A pile of slash at a quarry site for the Pacific Trail Pipeline near the Little Wedeene River. (Robin Rowland)
Category: environment
Chevron applies to update permit to discharge storm water to Bish Cove and Douglas Channel
 Chevron has applied to the BC Ministry of the Environment for a permit to discharge storm water from the liquified natural gas construction site at Bish Cove and along the shore of Douglas Channel.
Chevron has applied to the BC Ministry of the Environment for a permit to discharge storm water from the liquified natural gas construction site at Bish Cove and along the shore of Douglas Channel.
The construction site is currently operating on a Waste Water Discharge Approval that expires on Oct. 31.
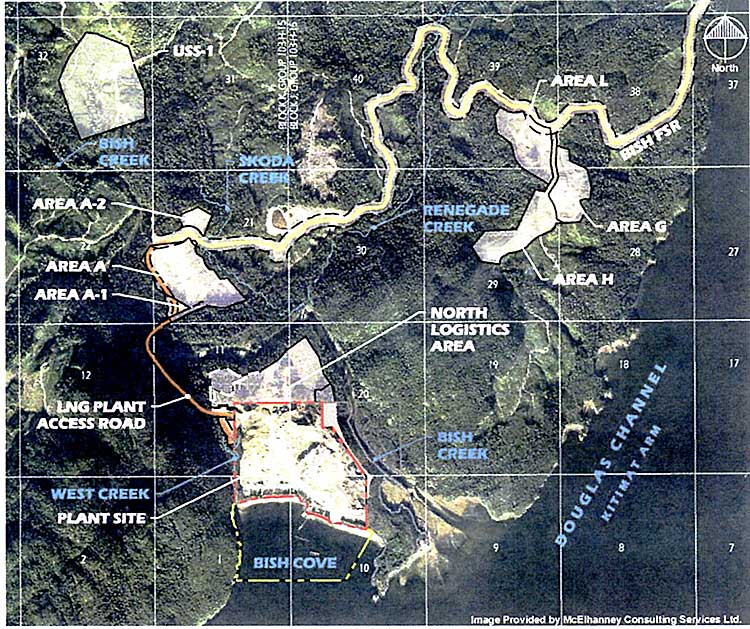
The application sets new objectives that “will be protective of the receiving environment.” Various construction areas will discharge storm water (likely due to clearing of the bush cover) from areas at Bish Cove itself and the Bish Creek watershed “including the following watercourses and associated tributaries: Bish Creek, West Creek, Skoda Creek and Renegade Creek.”
The application says that the “maximum rate of effluent discharged from this project and support areas will vary based upon seasons and weather.” Areas and amounts of water may change as the construction proceeds. “The characteristics of the stormwater runoff will be water produced from precipitation, including snowmelt that contains suspended sediment from earthworks and construction.” The application adds, “The types of treatment to be applied to the discharges are: erosion prevention and sedimentation control management practices and devices which may include sedimentation ponds, oil water separators, pH adjustment, flocculent addition and sand filtration.
The public and concerned individuals or groups can provide “relevant information” to the Regional Manager, Environmental Protection, #325-1011 Fourth Ave, Prince George BC V2L 3H9 until September 20, 2014 or call Marc Douglas at 844-800-0900.
Ocean acidification growing risk to west coast fishery, including crab and salmon, US studies show
The United States says acidification of the oceans means there is an already growing risk to the northwest coast fishery, including crab and salmon, according to studies released by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
As more carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere and absorbed by the oceans, the water is becoming more acidic and that affects many species, especially shellfish, dissolving the shells.
A NOAA study released today of environmental and economic risks to the Alaska fishery says:
Many of Alaska’s nutritionally and economically valuable marine fisheries are located in waters that are already experiencing ocean acidification, and will see more in the near future…. Communities in southeast and southwest Alaska face the highest risk from ocean acidification because they rely heavily on fisheries that are expected to be most affected by ocean acidification…
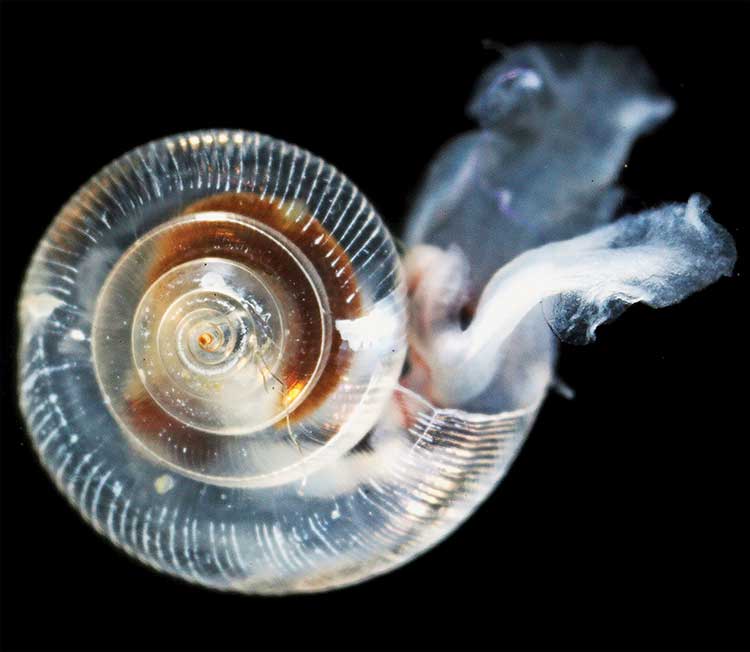
An earlier NOAA study, released in April, identified a long term threat to the salmon fishery as small ocean snails called pteropods which are a prime food source for pink salmon are already being affected by the acidification of the ocean.

NOAA says:
The term “ocean acidification” describes the process of ocean water becoming more acidic as a result of absorbing nearly a third of the carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere from human sources. This change in ocean chemistry is affecting marine life, particularly the ability of shellfish, corals and small creatures in the early stages of the food chain to build skeletons or shells.
Today’s NOAA study is the first published research by the Synthesis of Arctic Research (SOAR) program, which is supported by an US inter-agency agreement between NOAA’s Office of Oceanic and Atmospheric Research and the Bureau of Ocean Energy Management (BOEM) Alaska Region.
Canada’s Department of Fisheries and Oceans says it has ongoing studies on oceanic acidification including the role of petropods in the lifecycle of the salmon.
Des Nobles, President of Local #37 Fish [UFAWU-UNIFOR] told Northwest Coast Energy News that the fisheries union and other fisheries groups in Prince Rupert have asked both the Canadian federal and the BC provincial governments for action on ocean acidification. Nobles says so far those requests have been ignored,
Threat to crabs
The studies show that red king crab and tanner crab grow more slowly and don’t survive as well in more acidic waters. Alaska’s coastal waters are particularly vulnerable to ocean acidification because of cold water that can absorb more carbon dioxide and unique ocean circulation patterns which bring naturally acidic deep ocean waters to the surface.
“We went beyond the traditional approach of looking at dollars lost or species impacted; we know these fisheries are lifelines for native communities and what we’ve learned will help them adapt to a changing ocean environment,” said Jeremy Mathis, Ph.D., co-lead author of the study, an oceanographer at NOAA’s Pacific Marine Environmental Laboratory in Seattle, and the director of the University of Alaska Fairbanks School of Fisheries and Ocean Sciences Ocean Acidification Research Center.
As for Dungeness crab, Sarah Cooley, a co-author of the Alaska study, who was with the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution at the time, told Northwest Coast Energy News, “The studies have not been done for Dungeness crab that have been done for king and tanner crab, that’s something we’re keenly aware of. There’s a big knowledge gap at this point.” She says NOAA may soon be looking at pilot study on Dungeness crab.
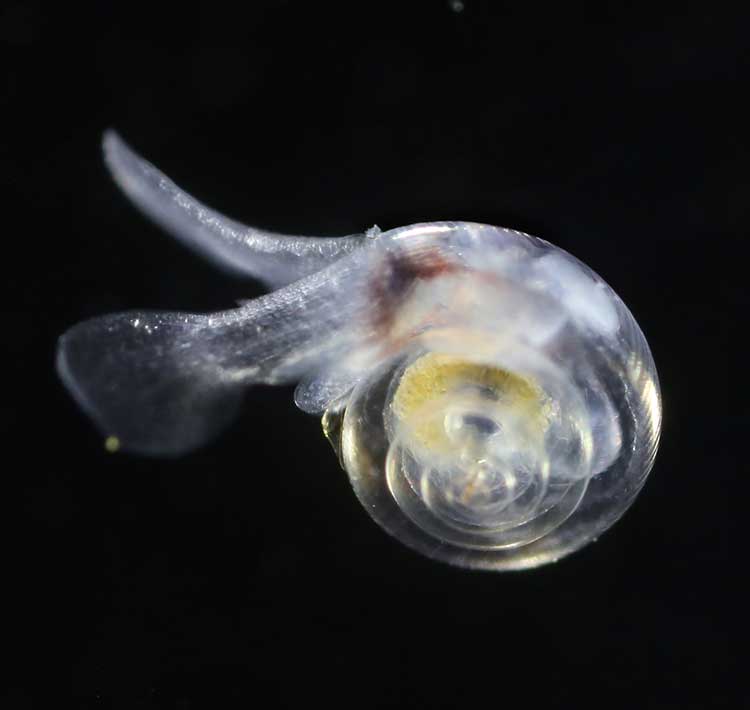

Risk to Salmon, Mackerel and Herring
In a 2011-2013 survey, a NOAA-led research team found the first evidence: “that acidity of continental shelf waters off the West Coast is dissolving the shells of tiny free-swimming marine snails, called pteropods, which provide food for pink salmon, mackerel and herring.”
The survey estimated that the percentage of pteropods along the west coast with dissolving shells due to ocean acidification had “doubled in the near shore habitat since the pre-industrial era and is on track to triple by 2050 when coastal waters become 70 percent more corrosive than in the pre-industrial era due to human-caused ocean acidification.”
That study documented the movement of corrosive waters onto the continental shelf from April to September during the upwelling season, when winds bring water rich in carbon dioxide up from depths of about 120 to 180 metres to the surface and onto the continental shelf.
“We haven’t done the extensive amount of studies yet on the young salmon fry,” Cooley said. “I would love to see those studies done. I think there is a real need for that information. Salmon are just so so important for the entire Pacific Northwest and up to Alaska.”
In Prince Rupert, Barb Faggetter, an independent oceanographer whose company Ocean Ecology has consulted for the fisherman’s union and NGOs, who was not part of the study, spoke generally about the threat of acidification to the region.
She is currently studying the impact of the proposed Liquified Natural Gas terminals that could be built at Prince Rupert near the Skeena River estuary. Faggetter said that acidification could affect the species eaten by juvenile salmon. “As young juveniles they eat a lot of zooplankton including crustaceans and shell fish larvae.”
She added, “Any of the shell fish in the fishery, including probably things like sea urchins are all organisms that are susceptible to ocean acidification because of the loss of their capacity to actually incorporate calcium carbonate into their shells.”
Faggetter said her studies have concentrated on potential habitat loss near Prince Rupert as a result of dredging and other activities for liquified natural gas development, She adds that ocean acidification “has been a consideration that climate change will further worsen any potential damage that we’re currently looking at.”
Her studies of the Skeena estuary are concentrating on “rating” areas based on the food supply available to juvenile salmon, as well as predation and what habitat is available and the quality of that habitat to identify areas that “are most important for the juvenile salmon coming out of the Skeena River estuary and which are less important.”
She said that climate change and ocean acidification could impact the Skeena estuary and “probably reduce some of the environments that are currently good because they have a good food supply. If ocean acidification reduces that food supply that will no longer be good habitat for them” [juvenile salmon].
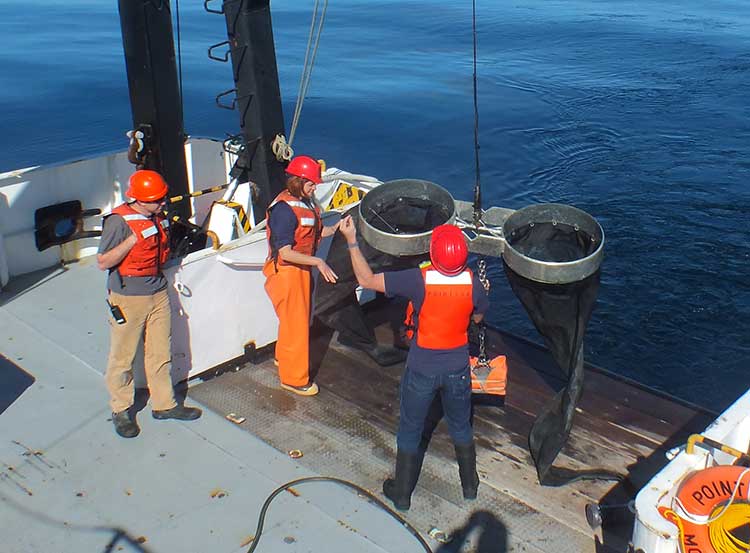

The August 2011 NOAA survey of the pteropods was done at sea using “bongo nets” to retrieve the small snails at depths up to 200 metres. The research drew upon a West Coast survey by the NOAA Ocean Acidification Program in that was conducted on board the R/V Wecoma, owned by the National Science Foundation and operated by Oregon State University.
The DFO study, according to the agency website is “being examined in the context of model predictions.”
Nina Bednarsek, Ph.D., of NOAA’s Pacific Marine Environmental Laboratory in Seattle, the lead author of the April pteropod paper said, “Our findings are the first evidence that a large fraction of the West Coast pteropod population is being affected by ocean acidification.
“Dissolving coastal pteropod shells point to the need to study how acidification may be affecting the larger marine ecosystem. These near shore waters provide essential habitat to a great diversity of marine species, including many economically important fish that support coastal economies and provide us with food.”
Ecology and economy
Today’s study on the effects of acidification on the Alaska fishery study examined the potential effects on a state where the fishing industry supports over 100,000 jobs and generates more than $5 billion in annual revenue. Fishery-related tourism also brings in $300 million annually to the state.
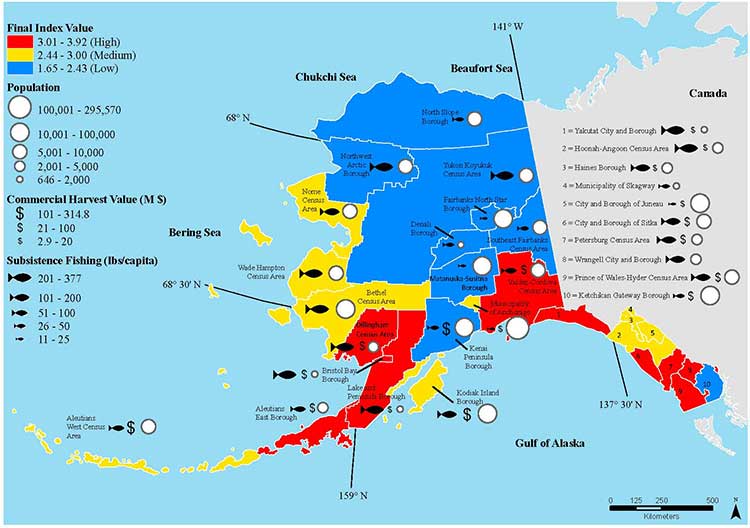
The study also shows that approximately 120,000 people or roughly 17 percent of Alaskans rely on subsistence fisheries for most, if not all of their dietary protein. The Alaska subsistence fishery is open to all residents of the state who need it, although a majority of those who participate in the subsistence fishery are Alaska’s First Nations. In that way it is somewhat parallel to Canada’s Food, Ceremonial and Social program for First Nations.
“Ocean acidification is not just an ecological problem—it’s an economic problem,” said Steve Colt, Ph.D., co-author of the study and an economist at the University of Alaska Anchorage. “The people of coastal Alaska, who have always looked to the sea for sustenance and prosperity, will be most affected. But all Alaskans need to understand how and where ocean acidification threatens our marine resources so that we can work together to address the challenges and maintain healthy and productive coastal communities.”
The Alaska study recommends that residents and stakeholders in vulnerable regions prepare for environmental challenge and develop response strategies that incorporate community values and needs.
“This research allows planners to think creatively about ways to help coastal communities withstand environmental change,” said Cooley, who is now science outreach manager at Ocean Conservancy, in Washington, D.C. “Adaptations can be tailored to address specific social and environmental weak points that exist in a community.
“This is really the first time that we’ve been able to go under the hood and really look at the factors that make a particular community in a borough or census are less or more vulnerable from changing conditions resulting from acidification. It gives us a lot of power so that we don’t just look at environmental issues but also look at the social story behind that risk.”
As for the southern part of the Alaska panhandle nearest British Columbia, Cooley said, “What we found is that there is a high relative risk compared to some of the other areas of Alaska and that is because the communities there undertake a lot of subsistence fishing, There tend not be a whole lot of commercial harvests in the fisheries there but they are very very important from a subsistence stand point… And they’re tied to species that we expect to be on the front line of acidification, many of the clam species that are harvested in that area and some of the crab species.”
Long term effects
Libby Jewett, Director of the NOAA Ocean Acidification Program and author of the pteropod study said, “Acidification of our oceans may impact marine ecosystems in a way that threatens the sustainability of the marine resources we depend on.
“Research on the progression and impacts of ocean acidification is vital to understanding the consequences of our burning of fossil fuels.”
“Acidification is happening now,” Cooley said. “We have not yet observed major declines in Alaskan harvested species. In Washington and Oregon they have seen widespread oyster mortality from acidification.
“We don’t have the documentation for what’s happening in Alaska right now but there are a lot of studies staring up right now that will just keep an eye out for that sort of thing, Acidification is going to be continuing progressively over the next decades into the future indefinitely until we really curb carbon dioxide emissions. There’s enough momentum in the system that is going to keep acidification advancing for quite some time.
“What we need to be doing as we cut the carbon dioxide, we need to find ways to strength communities that depend on resources and this study allows us to think differently about that and too really look at how we can strengthen those communities.
Faggetter said. “It’s one more blow to an already complex situation here, My study has been working particularly on eel grass on Flora Bank (pdf) which is a very critical habitat, which is going to be impacted by these potential industrial developments and that impact will affect our juvenile salmon and our salmon fishery very dramatically, that could be further worsened by ocean acidification.”
She said that acidification could also be a long term threat to plans in Prince Rupert to establish a geoduck fishery (pronounced gooey-duck).
The popular large 15 to 20 centimetre clam is harvested in Washington State and southern BC, but so far hasn’t been subject to commercial fishing in the north.
NOAA said today’s study shows that by examining all the factors that contribute to risk, more opportunities can be found to prevent harm to human communities at a local level. Decision-makers can address socioeconomic factors that lower the ability of people and communities to adapt to environmental change, such as low incomes, poor nutrition, lack of educational attainment and lack of diverse employment opportunities.
NOAA’s Ocean Acidification Program and the state of Alaska are also developing tools to help industry adapt to increasing acidity.
The new NOAA study is the first published research by the Synthesis of Arctic Research (SOAR) program. which is supported by an inter-agency agreement between NOAA’s Office of Oceanic and Atmospheric Research and the Bureau of Ocean Energy Management (BOEM) Alaska Region.
The pteropod study was published in April in Proceedings of the Royal Society B. The ecological and economic study is published in Progress in Oceanography.
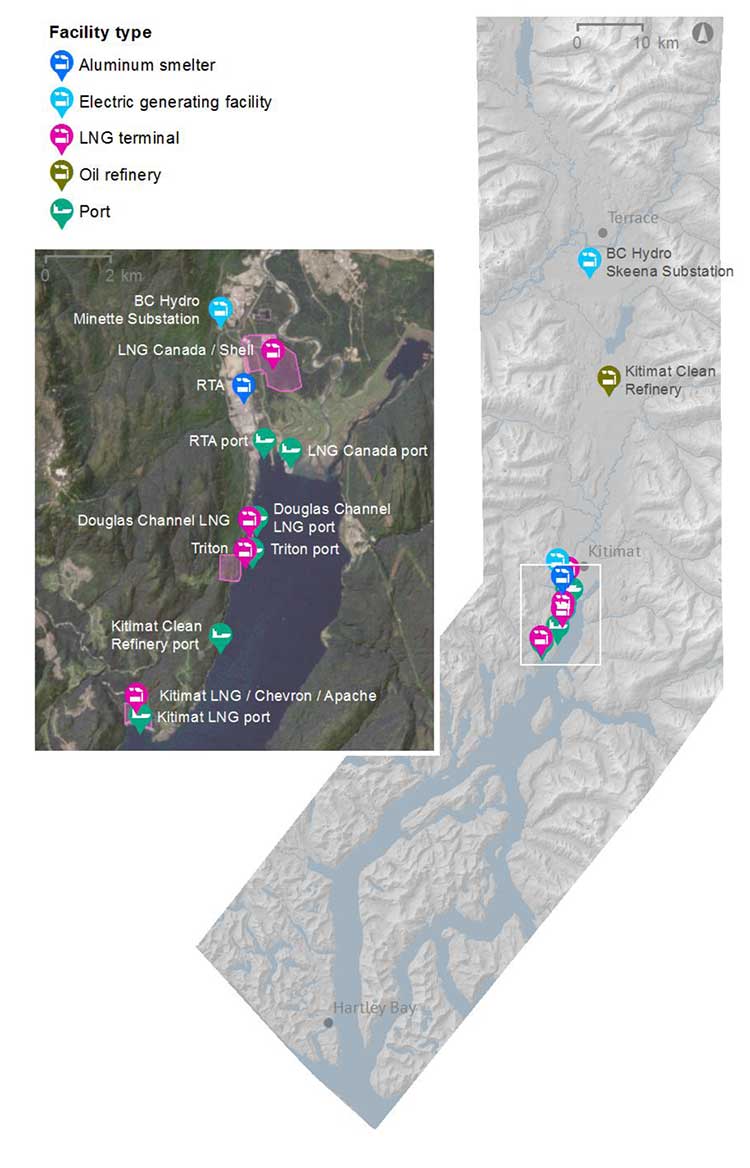
Kitimat air shed study raises more questions than it actually answers
The sudden release early Friday, July 18, by the British Columbia Ministry of the Environment about the Kitimat Valley air shed study brings more questions than the answers it provides; some questions are political, some technical.
The questions include
1. Why was the study suddenly released after the province said it was “privileged?”
2. Did the apparently rushed release mean that the study, as far as the public is concerned, is incomplete?
3. While most people in Kitimat believed that the study would be a wide ranging look at all parameters of industrial development in the valley, it was limited to just two factors, sulphur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide.
4. It appears that everyone involved were consulted prior to the release with one key execption, the District of Kitimat. Why?
5. The study appears to have changed in its criterion from the time of the request for proposal and the final release one issue—an oil export terminal, which went from “crude” in the request for proposal to refined in the final report.

While the study is spun has a showing that industrial development in the Kitimat Valley can proceed as long as the environment is properly managed, the gaps and the spin will likely bring doubt to the results. That means that a wider ranging and truly independent study of the air shed is needed so that both residents and industry can then make the proper decisions.
Ironically, a proper study may actually come from industry, rather than government since LNG Canada has said that a full air shed study will be part of its environmental assessment filing expected in the fall.
The air shed proposal
In October 2013, the Ministry of the Environment issues a “request for proposal” to “study potential cumulative effects to environment and human health from existing and proposed industrial facilities in the Kitimat airshed.” to be filed by March 31, 2014.
According to the government website,
The Province will fund a $650,000 scientific study to help inform regulatory and policy development for future industrial activity in the Kitimat area. The goal is to ensure the potential impacts from industrial air emissions are clearly understood prior to new projects being approved and in operation.
The Kitimat Airshed Impact Assessment Project will look at the cumulative effects of existing and proposed industrial air emissions in the airshed. These include emissions from: an existing aluminium smelter, three proposed LNG terminals, a proposed oil refinery, a crude-oil export facility, and gas-turbine-powered electrical generation facilities. The study will focus on sulphur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide emissions from these facilities.
The study will assess the impact of emissions through a number of scenarios, including their potential effects on water and soil, as well as on vegetation and human health from direct exposure.
With that news release, it appears that many people assumed that “cumulative effects of existing and proposed industrial air emissions in the air shed,” would include all possible scenarios and contaminants.
The report, when it was released on Friday, covered just the “focus” sulphur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide and no other factors in air quality.
Crude or refined oil export?
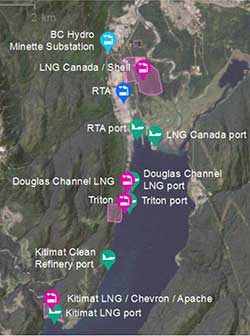 As Northwest Coast Energy News noted that the report, as released, doesn’t include any references to the Enbridge Northern Gateway project, even though Northern Gateway is a source of “proposed industrial air emissions in the air shed.” The request for proposal also mentions “a crude-oil export facility” but the report as issued concerns a marine terminal for Black’s refinery
As Northwest Coast Energy News noted that the report, as released, doesn’t include any references to the Enbridge Northern Gateway project, even though Northern Gateway is a source of “proposed industrial air emissions in the air shed.” The request for proposal also mentions “a crude-oil export facility” but the report as issued concerns a marine terminal for Black’s refinery
David Black’s Kitimat Clean website says
The products will be exported via a marine terminal on the Douglas Channel. Projected volumes include 320,000 barrels per day of diesel fuel, 110,000 barrels per day of gasoline and 60,000 barrels per day of jet fuel.
The map in the main report clearly shows that the study concerned the “Kitimat Clean Refinery Port” not a crude oil export facility—in other words likely Enbridge Northern Gateway.
Kitimat excluded
On October 21, 2013, District of Kitimat Council endorsed a motion by former Councillor Corinne Scott:
“The BC Government has recently announced a budget of $650,000 to study the cumulative effects on the air quality due to the proposed industrial development in the District of Kitimat. It would be beneficial to have a representative from the District of Kitimat as an active participant on the committee to provide input and feedback as the study progresses.”
At the time Chief Adminstrative Officer Ron Poole told council that the minister’s office had called and promised to “involve the District.”
At that meeting, Councillor Mary Murphy reported that member were “vocal” at the Union of BC Municpalities that it was essential that Kitimat be involved. Councillors suggested that the study be wide ranging and include emissions already in the area and residual emissions left over from the closed Eurocan and Methaex operations.
The provincial final air shed report makes no mention at all of the District of Kitimat, Eurocan or Methanex.
In April, 2014, after the March 31, reporting deadine, the District and Council had heard nothing from the province. So in April, District Council passed a motion asking for a report on the status of the study.
Crown Privilege
In June, the province refused to release the report to lawyers involved in a suit against the Environmental Assessment Board which is challenging Rio Tinto Alcans’ permit to increase sulphur dixoide emission in the valley. According to the Globe and Mail, Dennis Doyle, a lawyer with the Ministry of the Attorney General, in the RTA suit, wrote to the Environmental Law Centre in Victoria
In a follow-up letter dated June 12, Mr. Doyle said, “On the matter of the Kitimat Airshed Study I am instructed that this report was prepared to guide development of government policy on industrial development in the Kitimat area and to assist the executive council in its ongoing deliberations. It is not a report that was prepared for the Respondent and played no part of the decision-making process for the permit amendment which is now under appeal.”
In mid-July, the lawyers then asked the Environment Assessment Board to either turn over the air shed report or explain why it was covered by Crown Privilege.
The EAB told the province to respond to that question by July 18. Instead there was a hastily called news conference and the report was released. However, a close look at the report shows that it was likely rushed to meet the EAB deadine and was incomplete—rather surprising for a report that was supposed to be complete by March 31.
Rushed report
 What evidence is there that the report was rushed out by the Ministry of the Environment? The most compelling indication is that instead of a public-friendly Summary Report with an executive summary and clear conclusions, there was nothing more than a short Power Point presentation.
What evidence is there that the report was rushed out by the Ministry of the Environment? The most compelling indication is that instead of a public-friendly Summary Report with an executive summary and clear conclusions, there was nothing more than a short Power Point presentation.
Most people in Kitimat who follow the energy debate are familiar with the approach of combining a readable summary with technical data. It is most evident in the report of the Enbridge Northern Gateway Joint Review, which issued a relative short summary, Connections along with the long technical report, Considerations.
Let’s take as a prime example, the original report on the Kitimat airshed commissioned by Rio Tinto Alcan. In that case, ESSA Technologies Ltd of Vancouver, the company hired by the RTA Kitimat Modernization Project to study the effects of increased sulphur dioxide emissions in the Kitimat Valley, issued three documents, an easy to understand 37-page summary report, a much longer 456 page Technical Assessment Report and a third 332 page volume of appendices, technical data and tables.
It was the same company, ESSA Technologies, that was retained by the province to do the much larger study of the airshed. However, the only public-friendly information was the 16 page highly simplified Power Point presentation.
The ESSA summary report for RTA shows in plain language, the reasons for its conclusions that the increased sulphur dioxide from KMP on human health “is characterized as moderate, an acceptable impact, but in need of closer scrutiny with moderate monitoring.” That report also outlines the limitations and uncertainties of the study.
There was no similar plain language summary released for the overall provincial air shed study, even though it was produced by the same company and came to similar conclusions. To find any limitations or uncertainties in the provincial air shed study you have to do a computer search for those key words.
So it is apparent that intended audience for the report is not really those who live in Kitimat, where over the past five years there is wide knowledge that a summary release along with a technical report is considered a standard procedure.
Kitimat not consulted
At the Friday news conference, reporters asked Environment Minister Mary Polak several times about the delay in releasing the report, and then why it was suddenly released.
In answer to the initial question, Polak said, “We had always intended to release it.” She refused to comment on the claim of cabinet privilege, saying that was the responsibility of government lawyers at the Ministry of the Attorney General. She said that the government had received the March 31 report “by the end of April and “it went through quite a rigorous and thorough review by different agencies… we are satisfied now that the findings have been given the kind of rigorous overview and we’re pleased with what has resulted from that.”
Polak said the Haisla Nation were consulted before the commissioning of the report.
Asked again about who the BC government consulted during the review period, she replied, “There were a number of other groups involved in technical review, so not just Ministry of Environment, you’ll be aware of Northern Health authority, but Ministry of Natural Gas Development, Health Canada, Environment Canada and also specialist reviewers from the Province of Quebec, the University of Helsinki, UBC, also private consultants. Then we spent some time going over and having a technical review with Gitga’at and Coastal Coastal First Nations. So it was a matter of ensuring that we had done the very best review of the work before the occasion on which we released it.”
Which leaves one big question, why was the Province of Quebec and the University of Helsinki consulted and Kitimat, despite requests, was not?
Not in the report, not my department
The provincial government called for a report on the “cumulative effects of existing and proposed industrial air emissions” and noted it would focus “ focus on sulphur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide emissions from these facilities.” It is clear that the report did not go beyond the narrow focus on those two substances.
At the Vancouver news conference, a reporter asked Polak why green house gases were not included.
She replied, “That’s not what this study was intended to look at. This department deals with pollutants and pollution and protecting our environment from it, whereas GHG [green house gas] emissions are dealt with in our department around climate change and climate action. These particular substances have an immediate impact on human health and vegetative health and the receiving environment generally unlike GHGs which are a more global impacted and of course have an impact on climate change. This study only looked at those pollutants sulphur doixide and nitrogen dioxide
Then a second reporter asked here about particulate matter, to which Polak replied, “Coming from the Fraser Valley I am very aware of the impact of particulate matter. Any industrial development that we permit in British Columbia or receives an environmental assessment certificate, particulate matter and the release of particulate matter is one of the things that gets evaluated as we determine whether or not to grant those permits. Or to put stipulations on those permits in order to ensure a reduction or management of particulate matter. That’s where that’s dealt with and we have some pretty good understanding of how that operates. We also have some modelling from this study.
“The reason this study didn’t report on that because we hadn’t asked them to. We specifically wanted to get at the issue of sulphur disoxide and nitrogen dioxide but please do not take frm that because it’s not in the study, it doesn’t get looked at. It simply gets looked at in a different process. In this case it was the understanding of the Kitimat air shed with respect to sulphur dixoide and nitrogen dioxide that we needed to have a better answers and better information.”
In other words, despite what the original proposal said: “The goal is to ensure the potential impacts from industrial air emissions are clearly understood prior to new projects being approved and in operation,” the provincial government is content to wait until the permit phase to consider particulate matter, rather than include particulate matter in the long term planning for the air shed.
And for green house gases, the same attitude seems to apply, either it’s not her department or it will be dealt with sometime in the future.
What’s going on in the air shed?
Although the provincial government has been able to spin that the air shed report clears the way for more industrial development in the region, the report isn’t much help for long term planning for those both for and against industrial development in the valley.
First one has to wonder just how comprehensive was the study, even when it comes to sulphur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide?
The report for Rio Tinto Alcan for just one substance—sulphur dixoide—from one industry—aluminum smelting–led to a 456 page technical report with 332 pages of appendices.
The provincial technical report adds one more substance, nitrogen dioxide, and adds four LNG facilities, an oil refinery, different export terminals for those industries, and two hydro generating stations plus related shipping, including a passing mention of vehicular and train traffic. The new report is 363 pages, including the appendices. (It should be noted that the air shed report does reference some of the information in the RTA report)
The various studies for the Enbridge Northern Gateway, which often contained material on air emissions, included a much longer list of what in industry jargon are called CPOC “chemicals of potential concern,” including chemicals that might be released in trace amounts from the Northern Gateway terminal, but may be of more concern from LNG projects. Who knows unless those substances are studied?
As was required by the Joint Review Panel, Enbridge also studied potential problems from accidental release of air-borne contaminants from the Northern Gateway project. There is no mention of accidental release in the current air shed study.
Although the increase in truck traffic in Kitimat is clearly visible to people who live in the town, the air shed report also speculates that with LNG and a possible refinery, there will also be a significant increase in rail traffic coming into Kitimat, hauled, of course, by diesel locomotives, which the report says is “expected to be conservatively captured within the background concentration adjustment.”
Can the Valley “handle industrial expansion”
Stakeholders in the region from the District of Kitimat to the Gitga’at First Nation to various environmental groups asked for a comprehensive review of what is going to happen in the Kitimat air shed with industrial expansion.
So the answer to the question can the valley “handle industrial expansion” after the flawed and limited report from the provincial government is not “yes,” but “we don’t know yet.”
It appears that the report is part of Christy Clark’s ongoing campaign that LNG will save the provincial economy.
There are two factors the report ignores.
First the energy companies are going to make their final investment decision on cold hard facts, including their own assessment of the potential problems from the air shed, not spin from the provincial government.
Second, until there is a proper air shed study, the First Nations, including the Haisla in Kitimat, the Gitga’at at Hartley Bay, the Kitselas in Terrace will not have solid evidence to make a decision on the details of the LNG or refinery development on their traditional territory and increased ship traffic along the coast and that will come into immediate conflict with the Supreme Court ruling on the Tsilhqot’in decision and the finding that “Whether a particular use is irreconcilable with the ability of succeeding generations to benefit from the land will be a matter to be determined when the issue arises.”
There is a new Orwellian phrase used by both the federal and provincial government. Every report is “independent” and “science-based,” although all they all tend to support the policy of the commissioning agency.
What the Kitimat Valley, Douglas Channel and the Terrace region need is a truly independent and truly science based and truly comprehensive evaluation of the air shed. At the moment, that doesn’t exist. It should whether it comes from industry or if the local governments can find the budget to fund a proper study or some combination of the two.
Links
Kitimat Airshed Assessment
RTA report Sulphur-dioxide-technical-assessment.html
(Scanned version of copy in Kitimat public library)
Related
Business in Vancouver
Kitimat airshed modelling has narrow focus
Vancouver Observer
Province’s air pollution study green lights LNG build-up, but ignores climate change
News release: Andrew Weaver MLA
New airshed study is a “nail in the coffin” for government LNG dreams in Kitimat
Kitimat can accommodate industrial growth, air shed study says. But where’s Northern Gateway?
The long awaited Kitimat air shed study, released by the province Friday, July 17, 2014, says “that with proper management, Kitimat’s ai rshed can safely accommodate new industrial growth” without major affects on either human health or the environment.
Link to news release : Study shows Kitimat airshed can handle new industrial development
The Kitimat Airshed Assessment looked at the cumulative effects of industrial air emissions, primarily sulphur and nitrogen oxides, and their potential impacts on both human health and the environment from
- Rio Tinto Alcan’s existing aluminium smelter and its planned modernization
- David Blacks proposed “Kitimat Clean” oil refinery at Onion flats
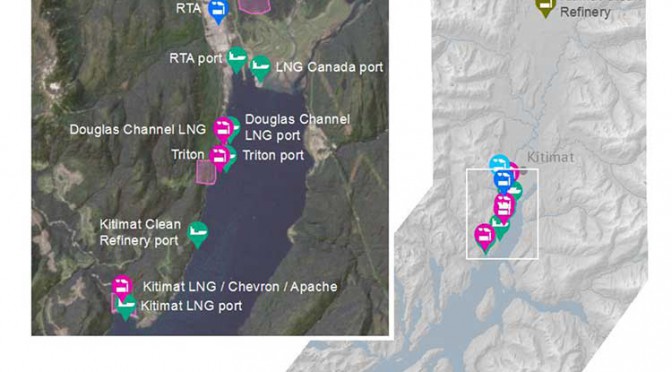
- Four proposed LNG facilities; Shell-led LNG Canada, Chevron lead Kitimat LNG, the floating Douglas Channel LNG at the old log dump and a second floating LNG project called Triton.
- BC Hydro gas turbine powered electrical generation facilities in Kitimat and near Terrace
- Predicted increased to marine shipping in Douglas Channel.
The study was divided into two zones.
Health results were first examined for Kitimat townsite, the Kitimat Industrial Service Centre and Kitamaat Village.
The wider study included Gitga’at Old Town, Hartley Bay (Kulkayu), Kitimat-Stikine, Kitselas, Kitsumkaylum, Kshish, and Terrace.
Enbridge missing
There was one big factor missing from the study, it does not include the Enbridge Northern Gateway project, although the consultants who did the study do cite a couple of the air quality studies that Enbridge filed with the Northern Gateway Joint Review Panel. That despite the fact the Joint Review Panel under Condition 82 required that Enbridge file with the NEB for approval, at least four months prior to commencing construction, “an Air Quality Emissions Management and Soil Monitoring Plan for the Kitimat Terminal.”
The JRP report acknowledged that emissions from the Enbridge terminal would be minimal but would contribute to the cumulative effect of pollutant emissions from other industries and required Enbridge to consult with the District of Kitimat, the environment ministries and other industries in planning for emissions.
The map from the airshed study also shows that the possible marine terminal for David Black’s proposed Kitimat Clean refinery project is at or close to where the proposed Enbridge Northern Gateway terminal would be.
Health and environment
The study looked at proposed emission levels and the effect of emissions elsewhere in the world and then compared those studies with the Kitimat Valley. It found that the risk of sulphur dioxide was “directly related to proximity to industrial area”–largely the Kitimat Service Centre area–and that there would be a minor increase in respiratory incidents of 0.5 per cent to 2 per cent, with a slight increase of nitrogen dioxide but those were within existing guidelines.
As for environmental impact, the study says nitrogen dioxide impacts will be low. There wil be “some increased risk of soil impacts” from sulphur dioxide. The study says there will be “no negative impacts to vegetation across all scenarios” but did find “potential for acidification” of seven small lakes. Lakelese Lake is not one of those affected.
The study also doesn’t include particulate matter and although it does consider climate change, did not take into consideration possible increase of green house gases in the Kitimat Valley.
The consultants, Esssa Technologies of Vancouver, based its findings on an earlier study by Rio Tinto Alcan on emissions from the Kitimat Modernization Project and worked on those findings by adding new industries and a greater area to the models they used.
The province and industry says they will continue to monitor air, water, soil and vegetation “to ensure these values are protected.”
The higher levels of sulphur dioxide emissions from the Rio Tinto Alcan Kitimat Mondernization Project will be allowed to continue under the current permit. Environment Minister Mary Polack told reporters that will only change if the current court challenge to the sulphur dioxide levels are successful.
| What Northern Gateway Joint Review said about emissions in the air shed | |
| Among the 209 conditions imposed on the Enbridge Northern Gateway project is No. 82, an Air Quality Emissions Management and Soil Monitoring Plan.
Northern Gateway must file with the NEB for approval, at least 4 months prior to commencing construction, an Air Quality Emissions Management and Soil Monitoring Plan for the Kitimat Terminal…
One of the things that the Joint Review Panel noted in requiring Enbridge Northern Gateway to have an updated plan and to collaborate with Kitimat and other industries is that levels of acceptable sulphur doixide in the atmosphere are changing and much of Northern Gateway’s modelling was based on standards that were becoming obsolete. In the Joint Review Panel report, section 8.7, the JRP said:
The provincial air shed report considered only two contaminants, sulphur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide. Northern Gateway said there would be minimal atmospheric emissions from the construction and operation of the pipeline. The focus was on the Kitimat marine terminal.
Northern Gateway said there “no exceedances of hazardous air pollutant guidelines were predicted as a result of the project itself” but there could be a cumulative effect with other industries in the Kitimat waterfront. The Joint Review Panel ruled:
|
Related
Kitimat air shed study raises more questions than it actually answers
Tropical fish, climate change migration growing threat to seagrass, kelp beds, study says
Tropical fish are migrating into what were once temperate water as a result of ocean warming and that poses a serious threat to the areas they invade, because they overgraze on kelp forests and seagrass meadows, according to a new study from the University of New South Wales in Australia
The study says the harmful impact of tropical fish is most evident in southern Japanese waters and the eastern Mediterranean, where there have been dramatic declines in kelps.

There is also emerging evidence in Australia and the US that the spread of tropical fish towards the poles is causing damage in the areas they enter.
“The tropicalisation of temperate marine areas is a new phenomenon of global significance that has arisen because of climate change,” according to the study lead author, Dr. Adriana Verges, of the University of New South Wales.
“Increases in the number of plant-eating tropical fish can profoundly alter ecosystems and lead to barren reefs, affecting the biodiversity of these regions, with significant economic and management impacts.”
The study is published in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B.
As the oceans have warmed and the climate has changed, hotspots are developing in regions where the currents that transport warm tropical waters towards the poles are strengthening.
Increased flow of the East Australian Current, for example, has meant waters south-east of the continent are warming at two to three times the global average.
Tropical fish are now common in Sydney Harbour during the summer months.
Japan, the east coast of the US, northern Brazil and south eastern Africa are also strongly influenced by coastal currents that transport warm tropical waters.
“In tropical regions, a wide diversity of plant-eating fish perform the vital role of keeping reefs free of large seaweeds, allowing corals to flourish. But when they intrude into temperate waters they pose a significant threat to these habitats. They can directly overgraze algal forests as well as prevent the recovery of algae that have been damaged for other reasons,” Dr Verges said.
Tropical fish expanding their ranges into temperate areas include unicornfish, parrotfish, and rabbitfish.
The study authors include researchers from Australia, the US, Spain, Singapore, the UK and Japan.
Kelp disappears in southern Japan
The study reports that more than 40 per cent of the kelp and algal beds have disappeared since the 1990s, a phenomenon known in Japan as isoyake.
Tropical species including rabbitfish and parrotfish appear to be mainly responsible.
Although these fish have been present for a long time, their annual grazing rates have increased dramatically as ocean temperatures in winter have risen. Corals now dominate the ecosystem in many locations. The changes have led to the collapse of the abalone fishery.
Rabbit fish expand in eastern Mediterranean
Tropical fish moved into the eastern Mediterranean from the Red Sea after the opening of the Suez Canal. In recent decades, rabbitfish numbers have increased, resulting in hundreds of kilometres of deforested areas and a 40 per cent decrease in the variety of marine species.
As the Mediterranean warms the rabbitfish are expanding their range westward, putting other shallow ecosystems at risk.
Gulf of Mexico
There has been a more than 20-fold increase in the number of parrotfish in the Gulf of Mexico – a species which consumes seagrass at five times the rate of native grazers. The number of plant-eating green turtles and manatees has also increased.
Australia
In Western Australia, emerging evidence suggests that increases in the number of tropical fish are preventing the recovery of kelp forest damaged by a heat wave in 2011.
In eastern Australia, kelp has disappeared from numerous reefs in the past five years and Dr Verges’ research suggests intense grazing by tropical fish on the kelp preceded this.
Rebar in hatcheries could distort navigation sense in young salmon and trout
Iron and steel in hatcheries, including rebar supporting concrete structural elements, could be distorting the ability of salmon and trout to navigate using the earth’s magnetic fields according to a study released today by Oregon State University.
The exposure to iron and steel distorts the magnetic field around the young fish, affecting the fish’s “map sense” and their ability to navigate, said Nathan Putman, who led the study while working as a postdoctoral researcher in the Oregon Department of Fisheries and Wildlife, part of OSU’s College of Agricultural Sciences.
For decades, scientists have studied how salmon find their way across vast stretches of ocean.
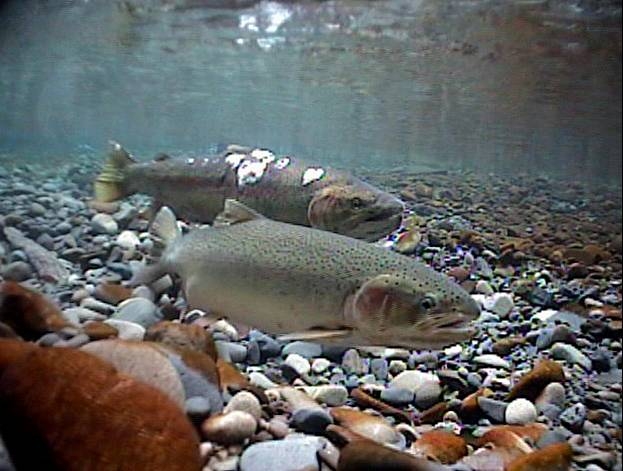

In a study last year, Putman and other researchers presented evidence of a correlation between the oceanic migration patterns of salmon and drift of the Earth’s magnetic field. They confirmed the ability of salmon to navigate using the magnetic field in experiments at the Oregon Hatchery Research Center.
That earlier research confirmed that fish possess a map sense, determining where they are and which way to swim based on the magnetic fields they encounter.
“The better fish navigate, the higher their survival rate,” said Putman, who conducted the research at the Oregon Hatchery Research Center in the Alsea River basin last year. “When their magnetic field is altered, the fish get confused.”
Subtle differences in the magnetic environment within hatcheries could help explain why some hatchery fish do better than others when they are released into the wild, Putman said.
The study suggests that stabilizing the magnetic field by using alternative forms of hatchery construction may be one way to produce a better yield of fish, he said.
“It’s not a hopeless problem,” he said. “You can fix these kinds of things. Retrofitting hatcheries with non-magnetic materials might be worth doing if it leads to making better fish.”
The new findings follow the earlier research by Putman and others that confirmed the connection between salmon and the Earth’s magnetic field.
Researchers exposed hundreds of juvenile Chinook salmon to different magnetic fields that exist at the latitudinal extremes of their oceanic range.
Fish responded to these “simulated magnetic displacements” by swimming in the direction that would bring them toward the center of their marine feeding grounds.
Putman repeated that experiment with the steelhead trout and achieved similar results. He then expanded the research to determine if changes to the magnetic field in which fish were reared would affect their map sense. One group of fish was maintained in a fiberglass tank, while the other group was raised in a similar tank but in the vicinity of iron pipes and a concrete floor with steel rebar, which produced a sharp gradient of magnetic field intensity within the tank. Iron pipes and steel reinforced concrete are common in fish hatcheries.
The scientists monitored and photographed the juvenile steelhead, called parr, and tracked the direction in which they were swimming during simulated magnetic displacement experiments. The steelhead reared in a natural magnetic field adjusted their map sense and tended to swim in the same direction. But fish that were exposed to the iron pipes and steel-reinforced concrete failed to show the appropriate orientation and swam in random directions.
More research is needed to determine exactly what that means for the fish. The loss of their map sense could be temporary and they could recalibrate their magnetic sense after a period of time, Putman said. Alternatively, if there is a critical window in which the steelhead’s map sense is imprinted, and it is exposed to an altered magnetic field then, the fish could remain confused forever, he said.
“There is evidence in other animals, especially in birds, that either is possible,” said Putman, who now works for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. “We don’t know enough about fish yet to know which is which. We should be able to figure that out with some simple experiments.”
Putman’s findings were published this week in the journal Biology Letters. The research was funded by Oregon Sea Grant and the Oregon Department of Fish and Wildlife, with support from Oregon State University. Co-authors of the study are OSU’s David Noakes, senior scientist at the Oregon Hatchery Research Center, and Amanda Meinke of the Oregon Hatchery Research Center.
Kitimat Council urges heavy turnout for North Coast Draft Marine Plan meeting

District of Kitimat Council has urged residents to turn out in large numbers for consideration of the North Coast Draft Marine Plan at the Kitimat Valley Institute Tuesday, May 13, from 5:30 to 8:30.
In introducing the motion, Mayor Joanne Monaghan said she was worried that not enough Kitimatians, especially charter operators, boaters and fishers were aware of the meeting.
Another council member privately said he was worried that the Open House and Forum weren’t publicized enough so that the town could be checked off as having “been consulted.”
Residents can download the plan from the Mappocean website at http://mappocean.org/north-coast/draft-plan-for-input/.
MAPP stands for Marine Planning Partnership for the North Pacific Ocean.
According to the documents the purpose of the North Coast Marine Plan “is to provide recommendations for achieving a sustainable balance between ecosystem health, social and cultural well-‐being and economic development through an ecosystem-‐based approach to planning and management.”
The plan is all about managing “common First Nation and provincial interests related to marine areas.”
The parners include the province and the Skeena First Nations Stewardship Society (NCSFNSS), representing the Metlakatla, Kitsumkalum, Kitselas, Haisla, Gitga’at, and Gitxaala Nations.
According to the doucments the North Coast plan area covers 27,000 kilometres of coastline;
that is indented with deep fjords and dotted with thousands of islands. It is a region of profound beauty, significant ecological diversity and remarkable cultural richness. Prince Rupert, Terrace and Kitimat are the largest communities in the North Coast plan area, which supports an overall population of approximately 42,000.
According to the summary of the plan:
The physical complexity of the North Coast includes a range of ecosystem types, including important estuaries that support distinct marine ecosystems and species. A diverse range of economic and community activities occur within the North Coast plan area. Commercial fisheries and associated processing facilities and logging have supported communities along the coast since the early 1900s. These activities continue to be important to the well-‐being of coastal communities. Port activities centered around the communities of Prince Rupert, Kitimat and Stewart, and active recreational fishing and tourism sectors, continue to be strong economic drivers in the area. North Coast First Nations living in the region have distinct cultural and spiritual heritages that are intricately linked to the marine environment and the long-‐standing sustainable use and management of marine resources.
The plan appears to overlap some areas where there have been environmental assessments of the Northern Gateway and the numerous liquified natural gas proposals.
The plan summary goes on to say:
The draft plan brings together science and Aboriginal knowledge, input from the technical staff of NCSFNSS (representing the Gitga’at, Gitxaała, Metlakatla, Kitsumkalum, Kitselas and Haisla Nations) and the Province. Key information and direction was provided by First Nations strategic marine use plans and existing provincial planning and policy documents.
Ecological, cultural and social and economic data sources were compiled and analysed by the joint technical team and contract support. Relevant background scientific reports and technical documents from the Pacific North Coast Integrated Management Area (PNCIMA) process were also used, along with the BC Marine Conservation Analysis. Additional information was drawn from government reports and publications, academic literature, industry or sector publications, discussions with experts and local knowledge. Advice was also incorporated from the North Coast Marine Plan Advisory Committee and public and stakeholder engagement.
The Pacific North Coast Integrated Management Area process was killed by the Harper government in the fall of 2011 . The decision to kill the PNCIMA was officially for budget reasons, but general speculation at the time was that Harper and then Natural Resources Minister Joe Oliver wanted to kill PNCIMA as one way of ensuring the government could push through the Northern Gateway project. The MAPP program was set up by the province and First Nations as a reaction to Harper’s decision.
Genetics show stronger pine beetle evolving; stream flow increases in infected forests: studies
A new study, based at the University of Alberta, released this week, indicates that natural selection may be making the mountain pine beetle more tolerant of colder temperatures and that the beetle may be evolving the ability to fly longer distances.
A second study, from the Colorado School of Mines, also released this week, is tracking how the extent of pine beetle infected or killed trees in forests is changing ground water and stream flows.
The mountain pine beetle infestation has wreaked havoc in North America, across forests from the American Southwest to British Columbia and Alberta. Millions of hectares of forest have been lost, with severe economic and ecological impacts from a beetle outbreak ten times larger than previous ones.
Dust from beetle killed wood is believed partially responsible for the explosions at the Lakeland Mill in Prince George and the Babine Forest Products mill in Burns Lake. The explosion in early 2012 at the Babine Forest Products mill killed two workers and injured another twenty. The Lakeland Mill explosion killed two workers and injured twenty four others.
As part of the fight to contain the mountain pine beetle, scientists recently sequenced the pine beetle genome.
Using that genome, Jasmine Janes and colleagues at the University of Alberta, with assistance from the University of British Columbia and the University of Northern British Columbia, used genetics to track how the pine beetle was able to expand its range so rapidly. The study was published in Molecular Biology and Evolution.
Studied at molecular level
While teams of researchers have tracked the path of the pine beetle across BC on the ground, how the beetle spread so easily “is only beginning to be understood at the molecular level,” the study says.
Pine beetles were collected from 27 sites in Alberta and British Columbia. The University of Alberta scientists were especially interested in how the pine beetle was able to jump across the Rockies, something that earlier researchers believed would not happen.
By looking at the genetic markers, the team concluded that the pine beetle may have been able to spread by adjusting its cellular and metabolic functions to better withstand cooler climates and facilitate a larger geographic dispersal area.
In an e-mail to Northwest Coast Energy News, Janes said the research looked at genomic signatures to find out how the beetle had been able to spread into Alberta – where did it come from, what route did it take and how did it overcome the physical and climatic barriers that we had always assumed?
The research discovered that there are two genetically different populations of pine beetles, one from the south of British Columbia and Alberta and one in the north. Another group of pine beetles, found near Valemount, “were harder to classify as being from either north or south genetically. The beetles in this area were showing higher genetic diversity.”
The pine beetle has always been around and killed older trees (called “low quality hosts”), helping to renew the ecosystem. There were also larger five-year infestations that occurred on a 20 to 40 year cycle. The current pine beetle “epidemic” in BC has gone on now for more than 20 years, with the pine beetle “observed in previously unrecorded numbers” over a much wider area
It is generally believed that climate change has help the pine beetle survive milder winters.
The study notes:
Successful establishment of mountain pine beetle on pure jack pine in northern Alberta has raised concerns that the mountain pine beetle will continue to expand its range into the vast boreal forest of jack pine that extends across North America from the Northwest Territories to the Atlantic Coast.
The teams concludes that one group of the beetles originated in southwestern BC perhaps from Whistler or Manning Park. Then the beetles spread north up the west coast of BC toward Houston “with rapid population size increases in central and northern BC and then dispersed long distances with prevailing winds toward the east and Alberta.”
Some of the beetles from southwestern BC appear to have taken a different route, moving more slowly eastward in the south of BC toward Crowsnest Pass area and then moving northward along the base of the Rockies, Janes said, adding. “Our research suggests that these two routes have then met in the middle again, around Valemount and that is why we see the genetic patterns across the landscape that we observed.”
Selective pressure
The second part of the research was answering the question of how the beetles were able to do this. How could they withstand the colder temperatures to spread further north and east?
To answer the scientists used the same genetic markers (single nucleotide polymorphisms) to conduct “selective sweeps” of the beetle genome. The sweeps look for unusual genetic markers that could indicate the beetles are under “selective pressure.”
The study looked at specific functions in the beetle: the genes that govern “actin filaments” that “control muscle contractions like shivering and moving wings”; “the synthesis of cholesterol that provides energy for metabolic activities” and transport of ions across cell membranes.
Normally, female pine beetles can only fly short distances to find a new host tree to lay eggs. They can travel longer distances if they are up in the tree canopy and are then carried by the wind. Stronger pine beetles that can fly longer distances show the threat is likely evolving.
The study concludes that Canadian Mountain Pine Beetle range expansion:
may continue as populations are currently exhibiting signals of selection. These signals suggest ongoing adaptation of metabolic and cellular processes that could potentially allow them to withstand colder temperatures, shift developmental timing and facilitate longer dispersal flights.
Janes said further research is required to fully validate and understand these signatures of selection, but it does suggest that the beetle is adapting and that is why it “may have been able to breach the Rocky Mountains”
Water and trees

The Colorado study asked how all those dead trees are changing stream flow and water quality?
“The unprecedented tree deaths caused by these beetles provided a new approach to estimating the interaction of trees with the water cycle in mountain headwaters like those of the Colorado and Platte Rivers,” said Reed Maxwell a hydrologist at the Colorado School of Mines.
Maxwell and colleagues have published results of their study of beetle effects on stream flows in this week’s issue of the journal Nature Climate Change.
As the trees die, they stop taking up water from the soil, known as transpiration. Transpiration is the process of water movement through a plant and its evaporation from leaves, stems and flowers.
The “unused” water then becomes part of the local groundwater and leads to increased water flows in nearby streams.
“Large-scale tree death due to pine beetles has many negative effects,” says Tom Torgersen of the US National Science Foundation’s Directorate for Geosciences and program director for the NSF’s Water, Sustainability and Climate program.
“This loss of trees increases groundwater flow and water availability, seemingly a positive,” Torgersen says.
“The total effect, however, of the extensive tree death and increased water flow has to be evaluated for how much of an increase, when does such an increase occur, and what’s the water quality of the resulting flow?”
Under normal circumstances, green trees use shallow groundwater in late summer for transpiration.
Red- and gray-phase trees–those affected by beetle infestations–stop transpiring, leading to higher water tables and greater water availability for groundwater flow to streams.
The Colorado study shows that the fraction of late-summer groundwater flows from affected watersheds is about 30 per cent higher after beetles have infested an area, compared with watersheds with less severe beetle attacks.
“Water budget analysis confirms that transpiration loss resulting from beetle kill can account for the increase in groundwater contributions to streams,” write Maxwell and scientists Lindsay Bearup and John McCray of the Colorado School of Mines, and David Clow of the U.S. Geological Survey, in their paper.
Dead trees create changes in water quality
“Using ‘fingerprints’ of different water sources, defined by the sources’ water chemistry, we found that a higher fraction of late-summer stream flow in affected watersheds comes from groundwater rather than surface flows,” says Bearup.
“Increases in stream flow and groundwater levels are very hard to detect because of fluctuations from changes in climate and in topography. Our approach using water chemistry allows us to ‘dissect’ the water in streams and better understand its source.”
With millions of dead trees, adds Maxwell, “we asked: What’s the potential effect if the trees stop using water? Our findings not only identify this change, but quantify how much water trees use.”
An important implication of the research, Bearup says, is that the change can alter water quality.
The new results, she says, help explain earlier work by Colorado School of Mines scientists. “That research found an unexpected spike in carcinogenic disinfection by-products in late summer in water treatment plants.”
Where were those water treatment plants located? In bark beetle-infested watersheds.
The TRIA project (a collaboration of researchers at the University of Alberta, University of British Columbia, University of Montreal, University of Northern British Columbia). The TRIA project investigates the physiology, genetics and ecology of all three players in the mountain pine beetle system – the pines (lodgepole and jack pine, and their hybrids), the beetle and the fungus (several types).
The Colorado study is funded by the National Science Foundation’s (NSF) Water, Sustainability and Climate (WSC) Program. WSC is part of NSF’s Science, Engineering and Education for Sustainability initiative.
Rio Tinto donates $19 million Pebble Mine stake to charity: Financial Times
Britain’s Financial Times is reporting that Rio Tinto has donated its stake in Alaska’s controversial Pebble Mine to two Alaska charities, one run by a local First Nation.
Rio Tinto donates Alaska copper mine stake to charities (registration/subscription required)
Rio Tinto had a 19 per cent stake in Northern Dynasty, a Vancouver-based mining company whose main asset is the Pebble project in Alaska.
The FT reports that Pebble is one of the world’s largest known undeveloped copper resources. The project is mired in disagreement because of concern over its potential effect on salmon stocks.
The FT report says the US Environmental Protection Agency said that it would investigate whether fisheries in the region could be protected. The EPA investigation stops any award of environmental permits for the mine in the meantime, and could lead to a permanent block on the project by the EPA.
According to the report, Rio Tinto said it would donate its shares in Northern Dynasty – worth about $19 million Canadian – to two charitable foundations in Alaska: the Alaska Community Foundation, which funds educational and vocational training, and the Bristol Bay Native Corporation Education Foundation, which supports educational and cultural programmes in the region.
The Pebble Mine would be near rich salmon rivers which flow into Bristol Bay, Alaska. Opponents of the project fear that the giant mine would irreversibly damage salmon stocks for centuries to come.
Related:
Pension funds pressure Rio Tinto to dump out of controversial Alaska Pebble Mine