 barrels (10,000 tonnes).
Further, Alaska allows responders 72 hours to reach the spill site, while Canada allows 72 hours plus travel time, which can sometimes add days to the response.
Encourage the federal government to enhance tanker requirements and available response capacity.
In shared bodies of water, the United States’ requirements exceed Canada’s. For example, the United States requires escort tugs for laden tankers and mandates industry pay for designated and strategically placed emergency response tugs. Canada does not have any similar requirements.
Ensure the Canadian Coast Guard adopts a unified command/incident command structure.
The Canadian Coast Guard has a unique response system which is only used in B.C. The United States, companies and governments worldwide use a unified command/incident command response structure for a range of emergency responses, including marine spills. By bringing the Coast Guard under this system, an effective, co-ordinated response is better ensured while reducing layers of approvals that can delay critical, prompt decision-making.
Current limits of liability rules strengthened to reduce government and public exposure to financial risk.
The federal government should review its rules and requirements to ensure industry-funded response funds are sustainable and adequate to fully cover a major response without requiring public money. Currently, the total amount of ship owner insurance and industry funding available for spill response is $1.3 billion. By comparison, the U.S. federal government maintains a spill fund that is forecast to grow to nearly $4 billion by 2016.
BACKGROUNDER 2
World-Leading on-land spill preparedness and response system for British Columbia
Land-based spill response is an area where the province has significant management responsibilities. The safe transportation and use of hazardous materials – including oil and natural gas – is critical to British Columbia’s economy and way of life. While land-based spills can be mitigated, they cannot be completely avoided; they are a consequence of a modern economy.
Major resource developments in the province’s northeast, coupled with proposals to open new, and expand existing, transportation corridors for petrochemicals, makes it timely for the province to consider its spill management capacity.
B.C. government’s proposed policy:
A provincial policy review has confirmed support for the “polluter pays” principle. In other words, those sectors (i.e. the oil and gas industry) that pose the risk must be responsible for all related mitigation and response costs.
Ministry of Environment staff are in the process of reviewing options to implement industry-funded and enhanced spill-management for land-based operations. It has three central elements:
An industry-funded terrestrial spill response organization.
An enhanced provincial Environment Emergency Program.
Natural resources damages assessment.
These changes would address some key issues facing B.C.’s land-based spill response practice, including new requirements for:
industry to have tested and government-approved geographic response plans; and
provincial response capacity that matches the known risk, including staff and resources to address spills.
The proposed policy would strengthen the province’s oversight role and facilitate the verification of industry capacity. Further, it would ensure that a stable source of funding is available to ensure the program continues to have a strong presence on-scene when a spill occurs. This role for government is critical to protecting the provincial economic, social and environmental interests that can be impacted when a spill takes place.
Next steps:
Immediately strike a terrestrial spill response working group.
Engagement with key industry associations and federal agencies.
Complete in-depth technical analysis of policy and options.
Public consultation on policy intentions paper.
Draft legislation based on the chosen policy direction.
Media Contact:
BACKGROUNDER 3
Consultation and partnerships with First Nations
In British Columbia, case law requires the B.C. government to consult with First Nations on any decision that may infringe on their treaty or Aboriginal rights. Where government makes a decision that will infringe on rights, there is a legal duty called “accommodation,” which can include mitigation measures, or even economic compensation. These legal requirements impact resource development and government decision-making.
Consultation is not only a legal obligation, it is part of good governance, and the B.C. government takes consultation and the courts’ direction on consultation very seriously.
B.C.’s approach is to work in partnership to give First Nations a meaningful role in land and resource management. B.C. is also the first province to share resource development revenue with First Nations, creating opportunities that flow benefits directly back into Aboriginal communities. B.C. has reached a suite of strategic agreements that create certainty for First Nations and industry by making it easier for business and First Nations to work together.
B.C. has achieved nine Reconciliation and Strategic Engagement Agreements with First Nations. These agreements provide First Nations with a defined role in the management of lands and resources and often include tools to allow for increased First Nation participation in local economies.
B.C. has 189 active forestry revenue-sharing agreements with First Nations. Since 2003, B.C. has provided approximately $323 million and access to 63.9 million cubic metres of timber to First Nations.
B.C. signed mine revenue-sharing agreements with Nak’azdli First Nation and McLeod Lake Indian Band for the Mount Milligan Mine and the Tk’emlúps and Skeetchestn Indian bands for the New Afton Mine. Further agreements are being negotiated.
Economic Benefit Agreements with five Treaty 8 First Nations have provided $52 million to date in First Nation benefits from gas and other development in northeast B.C.
The First Nations Clean Energy Business Fund provides capacity, equity and revenue-sharing funding for First Nation participation in this sector. Since 2010, the fund has provided nearly $2.5 million to 53 First Nations.
The B.C. government has collaborated with the Business Council of British Columbia to develop the best practices to increase general understanding of industry’s role. Increasingly, companies recognize that building relationships with First Nations makes good business sense, and are taking steps to form effective relationships that result in mutual benefits.
B.C. expects proponents to build strong, enduring relationships with First Nations potentially affected by development projects. Through those relationships, there should be discussion of possible impacts on Aboriginal interests, measures in place that would mitigate those impacts and a development of impact management and benefit agreements.
BACKGROUNDER 4
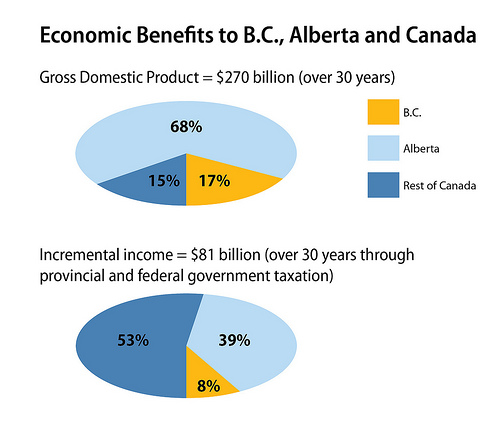
Fiscal benefits imbalance: Northern Gateway Pipeline
The Northern Gateway Pipeline is forecast to provide significant benefits to governments, communities and individuals through taxation and royalty revenues, employment and indirect and induced jobs.
According to a research report by Wright Mansell Research Ltd., the pipeline is likely to generate an incremental $81 billion in provincial and federal government taxation over a 30 year period between 2016 and 2046. Of the $81 billion, a full $36 billion is accrued by the federal government.
The remaining $45 billion in provincial revenues are split with $32 billion to Alberta, $6.7 billion to British Columbia and the remaining $6 billion split among the remaining provinces, with Saskatchewan appearing to benefit by nearly $4 billion. Thus, of the $81 billion in incremental taxation revenue, British Columbia stands to receive approximately only 8.2 per cent.
The $36 billion to the federal government is anticipated to be distributed across the country on a per capita basis as these revenues would be considered to be general and not dedicated revenues. There is no guarantee these revenues would be distributed in this manner.
In addition, with the creation of a new market for Alberta oil in Asia, prices are forecast to rise such that over the same 2016-46 period, there would be a price lift of $107 billion, split $103 billion to Alberta and $4 billion to Saskatchewan, which has begun to exploit its heavy oil and bitumen resources. This lift arises from an all increased value of all oil products that are being exported out of Canada with the elimination of the discount paid for Canadian oil.
Given the risk to British Columbia from land-based and coastal bitumen spills, British Columbia does not believe an equitable distribution exists for fiscal benefits. This imbalance must be addressed prior to British Columbia considering provincial support.
Update 3 Joe Oliver statement
Update 2 Statement from Alison Redford
Update 1 Enbridge statement
The government of British Columbia has outlined five what it calls “minimum requirements that must be met for the province to consider the construction and operation of heavy oil pipelines within its borders.”
But at a news conference announcing the conditions, Environment Minister Terry Lake says the province will still not take an official position on the pipeline project itself.
In news release, Premier Christy Clark said, “Our government is committed to economic development that is balanced with environmental protection. In light of the ongoing environmental review by the Joint Review Panel on the Enbridge pipeline project proposal, our government has identified and developed minimum requirements that must be met before we will consider support for any heavy oil pipeline projects in our province. We need to combine environmental safety with our fair share of fiscal and economic benefits.”
Later Monday afternoon, Enbridge released a statement saying:
We wish to reiterate our commitment to working with governments, including BC, in determining what we can do to further address concerns and to engaging in a dialogue to ensure full understanding of the assessments of risk, the many safety and environmental protection measures in the plan as well as the benefits that would come with the project.
The premier of Alberta, Alison Redford, Monday evening released a stinging news release on the conditions outlined by British Columbia for pipelines crossing the province and tanker traffic on the coast.
A key phrase in the release says:
Leadership is not about dividing Canadians and pitting one province against another—leadership is about working together.
In Ottawa, the pro-pipeline Minister of Natural Resource, Joe Oliver, issued an unremarkable statement promoting responsible resource development that managed to avoid mentioning the BC announcement; a statement that could be regarded as a classical press release that says absolutely nothing.
Details of the BC provincial approach are outlined in a “heavy oil policy paper.”
The government also released background information on the conditions.
The five conditions are
The release says that “any project proposal must be approved through appropriate environmental assessment (EA) processes.”

However, trust for the environmental processes has been falling since Stephen Harper’s government passed Bill C-38 which is designed to fast track approvals and is seen by may in the environmental movement as gutting the review process.
Action plan
The province is also proposing a joint plan of action with the federal government that would include the following elements:
In the release, BC Environment Minister Terry Lake said: “When we consider the prospect of a heavy oil pipeline, and of the increased oil tanker traffic that would result, it is clear that our spill prevention and response plans will require significant improvements. Our government has already initiated discussions with the federal government on improving our response plans and resources,” said Environment Minister Terry Lake. “This represents an opportunity for British Columbia and Canada to develop world-leading environmental protection regimes.”
First Nations
The government release says
The fourth requirement for the B.C. government to consider support for heavy oil pipeline proposals is First Nations participation. Governments in Canada have a duty to consult and accommodate First Nations, and British Columbia is committed to meeting this test. British Columbia has developed a set of tools to help First Nations to partner with industry and participate in economic development. These agreements help to create certainty for development that benefits all British Columbians. British Columbia remains committed to this approach.
“We believe the benefits to First Nations from major pipeline proposals must be clearly identified, along with the measures that will help protect against environmental impacts,” said Aboriginal Relations and Reconciliation Minister Mary Polak. “As recently as last week, such an approach was endorsed by the Canadian Council of CEOs in their report on Aboriginal participation.”
Show me the money
The government is also emphasizing that the province benefit from any heavy oil project:
Lastly, British Columbia must receive a fair share of the fiscal and economic benefits of any proposed heavy oil project. B.C. will shoulder 100 per cent of the risk in the marine environment and a significant proportion of the risk on the land should a spill event ever occur. Current heavy oil project proposals do not balance the risks and benefits for British Columbia.
“We have identified aggressive environmental requirements and principles for First Nations engagement, and we have clearly stated we expect a fair share of the fiscal and economic benefits for our province,” said Premier Clark. “British Columbians are fair and reasonable. We know we need resource and economic development, but we also expect that risks are managed, environmental protection is uncompromised and that generations will benefit from the decisions we make today.”
In its release, Enbridge repeated its earlier statements that the company will continue
to reach out and encourage conversation with British Columbians about the project through our website and blogs, community meetings and conversations. We have devoted much effort and resources into consultations with communities, First Nations, and Métis…”
The company went on to say:
Enbridge and the Northern Gateway project team have worked hard to ensure this unique project would be built and operated to the highest standards and has committed to further enhancements to make what is already a safe project even safer.
This project will bring real and tangible benefits to the communities and Aboriginal groups along the proposed route, and to the province of British Columbia as a whole.
.
The Vancouver Sun is reporting that the BC government has called a news conference for Monday to announce its position on the Northern Gateway pipeline project.
See B.C. government to announce stance on Northern Gateway pipeline on Monday
The Sun says Environment Minister Terry Lake and Aboriginal Relations and Reconciliation Minister Mary Polak as well as ministry officials and and representatives from the B.C. environmental assessment office.
CKNW says the province has called the news conference to outline its position on “heavy oil pipeline proposals.”
Negotiations between Rio Tinto Alcan and Canadian Auto Workers Local 2301 are going down to the wire. The current contact expires Monday, July 23.
The CAW says 96 per cent of members voted in favour of strike action during voting Thursday and Friday. The Local represents 1150 workers at the Alcan smelter. One of the main issues in the negotiations is a reduction in the workforce to 699.
CAW Local 2301 president Rick Belmont said the union received a 72 hour lockout notice this afternoon and the union responded with a strike notice.
RTA spokeperson Colleen Nyce says issuing lockout and strike notice is standard practice during negotiations.
Both sides say negotiations will continue through the weekend.
If there are picket lines it could be a confusing and possibly volatile situation because the Kitimat Modernization Project is on the same site with a work camp full of construction workers on RTA property.
Most construction workers are employed or contracted by Bechtel, the construction contractor and are not members of CAW 2301.
Enbridge Northern Gateway has filed thousands of pages of “reply evidence” to the Northern Gateway Joint Review panel, responding to questions from the panel, from government participants like DFO, and intervenors.
Enbridge also used the filing to issue a news release saying it is adding $500 million in new safety features for its pipeline plans.
Northern Gateway Pipelines Reply_Evidence_ (summary of filings PDF)
Link to 43 item reply filing on JRP website.
In the introduction to the summary of the evidence the JRP asks
Should the fact that Northern Gateway does not respond to all points in a particular intervenor’s evidence or to all intervenor evidence be taken as acceptance by
Northern Gateway of any of the positions of intervenors?
To which Enbridge replies:
No. Northern Gateway does not accept any of the intervenor positions that are contrary tothe Application or additional material filed by Northern Gateway. Some of those positions will be dealt with by Northern Gateway in cross examination and argument rather than reply evidence, and others will simply be left to the JRP to determine on the basis of the filed evidence alone.
Related: Vancouver Sun: Christy Clark toughens pipeline stance as Enbridge announces safety upgrades
The reply covers a multitude of topics including
In response to numerous questions about the Marshall, Michigan, oil spill, Enbridge repeats what it said in an e-mail to “community leaders” earlier this week and in this morning’s news release, saying: “Enbridge has made a number of improvements since the Marshall incident.”
As part of the filing Enbridge has also filed an update on its aboriginal engagement program.
There are also detailed and updated reports on the company’s plans for the Kitimat valley region.
Enbridge Northern Gateway today issued a news release saying that it has filed “Reply Evidence” to the Northern Gateway Joint Review panel that contains details of further enhancements in pipeline design and operations. Enbridge says the upgrades will add $500 million to the cost of the $5.5 billion project.
Enbridge has also filed updated plans for marine mammal protection.
The Enbridge news release is a summary of a 43-item filing of the reply evidence with the Joint Review Panel covering a vast number of topics from the pipeline projection to the possibility of earthquakes.
Related: Enbridge files thousands of pages in document dump reply evidence to Northern Gateway JRP
Northern Gateway Pipelines Reply_Evidence (summary of filings PDF)
Link to 43 item reply filing on JRP website
Framework for Marine Mammal Protection Plan (pdf)
According to the filing, the Marine Mammal Protection plan includes plans by Enbridge to fund research:
Northern Gateway has committed to funding a Marine Research Chair at a university in British Columbia.
Where it is agreed upon by the Marine Research Chair and Northern Gateway, programs and information from the MMPP will be integrated into research undertaken by the Marine Research Chair. Information from the Marine Research Chair may also be of value to the MMPP.
A spokesman for the University of British Columbia told Northwest Coast Energy News that no one from Enbridge has, so far, approached UBC about a Marine Research Chair. A spokesperson at the University of Victoria also said there had been no contact from Enbridge.
On the pipeline plan, Enbridge says “These extra measures build on the plan in the application presently before federal regulators that already far surpasses industry codes and standards.”
“We recognize that there are concerns among Aboriginal groups and the public around pipeline safety and integrity. We had already planned to build a state-of-the-art project, using the most advanced technology, safety measures and procedures in the industry today,” said Janet Holder, Executive Vice President, Western Access, Enbridge Inc. “With these enhanced measures, we will make what is already a very safe project even safer in order to provide further comfort to people who are concerned about the safety of sensitive habitats in remote areas.”
Enbridge and the Northern Gateway project team have worked hard to ensure this unique project would be built and operated to the highest standards. The measures contained in the Reply Evidence go above and beyond anything that has ever been done before in the industry.
The extra measures include:
Increasing pipeline wall thickness of the oil pipeline
Additional pipeline wall thickness for water crossings such as major tributaries to the Fraser, Skeena and Kitimat Rivers
Increasing the number of remotely-operated isolation valves. This would increase the number of isolation valves in BC by 50%
Increasing frequency of in-line inspection surveys across entire pipeline system by a minimum 50% over and above current standards
Installing dual leak detection systems
Staff pump stations in remote locations on a 24/7 basis for on-site monitoring, heightened security, and rapid response to abnormal conditions
Enbridge expects these extra measures will carry an additional cost of approximately $400 million – $500 million.
“After years of consultation with stakeholders and after personally attending many regulatory hearings for Northern Gateway, it has become clear – we have to do everything we can to ensure confidence in the project,” said Ms. Holder. “We’ve listened. We have often been asked if we could guarantee that we would never have a significant pipeline failure over the years on Northern Gateway. These initiatives will put the project closer than any pipeline system in the world to providing that guarantee.”
Marine Mammal Protection Plan
In the filing, created by Stantec Consulting, Enbridge says the plan will address all marine mammal species that could be directly or indirectly affected the Northern Gateway project, adding: “Attention will be given to species of cultural importance or heightened sensitivity to potential Project effects.”
The filing says Northern Gateway’s “commitment to a focused marine mammal monitoring and survey program is unprecedented for a marine project in Canada.”
It says that monitoring of marine mammals and “additional cooperative research initiatives” will also be of value to other organizations focused on supporting the recovery strategies for species of conservation concern.”
The report adds a caveat:
It is important to note ….it would be impractical to do a complete assessment of more than 30 different marine mammal species. Going forward, monitoring conducted in the CCAA will include additional marine mammal species For example, during marine mammal surveys, sightings of all marine mammal species would be recorded. In some cases, species-specific research initiatives (e.g., for northern resident (NR) killer whales) may also be implemented. Results from marine mammal monitoring surveys and research initiatives are expected to improve the regional understanding of all marine mammal species’ timing and distribution…
The report says the MMPP will include details on such measures as:
• low-noise propulsion systems on purpose built Project-related vessels (e.g., tug escorts and support
vessels for the marine terminal)
• reduced vessel speeds in the CCAA and in the “CCAA approaches”
• attempting to better understand the behavioural responses of NR killer whales to tankers and tugs
• identifying important habitat for NR killer whales and other cetaceans, as well as seasonal use of these habitats
• use of the results of a science-based quantitative vessel–marine mammal strike risk analysis
• to the extent practicable, allowing for tanker route adjustments (taking into account navigational andhuman safety) to avoid sensitive cetacean habitat during important seasonal periods
• undertaking a cooperative research initiative with other participating organizations to determine
potential effects on marine mammals and to develop industry protocols to limit these effects
Enbridge Northern Gateway has issued a detailed reply to the criticism of its operations contained in a preliminary report from the US National Transportation Safety Board to the 2010 oil spill at Marshall, Michigan, which called the company’s response like the silent movie era “Keystone cops.”
The note from Michele Parrett, Senior Manager, Community and Municipal Relations for Northern Gateway was sent to members of the District of Kitimat Council and presumably other politicians and community leaders along the proposed pipeline route.
The document was among those routinely released to the public at the regular council meeting on Monday, July 16, 2012 and is a much more detailed defence of Enbridge’s position than the news release issued after the NTSB report.
In the e-mail, Enbridge says it has updated its safety and response procedures and its corporate culture since the Michigan incident.
Despite widespread criticism of Enbridge from all sides of the political spectrum, that NTSB report does not seem to have had any impact on federal Environment Minister Peter Kent, who told The Canadian Press had had not yet read the NTSB report. Kent also said that unread report will not change the Conservative government’s mind about the Northern Gateway pipeline project, adding “Pipelines are still, by far, the safest way to transport petrochemicals in any form.”
Overview of NTSB Report into Line 6B incident at Marshall, Michigan
July 12, 2012
Dear Community Leader,
I’m writing you today to provide information regarding the United States’ National Transportation Safety Board’s (NTSB) release of its conclusions and recommendations yesterday, with regard to the Enbridge pipeline leak in Marshall, Michigan in July 2010.
Enbridge has not been waiting for the NTSB’s report before furthering to improve our safety standards. Since the incident we have undertaken our own internal investigation and incorporated the findings of that investigation into new practices and processes to improve our safety and reliability.
Enbridge and Enbridge Energy Partners has been working with the NTSB and other regulators throughout the course of the investigation so that we can take the necessary steps to prevent such an accident from occurring again. We are now reviewing the NTSB reports in detail to determine whether any further changes are required.
Enbridge has already implemented, in 2010 and 2011, appropriate operational and procedural changes based on its own detailed internal investigation. Enbridge’s overarching objective and business priority is to ensure the safety and reliability of our delivery systems for the people who live and work near our pipeline systems across North America, our employees and our customers.
In direct response to the Marshall accident, or as part of our ongoing improvement initiatives and activities, Enbridge has taken the following steps:
Pipeline and Facility Integrity
· Further heightened the importance of our pipeline and facility integrity program.
· Re-organized the functional areas that are responsible for pipeline and facility integrity.
· Substantially increased capital and operating budgets associated with maintenance and integrity programs.
· Undertook hundreds of internal inspections and thousands of investigative digs.
· Placed a renewed emphasis on the safety of our overall system.
Leak Detection
· Established the Pipeline Control Systems and Leak Detection department, doubling the number of employees and contractors dedicated to leak detection and pipeline control.
· Enhanced procedures for leak detection analysis.
· Updated control room management procedures.
· Implemented a Leak Detection Instrumentation Improvement Program to add and upgrade instrumentation across our system.
Pipeline Control and Control Centre Operations (CCO)
· Developed a Control Room Management (CRM) plan based on the U.S. Code of Federal Regulations and implemented a number of the sections, October 1, 2011, remaining sections implemented by August 1, 2012.
· Revised and enhanced all procedures pertaining to decision making, handling pipeline start-ups and shutdowns, leak detection system alarms, communication protocols, and suspected column separations.
· Changed organizational structures to better align, focus and manage employees’ span of control and workloads.
· Augmented CCO (Control Centre Operations) staff, adding training, engineering and operator positions.
· We also completed the design and construction of a new, world-class CCO in Edmonton, Alberta which was underway at the time of the accident.
Public Awareness
· Reviewed and strengthened Public Awareness Programs in the U.S. and Canada.
· Developing an industry-leading online and in-person training tool to provide Enbridge-specific information to emergency responders.
· In the U.S, we:
o Formalized the U.S. Public Awareness Committee.
o Improved the Program Effectiveness Evaluation process.
o Provided annual employee training for field employees across the company’s U.S. operations.
o Created a Public Awareness Hotline.
· In Canada, we:
o Formalized the Canadian Public Awareness Committee.
o Are creating a Canadian Public Awareness Database.
o Improved the landowner/tenant database.
o Developed a landowner newsletter.
o Established Community Relations positions in each region.
Emergency Response
· $50 million spent between 2012 and 2013 (projected) to improve our equipment, training and capabilities.
· Develop better tools for waterborne spills.
· In 2011, a cross-business unit response team was created for large-scale events requiring more resources that a single region could provide.
· In 2011, created a dedicated Emergency Response group in Operation Services for increased regional support.
· Conducting an Emergency Response preparedness assessment to enhance abilities to more rapidly respond and contain a significant release.
Safety Culture
· Reinforced a high level of safety and operational integrity across Enbridge in integrity management, third-party damage avoidance and detection, leak detection, incident response capacity, worker and contractor occupational safety, public safety and environmental protection.
· Implemented “Lifesaving Rules” and training for all Enbridge employees and contractors. The Lifesaving Rules are applicable to all employees and contractors, and are communicated, clarified and reinforced across all business units at Enbridge.
· Introduced new Safety Culture training sessions for all employees.
Over the past two years we have made significant improvements in the above areas. The NTSB’s findings will provide us with regulatory guidance and important information to help improve our performance and achieve our goal of zero spills.
We remain committed to a respectful, open and transparent review and discussion of the Northern Gateway Project. Should you have any questions, please do not hesitate to contact me or a member of the Northern Gateway team at the information provided below.
Sincerely,
Michele Perret
Senior Manager, Community and Municipal Relations
Enbridge Northern Gateway Pipelines
comments