
The possible effects of a bitumen spill on Pacific waters were not considered in the oil response preparedness report released last week by the Harper government, the background data study reveals.
The consulting firm that did the study for Transport Canada, Genivar Inc, had no reliable data on the effect of a bitumen tanker disaster—because, so far, there has been no major ocean disaster involving diluted bitumen.
Instead, Genivar, based its findings on potential hazards and response on existing data on crude oil spills.
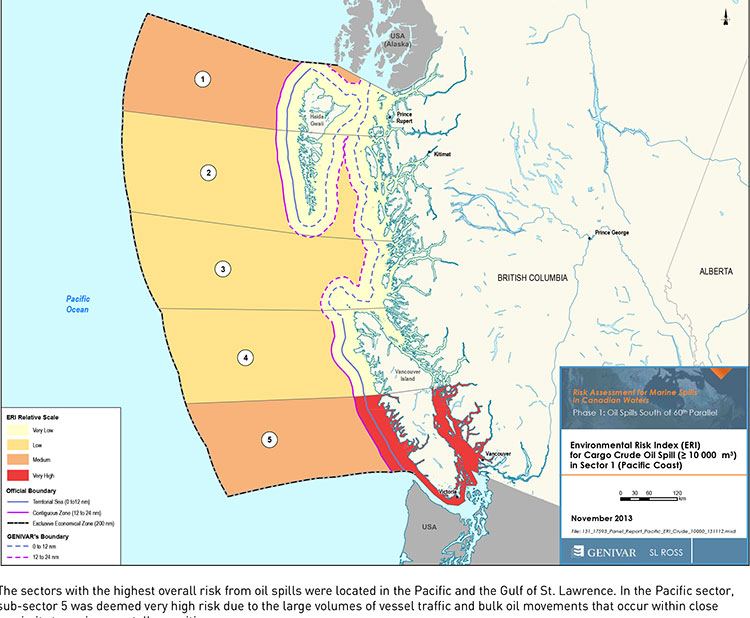
The Genivar study, however, does warn, that if the Enbridge Northern Gateway project does go ahead, the spill risk from diluted bitumen carrying tankers in Douglas Channel and along the north Pacific coast will jump from “low” or “medium” to “very high.” If the twinning of the Kinder Morgan pipeline goes ahead, then the risk in Vancouver also jumps to “very high.”
The question of how bitumen might behave in the cold and choppy waters of the North Pacific was hotly debated during the Northern Gateway Joint Review hearings earlier this year. Enbridge Northern Gateway based its position on laboratory studies, studies that were challenged by environmental and First Nations intervenors, pointing both to the unknowns of the ocean environment and the continuing problems Enbridge has in cleaning up the spill in the Kalamazoo River in Michigan.
Genivar tried to base its report to Transport Canada on existing data on oil spills and related hazards. What it found instead is that that there are often gaping holes in the reporting and monitoring of oil spills world wide, especially small and medium sized spills.
Lack of data also meant that Genivar had little to go on when it calculated the effect on an oil spill on key areas of interest to northwest British Columbia, the recreational fishery and tourism.
Genivar, however, did uncover disturbing data about the long term effects of oil spills, studies that show even minute amounts of remaining oil can still disrupt the marine environment 40 years after an event.
The Genivar report, Risk Assessment for Marine Spills in Canadian Waters Phase 1: Oil Spills South of 60th Parallel, was completed in November, then passed on to the “expert panel” that released their own report: A Review of Canada’s Ship-source Oil Spill Preparedness and Response Regime — Setting the Course for the Future. That second report was based not only on the data provided by Genivar but on the expertise of three panel members, their visits to some locations and input from government, industry, First Nations and municipalities.
Transport Minister Lisa Raitt and Natural Resources Minister Joe Oliver unveiled the second report at a glitzy media event in Vancouver on Tuesday, December 10. At that time the expert panel report was released to the media along with an abstract of the data.
The actual data report was not posted; it had to be requested through the Transport Canada website, which is how Northwest Coast Energy News obtained the background study.
High risk for Kitimat

The expert panel found “a very high risk” of oil spills in two areas of the Pacific Coast, in the north around the ports of Kitimat and Prince Rupert and in the heavy ocean traffic area of southern British Columbia, especially Port Metro Vancouver and into Washington State.
The expert panel made 45 recommendations that covered a wide range of issues including eliminating the present $161-million liability limit for each spill and replacing it with unlimited liability for polluters, annual spill training involving the Canadian Coast Guard, Environment Canada, provincial and local authorities and the private sector, increased and improved annual spill training exercises, basing risk assessment on local geography and conditions and faster emergency responses to spills.
The expert panel calls for greatly increased research on the ocean environment at a time that Harper government has been gutting environmental research across Canada, while spinning that its policies are “science based.”
The science and technology around both the movement of oil and spill response has advanced significantly over the past several decades. We feel that while some aspects of the Regime have kept pace with these developments, in some areas, Canada has fallen behind world-leading countries like Norway and France. This can be attributed to a general lack of investment in research and development as well as the lack of coordination between industry and government over research priorities.
The Government of Canada should work closely with industry to establish a national research and development program for oil spill preparedness and response. The program should be co-funded by industry and the Government, and the research priorities should be set through a collaborative process that involves academia, where possible. Like the Regime itself, we view this program as a partnership between industry and government.
We envision that this program would also seek to leverage the work being done internationally on oil spill preparedness and response. The program should seek to establish partnerships with other world-leading countries in order to stay current on international advances and new technologies.
The expert panel, however, does not say how the federal government is expected to pay for meeting BC Premier Christy Clark’s condition for a “world class” spill prevention and response system at a time that Finance Minister Jim Flaherty is determined to balance the budget and the Harper government is continuing to cut back government services.
Bitumen excluded
On bitumen, the Genivar data study says:
Modified bitumen products represent the majority of the “crude carried as cargo” in
Pacific sub-sector 5. They are not modelled as a separate category in this spill behaviour analysis but are represented as “persistent crude”.Changes in spill behaviour depend to some extent on the environmental conditions at the time of the spill, as described in greater detail below. However, over the range of wind and sea conditions typically experienced in the Canadian marine environment, changes in oil properties are not overly sensitive to variations in climatic values, so a single set of wind and sea conditions will be used in the analysis.
The idea that “changes in oil properties” not being sensitive to variations in climate was also frequently challenged before the Joint Review Panel.
On the increase in traffic volume if the Northern Gateway project goes ahead, the Genivar report says.
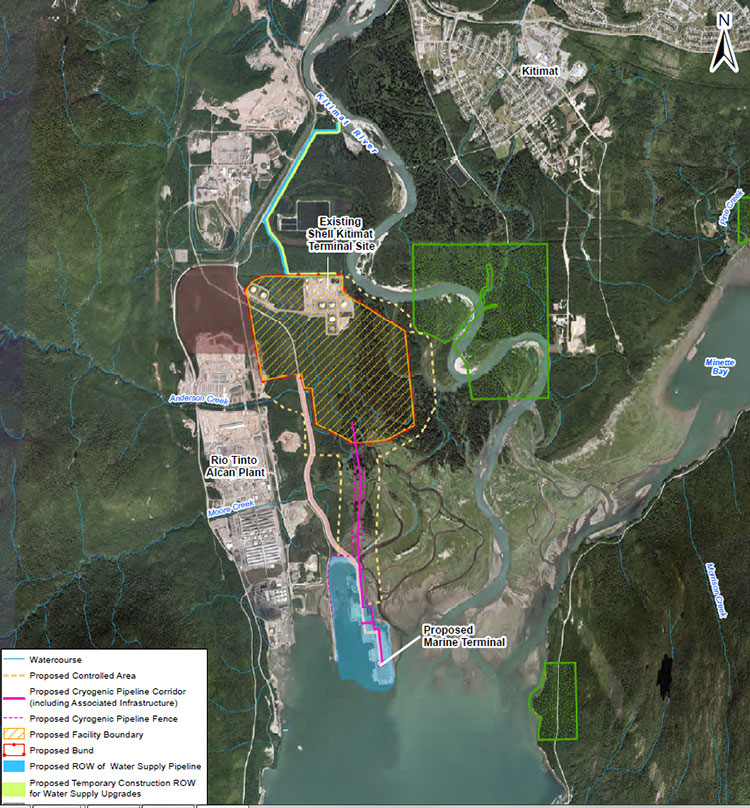
Enbridge Inc. has proposed to construct a marine terminal at Kitimat, B.C. and a dual pipeline from the terminal to oil sands production in northern Alberta. The terminal would handle up to 193,000 barrels/day of imported diluents (i.e., low-gravity condensate) that would be piped to Alberta and used to dilute bitumen to enhance its flow properties. The diluted bitumen would then be piped to Kitimat at rates up to 525,000 barrels/day that would be shipped by tanker to export to markets in Asia and California.
At full capacity, the import of diluent and export of diluted bitumen would total up to 35 Mt/year. This amount is comparable to the currently-shipped volume in the Pacific sector related to volumes being exported from Vancouver and related to volumes being exported from the Alaskan to Washington State trade.
It goes on to say that the current tanker traffic on the north Pacific coast “has negligible risk in the near shore and intermediate zones, but significant potential spill frequency in the deep-sea zone related to the Alaskan trade.” Similarly, according to Genivar the environmental risk in the region “currently ranges from ‘medium’ to “very low” from near shore to deep-sea zones, respectively…. mainly driven by a combination of physical and biological features.”
The increase in traffic from Northern Gateway would likely increase the environmental risks. The the near shore risk from would jump from “very low” to “very high.” For the largest spill category, deep-sea risk would likely increase from “low” to “medium.”
No data on recreational or traditional First Nations fishery
To study the effect on an oil spill on the fishery, Genivar used data from the Department of Fisheries and Oceans as the provinces to gauge “the port value of commercial fishing and the value of the fish, shellfish and aquaculture” in each zone it studied and then compared it to the the national averages for commercial fishery. Those figures included any commercial fishery by First Nations.
But Genivar noted, there is no reliable data on either the recreational fishery or the First Nations traditional, food, social and ceremonial fishery, saying:
It is important to highlight that this indicator does not consider recreational or traditional fishing. The importance of this industry is notable and an oil spill could damage the recreational fishing stock as well. However, the absence of comparable data and the fact that this study is restricted to federal and international data, and some provincial data from Quebec and Ontario for commercial fisheries, limits the ability to include recreational fishing… Nevertheless, as an absolute index, it will provide an overall vulnerability in the event of an oil spill.
The ongoing impact of cutbacks at Fisheries and Oceans has had a continuing impact on the northwest, especially in the controversial halibut recreational fishery, where DFO has admitted that it is basically guessing the size of each year’s recreational halibut catch.
Tourism
Genivar also notes that lack of reliable data on the effect on a oil spill on tourism. The consultants go so far as to say one of the indicators they will use to measure the effect of any oil spill on tourism would come from “data extracted from the 2011 National Household Survey at the census division level and the accommodation and food services data will be used.”
The “National Household Survey” is also known as the long form census and it is the National Household Survey that the Harper government made voluntary rather mandatory, decreasing the reliability of the data. Global News recently analyzed those who had contributed to the survey and found that it poor people, the very rich and people in low population areas were least likely to fill out the voluntary census—which means the data for northwest BC is likely highly unreliable from the 2011 survey even though “The census divisions in coastal regions will be selected for each of the sub-sectors. This method will express the economic vulnerability of each sub-sector to a potential collapse in tourism following a spill.”
Despite the importance of cruise ship traffic on the west coast, Genivar notes, “In Canada, data for passenger vessels were unavailable.”
It also notes that “this study does not specifically take into account national parks and other landmarks, since their influence on tourism is indirectly included in the tourism employment
intensity index” so that Genivar could create what it calls the Human-Use Resource Index (HRI), even though that index appears to be based on incomplete data.