Special report: Clio Bay cleanup: Controversial, complicated and costly

Ward Cove, just eight kilometres west of Ketchikan, Alaska, was so polluted by effluent from pulp and saw mills and a fish plant, and filled with 16,000 sunken lots that it qualified for a U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Superfund cleanup.
The Ward Cove project is now considered a benchmark for cleaning up similar bays. Alaska officials emphasized to Northwest Coast Energy News, that while Ward Cove does provide guidelines for capping and dredging logs, they were not aware of any project where logs were capped that did not have other forms of contamination.
If you take a look at satellite images of Clio Bay, BC and Ward Cove side by side you immediately you see the similarities and differences between the two bodies of water. (Note due to parameters of Google Earth, images are slightly different scales)


Both Clio Bay and Ward Cove are 1.6 kilometres long, somewhat elbow shaped, off a main channel and surrounded by mountains.Ward Cove is 0.8 kilometres wide. Clio Bay is about 0.5 kilmetres wide, 0.8 at its widest point. Both have steep slopes from the mountains. Ward Cove is 61 metres deep at the mouth of the cove, descreasing toward the head. Clio Bay is deeper, 182 metres at the mouth, 90 metres in the centre and between 20 metres and 9 metres at the head.
Both Clio Bay and Ward Cove are subject to tidal circulation. Both Clio Bay and Ward Cove are also influenced by fresh water. Ward Cove is fed by Ward Creek, a smaller Walsh Creek and runoff precipitation the enters the cover from the steep mountain slopes. Clio Bay is fed by one creek, a number of small streams and mountain slope runoff, especially during the spring melt.
Haisla Chief Counsellor Ellis Ross estimates there are between 10,000 and 20,000 sunken logs in Clio Bay. The official summary from the United States Environmental Protection Agency said there were 16,000 sunken logs in Ward Cove.
The major difference with Ward Cove is that it was the site of major industrial development including a pulp mill, a sawmill and a fish plant. That meant the level of pollutants in Ward Cove were much higher than in Clio Bay, which has never been used for an industrial plant. It was the pollutants in Ward Cove, mainly ammonia, hydrogen sulfide, and 4-methylphenol combined with the thousands of sunken logs that made the cove a target cleanup and the associated studies.
A fish plant, Wards Cove Packing opened in 1912 and ceased operations in 2002. The Ketchikan Paper Company mill began operating in 1954 and closed in 1997. Prior to 1971, with the rise of the enviromental movement no permits were required by KPC for discharging effluent into the cove. After that the US Environmental Protection Agency issued a discharge permit and monitored effluent. Throughout the time the KPC mill was operating, the EPA says, “high volumes of log storage (approximately 7 billion board feet) caused accumulation of bark waste and sunken logs at the bottom of the cove.” Gateway Forest Products, a sawmill and veneer plant, continued to store logs in Wards Cove until 2002.
A 2009 monitoring report, conducted by the US Army Corps of Engineers after the cleanup for the EPA noted:
An ecological risk assessment was also conducted using a food-web assessment to estimate risks of bioaccumulative chemicals to representative birds and mammals at the top of the Ward Cove food web. The chemicals evaluated were arsenic, cadmium, mercury, zinc, chlorinated dioxins/furans, and PAHs. The results of this assessment indicated that there are no unacceptable risks to higher trophic level organisms in Ward Cove.
A human health risk assessment was conducted to identify potential risks posed by chemicals detected in sediments or seafood (e.g., fish, shellfish). Ingestion of seafood that may contain chemicals bioaccumulated from the sediments was identified as the only complete exposure pathway for humans. The chemicals that were evaluated included: arsenic, cadmium, mercury, zinc, phenol, 4-methylphenol, chlorinated dioxins/furans, and PAHs. Results concluded that sediments in Ward Cove do not pose an unacceptable risk to human health.
A 2007 report on the Wards Cove remediation from the Alaska Department of Environmental Conservation, noted:
The continuing residues impairment in Ward Cove is caused by the historical accumulation of wood waste on the bottom of the cove. The waste includes an estimated 16,000 sunken logs over at least 75 percent of the bottom and decomposing pulp, wood, and bark waste in sediments in thicknesses up to 10 feet over at least 50 percent of the bottom. Wood waste residues can displace and smother organisms, alter habitat, release leachates, create anoxic conditions, and produce toxic substances, all of which may adversely affect organisms that live both on top of sediments and within sediments.
That is a similar problem to Clio Bay.
The report notes that problems with oxygen increase with depth, noting:
The dissolved oxygen impairment was due largely to the fish-processing waste discharge from the seafood processing facility until 2002, and it was limited to the summer months in deeper waters of the cove (below the picnocline, or stratification layer, approximately 10 meters deep). With that discharge removed, limited monitoring in August and September 2003 indicated that dissolved oxygen impairment might remain near the bottom in waters at depths of 30 meters and greater at certain times and locations due to low natural levels of dissolved oxygen and the continuing decomposition of wood waste. Above 30 meters depth, the waters of the cove appeared to meet the [Alaska state] standard for dissolved oxygen. However, there may be limited capacity for waters at 30 meters and deeper to receive additional loading of oxygen-demanding materials and still meet the standard in summer months.
That should mean that the worries about oxygen depletion at Clio Bay are justified due to Clio’s greater depth.
Studies of the biology of Ward Cove began in 1951, with more in the 1960s and one in 1974. In 1995, Ketchikan Paper Company signed a consent decree with the EPA that called for remediation of Ward Cove, In 2000, KPC and Gateway Forest Products signed a second consent decree with the EPA. Those agreements called on the companies to dredge sediments to improve navigation, remove logs and other debris from the dredging areas and “placing a thin-layer cap of 15-30 cm (six to 12 inches) of sand over about 11 hectares (27 acres) of sunken logs.”
The major studies of Ward Cove began in 1995 after first consent decree. The remediation did not take place until the initial studies were complete in 1999, with dredging and capping taking place from November 2000 to March 2001.
The EPA positioned 13 water quality monitoring stations which operated from 1997 to 2002, to measure salinity, temperature and disolved oxygen, nine inside Ward Cove and four outside the cove in Tongass Narrows. Those studies showed that levels of dissolved oxygen in the cove varied by season, depth and location. Many species from salmon to mobile bottom dwellers like crabs were often able to detect and avoid low oxygen areas.
The plan
The EPA and the companies involved planned the remediation so that it included both dredging, capping logs and sediment and leaving some areas where nature would take its course.
The reports say that complete dredging, removal and disposal of the contamination would have cost $200 million, The total actual cost of the Ward Cove Remediation Project, beginning with development of the Remedial Design Work Plan, was estimated to have cost $3,964,000 (in 2000 US dollars).
The EPA says cost for the capping component of the project “including preliminary field investigations and reporting, design and plans development, post construction engineering, procurement, construction management, project management, mobilizationm demobilization, engineering/QC and science support, surveys, and capping items” was $2,563,506. Based on the volume of capping material placed, the unit cost of log capping for the Ward Cove Remediation Project was $110 per cubic yard.

The plan called for dredging about 17,050 cubic yards in the area near the cove’s main dock and the dredging of 3,500 yards metres nearby to improved navigation. Before the dredging, 680 tonnes of sunken logs had to be removed. After dredging, a “thin-layer cap of clean, sandy material” was placed in dredged areas unless native sediments or bedrock was reached during dredging.
In other areas, most covered in sunken logs, the plan called for placement of a thin-layer cap (approximately 6- to 12-inches) of clean, sandy material, with the possibility of “mounding” dropping mounds of sand on specific areas. The 2009 report says the area of sand deposits actually increased “due to the fact that thin layer placement was found to be successful over a broader area, and it was not necessary to construct mounding.”
The plan called for natural recovery in areas where neither capping nor mounding was practicable and so about 50 acres was left alone. (DFO says it plans to leave some parts of Clio Bay uncapped as “reference areas.”)
Slope and sand
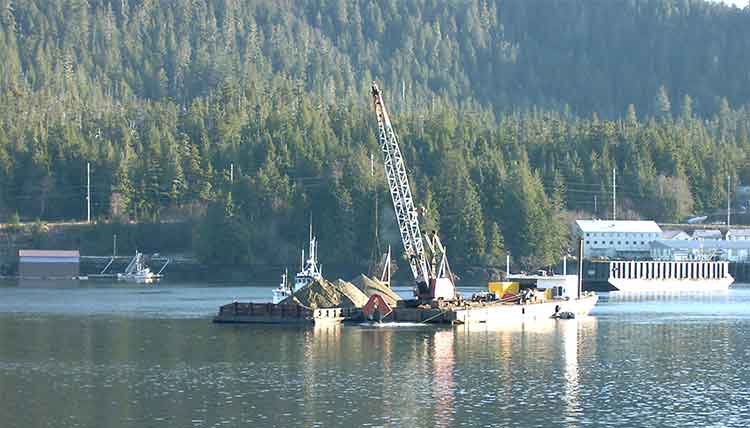

Two studies were carried out as part of the remediation at Ward Cove that do not appear to be contemplated at Clio Bay. The first looked at the “ability of the organic material to support the weight of 15 to 30 centimetres of sand.” Standard engineering equations used at other fill and capping sites were used as part of that study. A second study was carried out to determine the “minimum safety for a given slope,” which given the steep mountains that line Clio Bay, are likely to be factor in the deposit of marine clay. That study determined “For a silty fine sand and a factor of safety of 1.5, the maximum slope would be approximately 40 per cent.”
Those studies led to the conclusion that for the Ward Cove remediation project, the material to be placed on the fine organic sediment could not be gravel and course sand.”
That’s because the larger gravel and course sand “would tend to sink into the sediment and would not provide quality benethic (seabottom) habitat.”
The project decided to use “fine to medium sand with minimal fines.” It also concluded “Because of the very soft existing sediments and steep slopes at Ward Cove, the … material must be released slowly so that the settling velocity is low and bed impact minimized.”
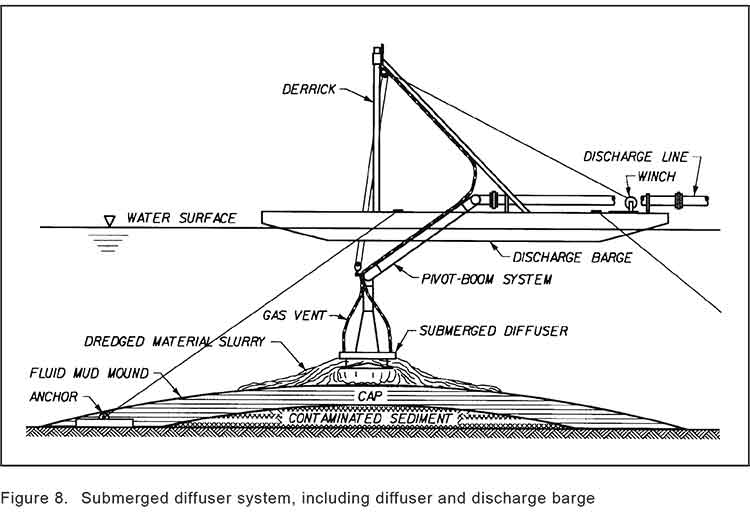
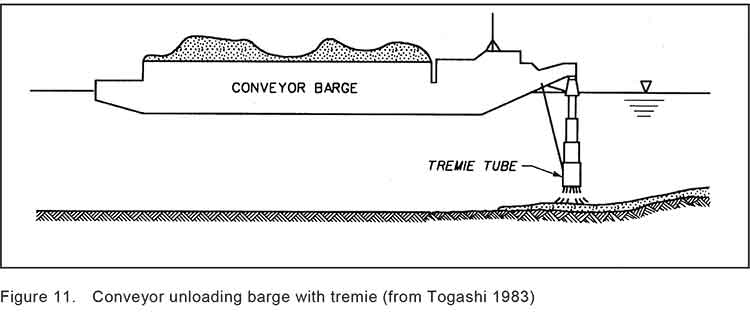
That meant that the EPA had look for a source of quality sand that met their criterion. The sand was found at Construction Aggregates in Sechelt, BC, loaded on 10,000 tonne deck barges, tugged up the coast, unloaded onto land using a conveyor and stockpiled while more tests were done to determine how to deposit the sand on the sunken logs.

Sand was placed on a smaller barge and taken to the deposit site. Initial tests were done with a mechanical dredge equipped with a clamshell bucket. The operator deposited the sand using “swaths” released from the bucket. To make it work properly, the bucket, as supplied by a manufacturer had to be modified by welding baffle plates to the bucket and lengthening the chains to insure consistent deposition of the sand. Two computers with special software called WINOPS, designed for dredging operations “provided the operator and deck engineer the precise locations of the derrick barge position” in order to ensure precise deposition of the sand. WINOPS dredge positioning and guidance software. The WINOPS system made use of three differential global positioning receivers. One GPS receiver was located at the top of the derrick and provided the center positioning of the dredge bucket. Two fixed receivers, one near the starboard center spud and one near the center aft, provided the barge position and heading.
Although using marine clay is likely to produce different engineering challenges at Clio Bay, it is not currently clear that the project has contemplated the level of precision that was used at Ward Cove.
While KM LNG must find a way to dispose of the marine clay from the Bish Cove excavation site, there is a silver lining for the Haisla Nation’s aim of restoring both Clio Bay and the other 50 sites in their traditional territory, since the Kitimat Sand Hill would likely be a ready resource for any future projects.
Monitoring
The EPA considered the project finished in September 2001, and long term monitoring began, with major updates every five years in 2004 and 2009.
An EPA report on the 2004 review showed that the three sand-capped areas and one shallow natural recovery area (not sand-capped) had achieved biological recovery; three other natural recovery areas tested had not achieved biological recovery but were making significant progress.
The 2004 studies showed that benethic (sea bottom) communities in uncapped areas showed “species commonly found in areas where organic enrichment is low or declining.” adding “In three other natural recovery areas, benthic communities have not progressed as far toward recovery but are making significant progress.
By the time of the 2009 update, most of the old industrial infrastucture on land at Ward Cove had been demolished and the land area was slated for redevelopment. Many of the companies that had been there had either gone out of business or had declared bankruptcy and the land was taken over by the Ketchikan Gateway Borough,mostly through foreclosure.
The EPA declared that “The remedial action construction is complete, and the remedial action is an operating or ongoing remedial action.”
The 2009 report says that the project was successful in eliminating sediment toxicity. The area was then quickly being recolonized by a diverse bottom dwelling macroinvertebrate species and those species were spreading beyond the specific study areas, so recovery of Ward Cove is expected to continue.
However the 2004 report went on to say that “the achievement of stable benthic biological communities with balanced species composition in more than 75 percent of the area with documented coverage by wood residues on the bottom of Ward Cove” would happen within 40 years from the 2004 study.
The next review of Ward Cove is slated for August 2015.

[rps-include post=5057]