You might not be seeing it at the gas pumps at the moment, but you soon will, the price of gas has gone down by 30 per cent since June.
Prices of key commodities, oil, coal and iron ore are dropping. And the weakness in the market for two of those commodities oil and iron ore should be setting off the alarm bells in Kitimat and the northwest.
The declining price of oil will soon affect all those energy-related projects that are supposed to bring an economic renaissance to northwest British Columbia.
As for iron ore, people might ask, what does iron ore have to do with us, there are no iron mines or steel mills around here.? However, in the highly integrated world economy, Rio Tinto is one of the world’s largest producers of iron ore, the decline in iron ore prices is affecting Rio Tinto’s bottom line and that is why, analysts say, the company may be vulnerable to a take over by the little known commodities giant Glencore.
There are two possibilities with commodity prices. Some analysts see the decline in commodity prices and the accompanying drop in prices on the world’s stock exchanges as a “correction” phase. However, others like Reuters analyst John Kemp says the downturn is an indication that the commodities “supercycle” has reached its peak and is on the way down.
The oil industry has always experienced very long, slow and deep cycles in supply, demand and prices: the current downturn is no exception.
Kemp says the current up cycle began around 2002, with rising oil prices. The financial collapse in 2007 and 2008 briefly interrupted the cycle but now according to Kemp and other analysts there is a glut of oil on the market and prices are falling world wide.
High prices meant not only new plays, especially in the Alberta bitumen sands, but also stronger efforts to save money by increasing energy efficiency and, yes, turning to cheap natural gas.
There are also new factors at play. In the past when there was a downturn in oil prices, OPEC led by Saudi Arabia, would limit supply to keep the price at a profitable level. However, the flood of oil on to the market from shale oil plays, mainly in the United States but also in Canada, has meant that OPEC can’t do that anymore. Too much competition. So the analysts say, the Saudis and other OPEC members are actually starting a price war to retain market share.
When Kemp was writing last week, he said the key marker, North Sea Brent crude:
if prices are adjusted for inflation (using average U.S. hourly earnings), Brent prices are at the lowest level in real terms since October 2007, exactly seven years ago.
There has always been a lot of skepticism among long term residents of Kitimat who have seen boom and bust cycles before and so they, rightly as it turns out, have been wary of industrial promises. Then there’s the current housing debate which may soon see the out of region speculators and developers caught with their pants down in the midst of a Kitimat January blizzard.
The commodity downturn also shows the foolishness of the politicians, business people and commentators who kept saying that BC is a “natural resource economy” and restrictions on corporations and strong environmental requlations will only hurt that economy. Who needs diversification? Who needs a fishing guide anway? It is fairly clear already that Christy Clark’s promises of a debt free province have as much credibility as speculating in Dutch tulip bulbs.
As for the idea among some here that if Kitimat had only voted in favour of Enbridge Northern Gateway, the gates to ecomonic paradise would open, that is foolishness. You can be certain when the Saudi princes decided on a price war to keep themselves in the luxorious lifestyle which they believe they are entitled, they didn’t consider whether Kitimat voted for or against Northern Gateway.
Editorial Part I: Kitimat needs a world class council
So what does Kitimat need to know
The nail in the coffin for Northern Gateway?
The Northern Gateway project was already in deep trouble before the downturn in oil prices.
Writing in The Globe and Mail last week, Jeff Rubin noted.
Part of the impetus behind constructing new pipelines to carry bitumen from northern Alberta to the U.S. Gulf Coast, Kitimat on the Pacific, or even all the way across the country to Saint John, N.B., was to help close the substantial discount between Canadian oil and world prices. Well, crude’s recent drop into the $85‑a‑barrel range has basically collapsed the once wide‑open spread that had existed between West Texas Intermediate and Brent crude with hardly any new lengths of pipe being laid into the ground at all.
Rubin went on to note that the decision by the Saudis to launch the price war has changed everything.
For pipeline companies with major proposals on the table, such as TransCanada and Enbridge, falling oil prices are a game‑changer of the same magnitude that rising prices were a decade ago. Back then, soaring prices created an urgent need to build new pipelines to connect North America’s burgeoning supply to coastal refineries and world markets.
We’re now in a different world. At the root of today’s problem is global demand that is no longer growing quickly enough to support the prices necessary to keep expanding expensive unconventional sources of supply such as the oil sands. Lower prices will effectively strand those reserves regardless of the transportation options that may become available. Even if President Obama approved Keystone XL or the National Energy Board gave the green light to Energy East, falling commodity prices mean that soon there might not be enough oil flowing out of northern Alberta to fill those new pipelines.
This week’s near disaster with the Russian container ship Simushir, where the coast of Haida Gwaii was saved by a change in the wind direction, hasn’t helped either.
Will the refinery fade to black?
Economists have always been skeptical about David Black’s plan for the Kitimat Clean refinery and Black has admitted that he also had not much support for the refinery idea either from the hydrocarbon indusry or from government.
Most important, Black has said that he as a businessman intends to eventually make a profit by selling refined product. In fact on his website, Black said he expected the refinery to go into profit after just seven to ten years of operation.
But now comes the flaw in Black’s business plan. According to the website, the Kitimat Clean project is based on North Sea Brent Crude priced at $110 US a barrel. The refinery would take advantage of the “discount” on deliveries of Alberta bitumen crude which the site estimated at $35 a barrel. Black’s site says the refinery would be profitable if it could purchase bitumen at a $23 discount, making $12 a barrel over the world price.
Unfortunately, as of this writing, 11 am on October 20, the price of Brent Crude is now $85.79 and dropping slightly. West Texas Intermediate Crude, the other bench mark is even lower at $82.79 a barrel.
It looks like the drop in oil prices wipes out Black’s plan for profitability, since Brent Crude is already $25 a barrel cheaper than Black had projected.
What’s that got to do with the price of gas?
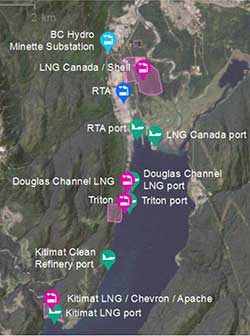
The falling price of crude oil is also going to have a major impact on the liquified natural gas projects in the northwest. The current economic situation will soon see the short term players and speculators cut and run, leaving, it is hoped, a couple of long term players in the west coast LNG terminal market. However the volatility in the dropping oil market may mean that the all important Final Investment Decisions are delayed yet again.
That’s because, at the moment, in Asia, the price of natural gas is calculated as a per centage of the price of crude oil, what is called the Japan Cleared Customs price. And as the LNG Journal has reported the price of LNG in Japan has dropped to the 2009 level.
East Asian Delivered LNG Indicator Price hit its lowest level since 2009 at $12.30 million British thermal units with European Brent crude oil prices collapsing to $82.85 per barrel. The East Asia LNG price is based on the Japanese Crude Cocktail method of assessing long-term contract cargo prices for Japan, based on oil which last hit current levels and then slipped below $80.00 per barrel during 2009.
The idea of LNG exports, especially since the Japanese earthquake in 2011, is that the companies can make a big profit by buying natural gas at low North American prices, exporting and then selling at the higher Asia price. In a free market world, however, the Asian countries and companies have, for the past few years been balking at buying at the higher JCC price and attempting to buy at the much lower North American Henry Hub price which at this writing was $3.72 MMBTu. Today’s JCC LNG price was $12.75, still higher than the North American price, but as LNG Journal notes, at a five year low.
Bloomberg reports that slump in oil prices is already threatening the Northwest’s greatest rival in LNG, Australia.
Weaker oil prices may put proposed LNG projects “to sleep for a number of years,” Fereidun Fesharaki, chairman of Facts Global Energy, an industry consultant, said in a phone interview. “For the projects that are already under construction, it hits their pocketbooks seriously.”
Prices below $80 a barrel may be a “disaster” for some projects, said Fesharaki, who forecasts Brent may decline to $60 a barrel before the end of the year, then rebound to about $80 by the end of 2015.
and
“There’s no doubt if we were to see the type of crude oil prices we’re seeing now continue they would be looking at lower LNG prices,” Daniel Hynes, senior commodity strategist at Australia and New Zealand Banking Group Ltd., said by phone. “On face value, it would put pressure on margins.”
Long term LNG prospects
On the other hand, long term prospects for LNG exports are good. Demand in the Asian markets is still growing.
 According to the Nikkei Asian Review, the Japanese Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry projects that by 2020, 70 per cent of Japan’s LNG will come from Australia and North America. That doesn’t mean that Canada won’t have rivals, the projections say that the United States, which is just starting many of its LNG export projects could be Japan’s third largest customer with Canada in fourth place.
According to the Nikkei Asian Review, the Japanese Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry projects that by 2020, 70 per cent of Japan’s LNG will come from Australia and North America. That doesn’t mean that Canada won’t have rivals, the projections say that the United States, which is just starting many of its LNG export projects could be Japan’s third largest customer with Canada in fourth place.
There are big benefits to getting LNG from North America and Australia. The unlikeliness of pirate attacks is one. There is also less political uncertainty. And then there is the price. U.S. shale gas, for example, costs about 20% less than what Japan currently pays for LNG.
Diversification
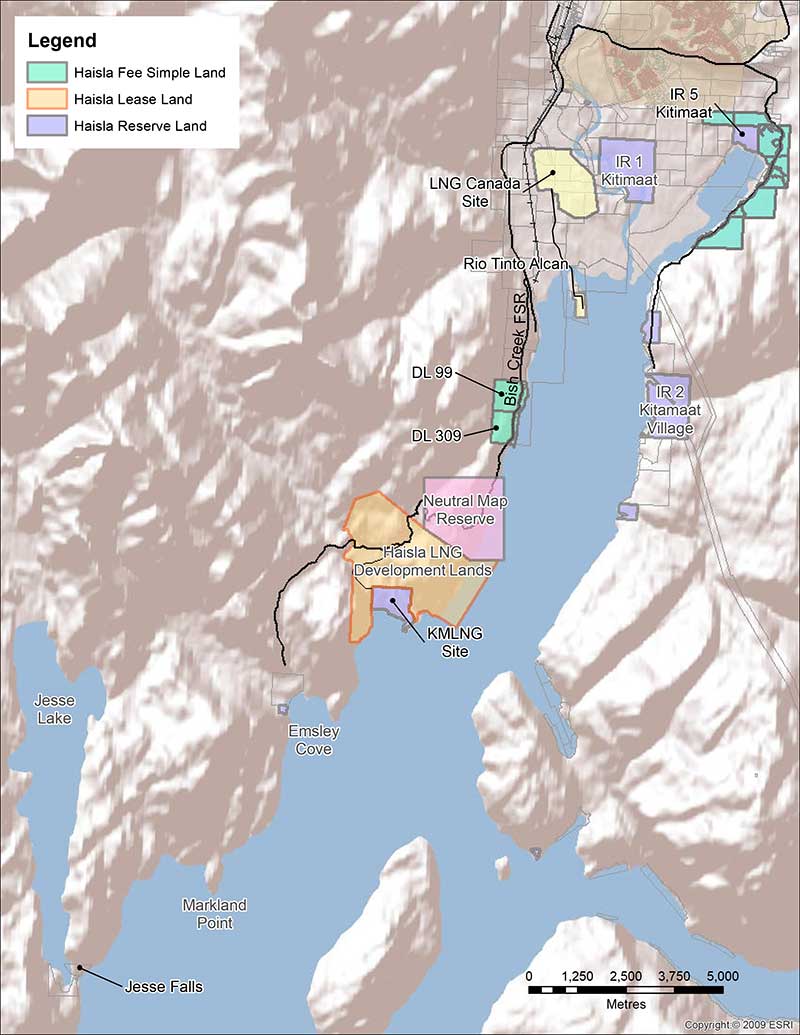
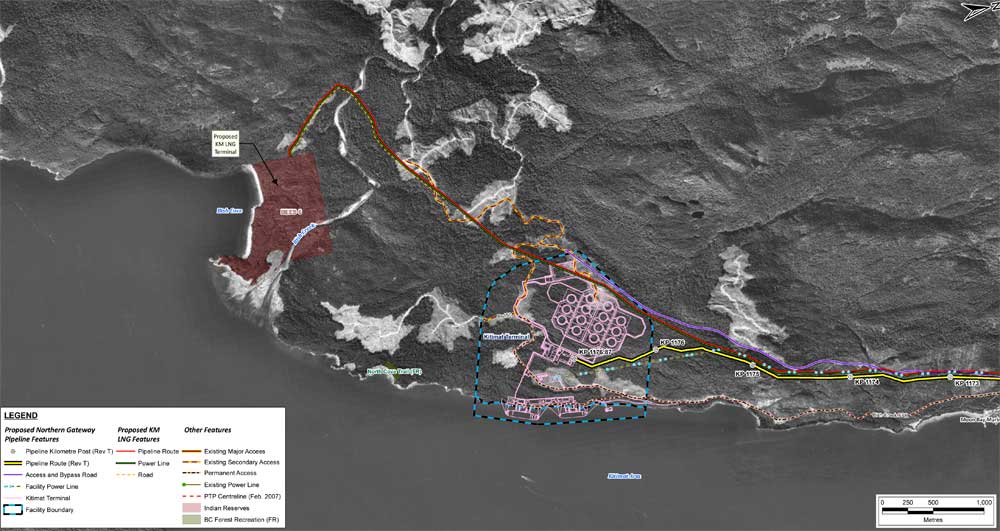
With the Rio Tinto Alcan Kitimat Modernization Project construction phase winding down, with some uncertainty about the future of Rio Tinto itself and with more possible delays in the Final Investment Decisions for LNG Canada and Kitimat LNG, Kitimat needs a Plan B (and a Plan C or D or E).
The idea of a retirement community is no longer viable, costs of housing, even if they drop, are just too great.
Kitimat’s second strength has always been tourism and fishing. In 2015, there must be stronger efforts of support both fishing and tourism, which, in the long term will support that regions economy through good times and bad.
That means the new council must be firm in demanding (yes demanding) full access to the Kitimat waterfront and that includes a well-managed marina or marinas that have the capacity for recreational, adventure and fishing guiding and industrial use.
The District of Kitimat must come up with a plan that will promote the advantages of the region as a tourist and fishing destination. While the Chamber of Commerce has being doing a good job, up to now as the main promoter of tourism, Kitimat’s public image across Canada and the world is soley industrial and the District should assume more responsiblity for changing that image. The economic development staff at the district have been working largely on large scale industry. It should devote more time and money to the natural wonders of the area.
The plan B should also mean balance. Balance between industry and environment. The sneering contempt for those who want to protect the environment of the northwest is short sighted thinking, because a large proportion of the economy will depend for decades to come on attracting visitors to the wild beauty of of this part of British Columbia. That means, as much as it can within municipal powers, the new council must strengthen environmental protection in Kitimat.
Back in the 50s, Kitimat was planned for a future, a future that didn’t exactly work out when the price of aluminum slumped in the early 60s. Now we’re facing a slump in energy prices, so those plans will change. The plan B must include, as much as possible, creating a mainstay base that will smooth out the boom and bust of the commodities cycle.
The motto on the Kitimat snowflake logo is “A marvel of nature and industry.” The new council should make sure that motto is applied during the coming years.