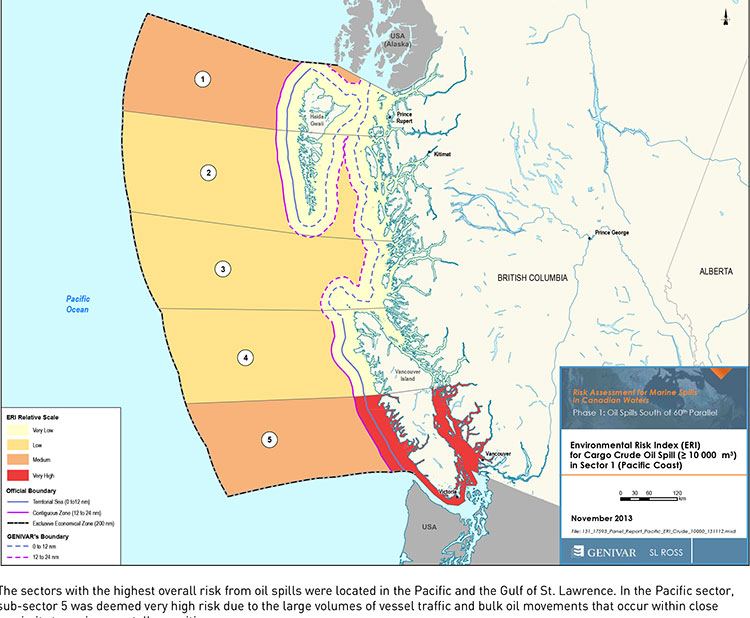
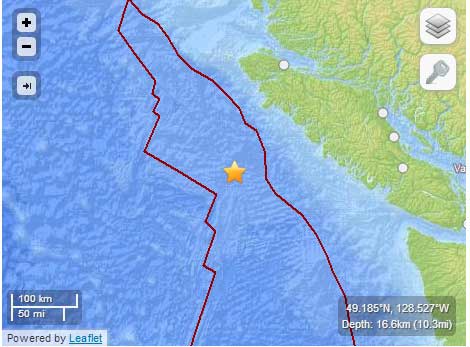
Here are edited portions of the EIS assessment for a major oil terminal at Prince Rupert
Environmental Setting
The EIS says “the local surface geology at the Prince Rupert site consists of bedrock (granitic rocks) overlain by glacial outwash and a thin soil cover.” and goes on to note that “Prince Rupert is located along the coastal region of Canada, which is seismically active.”
Potential Impacts
At Prince Rupert, depth to bedrock is expected to be relatively shallow, so rock ripping and some blasting could be necessary. The impacts of rock ripping and blasting are limited to the immediate area and would not result in any significant impacts to the underlying or nearby geology. Excavation activities, erosion of fossil beds exposed due to grading, and unauthorized collection can damage or destroy paleontological resources during construction.
(The report notes that The potential for finding paleontological resources in the areas that would be disturbed is unknown. But the area of the coast has been heavily metamorphisized and most fossils, so far, have been found further inland, largely along the Copper River near Terrace)
In terms of geologic hazards, the Prince Rupert terminals would be located along the coastal region of Canada, which is seismically active. In addition, the presence of steep slopes increases the risk of landslides and the port’s coastal location increases the risk of flooding…. The Prince Rupert rail terminals and port facilities would be designed to withstand potential seismic hazards and flooding…
Construction of the proposed terminals and port expansion in Prince Rupert would result in the disturbance of approximately 3,500 acres (1,400 hectares) of land for the construction of the rail terminal complex and approximately 1,200 acres (487 hectares) for the expansion of the port. Potential impacts to the soils resources of the area could result from vegetation clearance, landscape grading, and recontouring to ensure proper drainage, the installation of storm water drainage systems, construction of the required infrastructure, and other construction activities.
One of the primary concerns during construction activities is soil erosion and sedimentation.
Potential impacts to soils from erosion are expected to occur in areas where the slopes are greater than 20 per cent and where the erosion potential due to their nature is high. Based on available landscape and soils information, the soils found in the area are not highly erodible and the required infrastructure would be located in areas that are relatively flat. Therefore, the impact of the proposed terminal complex and port construction activities on soil erosion would be minor.
Groundwater
Environmental Setting
The Prince Rupert Terminals and port expansion would occur in British Columbia on Kaien Island, which receives about 102 inches of rainfall per year. The terminals would be located on an inlet that is part of the eastern Pacific Ocean on the Venn Passage near the much larger Inland Passage, which extends from Washington State to Alaska along the islands and mainland of British Columbia, Canada. Venn and Inland Passages are marine (salt water) waterbodies. The islands consist of bedrock (granitic rocks) overlain by glacial outwash and a thin soil cover.
Groundwater is shallow, poor quality, and unused. Drinking water is derived from lakes on the mainland. Water quality in the terminal complex area is seawater and inland brackish.
Potential Impacts
During construction of the facilities at Prince Rupert, the primary potential impacts to groundwater would be spills or leaks from construction equipment. Mitigation for these impacts includes having in place appropriate plans in place and appropriate cleanup materials available.
During operations of the facilities at Prince Rupert, the primary potential impacts to groundwater would again most likely be spills or leaks from operation equipment or associated with crude oil unloading of railcars. Although the initial impacts of potential releases or spills may be contained or limited to soil, potential impacts to groundwater may occur depending on the depth to groundwater, soil characteristics (e.g., porosity, permeability), spill volume and extent, and whether the spill reaches surface water bodies, some of which are interconnected to groundwater.
Surface Water
Environmental Setting
The upland character surrounding the potential Prince Rupert terminal area is dominated by bog forest uplands and the flowing surface water bodies are predominantly precipitation- and shallow groundwater-fed intermittent streams. Some open waterbodies are present in the southeast portion of Kaien Island. Tidal shore zones are of a rugged and rocky nature and receive wave energy generated by naturally occurring fetch and large wakes from marine traffic. Winter winds are strong and from the southeast to southwest, with surface currents predominantly northward from the Hecate Strait. Lighter summer winds have less influence on currents and allow freshwater runoff from land and deep water tidal effects to exert more control and provide variation in summer current patterns. Significant wind and tidal mixing tend to occur where waters are shallow and around islands and rocky points of land. The coastal landscape is predominantly fjords carved into the granitic Coast Mountains, created by the last of several glacial periods approximately 12,000 years ago. Shores tend to be rocky and steep with beaches restricted to sheltered areas adjacent to estuaries and the navigable straits and channels provide a wide variety of exposures and habitats.
Potential Impacts
Construction of the facilities at Prince Rupert would disturb approximately 4,700 acres. The primary potential impacts to surface waters include erosion and sedimentation and spills/leaks of hazardous materials. Mitigation for these impacts includes having in place appropriate SPCC plans in place and appropriate cleanup materials available.
During operations, the primary potential impacts to surface waters include storm water runoff, spills, or leaks from operation equipment or associated with crude oil unloading of railcars.
Provision of storm water management measures would mitigate the impacts of stormwater runoff.
Terrestrial Vegetation
Environmental Setting
The Prince Rupert terminals and port facilities would be located in the Coastal Gap Level III Ecoregion. The vegetation immediately adjacent to the Pacific Ocean includes stunted, opengrowing western red cedar, yellow cedar, and western hemlock with some stunted shore pine and Sitka spruce . There are also open areas present within the affected areas. It is unclear if biologically unique landscapes or vegetation communities of concern exist within the proposed Prince Rupert terminal complex boundary.
Potential Impacts
The proposed rail terminal complex and port facilities at Prince Rupert would require the clearing of up to 4,700 acres of natural vegetation, most of which is forested based on aerial photo interpretation. There does not appear to be any biologically unique landscapes or communities of conservation concern within the terminal complex boundary. Nearly all of these impacts would be permanent as natural habitats are converted for use as rail terminals and port facilities.
Wildlife
Environmental Setting
Many wildlife species use this coastal area for hunting, foraging, roosting, breeding, and nesting (Tourism Prince Rupert 2012). Wildlife characteristic of this ecoregion include grizzly bear (Ursus arctos horribilis), black bear (Ursus americanus), mountain goat (Oreamnos americanus), black-tailed deer (Odocoileus hemionus
columbianus), wolf (Canis lupus), moose (Alces alces), mink (Mustela sp.), bald eagle
(Haliaeetus leucocephalus), seabirds, shorebirds, waterfowl, and grouse (Tetraoninae)
The Prince Rupert terminal complex would be located in the Northern Pacific Rainforest(Region 5) bird conservation region, which is an ecologically distinct region in North America…
The coast of the Northern Pacific Rainforest is characterized by river deltas
and pockets of estuarine and freshwater wetlands set within steep, rocky shorelines. These wetlands provide critical nesting, wintering, and migration habitat for internationally significant populations of waterfowl and other wetland-dependent species. The area includes major stopover sites for migrating shorebirds, especially western sandpipers (Calidris mauri) and dunlins (Calidris alpina). Black oystercatchers (Haematopus bachmani), rock sandpipers (Calidris
ptilocnemis), black turnstones (Arenaria melanocephala), and surfbirds (Aphriza virgata) are common wintering species. Nearshore marine areas support many nesting and wintering sea ducks. Many seabirds breed on offshore islands, including important populations of ancient murrelet (Synthliboramphus antiquus), rhinoceros auklet (Cerorhinca monocerata), tufted puffin (Fratercula cirrhata), common murre (Uria aalge), western gull (Larus occidentalis), glaucouswinged gull (Larus glaucescens), and Leach’s storm-petrel (Oceanodroma leucorhoa). Pelagic
waters provide habitat for large numbers of shearwaters (Calonectris spp. and Puffinus spp.), storm-petrels (Hydrobatidae), and black-footed albatross (Phoebastria nigripes)
Potential Impacts
Direct impacts could occur due to vegetation removal or conversion, obstructions to movement patterns, or the removal of native habitats that may be used for foraging, nesting, roosting, or other wildlife uses (Barber et al. 2010). Indirect impacts to wildlife are difficult to quantify and are dependent on the sensitivity of the species, individual, type and timing of activity, physical parameters (e.g., cover, climate, and topography), and seasonal use patterns of the species (Berger 2004). Most of these impacts would be essentially permanent.
Fisheries
Environmental Setting
Prince Rupert is an important deepwater port and transportation hub of the northern coast of British Columbia. It is located on the northwest shore of Kaien Island, which is connected to the mainland by a short bridge. The town of Prince Rupert is just north of the mouth of the Skeena River, a major salmon-producing river. Key commercial fisheries include Pacific salmon, halibut, herring, and groundfish, which are processed from Prince Rupert.
Prince Rupert area supports a high density of streams and rivers that host an array of valuable recreational fisheries for salmon, steelhead (anadromous rainbow trout), rainbow trout, lake trout, cutthroat trout, char, Arctic grayling, and northern pike .
Potential Impacts
New impacts to commercial and recreational fisheries’ habitats from the construction and operation of the facilities in Prince Rupert could include marine intertidal zones as well as fish spawning zones (e.g., herring), if present. There would likely be short-term impacts to the benthic (bottom dwelling) community during construction of the berths and mooring facilities. Bottom-dwelling
fish (i.e., halibut, flounder, and rockfish) and marine invertebrates (i.e., clams, mussels, crabs, and other bivalves and crustaceans) could potentially be impacted during construction as well, but these affects are expected to be minor and temporary or short-term in duration.
Additional shipping traffic would increase underwater sound because large vessels, including tankers, put out relatively high noise levels. Fish and other aquatic organisms (including invertebrates and marine mammals) use sound as a means of communication and detection within the marine acoustic environment. Increased shipping traffic could mask natural sounds by increasing the ambient noise environment from Prince Rupert Harbor and along the marine route to the Gulf Coast area. Long-lasting sounds, such as those caused by continuous ship operation, can cause a general increase in background noise and there is a risk that such sounds, while not causing immediate injury, could mask biologically important sounds, cause hearing loss in affected organisms, and/or have an impact on stress levels and on the immune systems of aquatic species.
Exotic and invasive species are sometimes transferred in the ballast water of tanker ships.
Monitoring and controls would need to be implemented to treat ballast water discharged into Prince Rupert Harbor such that invasive or exotic species would not be released into the marine environment.
Threatened and Endangered Species
This section focuses on animal and plant species present in the Prince Rupert area that are Canada SARA protected. As a coastal area along the Pacific Migratory Bird Route, and an area that receives a lot of precipitation and is heavily forested, many wildlife species inhabit the area, as discussed in Section 5.1.3.6, Wildlife. According to the British Columbia (B.C.) Conservation Data Centre (2012), only one SARA threatened/endangered species is known to occur in Prince Rupert—the green sturgeon (Acipenser medirostris), a Pacific Ocean inhabitant. In addition, several SARA special concern species occur in Prince Rupert, including western toad (Anaxyrus boreas), coastal tailed frog (Ascaphus truei), North American racer (Coluber constrictor), grey whale (Eschrichtius robustus), and Stellar sea lion (Eumetopias jubatus)
Potential Impacts
The green sturgeon is typically found along nearshore marine waters, but is also commonly observed in bays and estuaries. The expansion of the proposed port facility could have minor adverse effects on the green sturgeon, but the sturgeon could readily avoid the port area.
Increased shipping traffic at Prince Rupert and as the vessels transit to the Gulf Coast area refineries may affect the feeding success of marine mammals (including threatened and endangered species) through disturbance, because the noise generated by tankers could reduce the effectiveness of echolocation used by marine mammals to forage for food. Whales use underwater vocalizations to communicate between individuals while hunting and while engaged in other behaviors. Increased underwater noise from additional shipping traffic could disrupt these vocalizations and alter the behavior of pods of whales. Moreover, additional boat and
tanker traffic could also increase the potential for collisions between marine mammals and shipping vessels. These effects would be additive in nature and could potentially add to existing disturbance effects and collision risks caused by the current level of shipping traffic, commercial and recreational fishing, and cruise ship passage.
Land Use, Recreation, and Visual Resources
Environmental Setting
Land use, recreation, and visual resources for the Prince Rupert area where the new terminals and expanded port facilities would be built differ sharply from the other terminal sites. Prince Rupert is located on an inlet of the Pacific Ocean in a heavily forested area of British Columbia.
Urban land use is generally limited to the communities in and around the city of Prince Rupert, with some small outlying communities and villages in the area. Given Prince Rupert’s role as a terminus of the Alaska Ferry System, many people see the port and surrounding areas in a recreational context. The area is largely undeveloped and would be sensitive to changes in the visual landscape.
Potential Impacts
If constructed on previously undeveloped land, the new facilities would primarily impact mixed forest… The construction and operational impacts on land use, recreation, and visual resources at the Lloydminster, Epping, and Stroud terminal complex sites and along the Cushing pipeline route would be the same as for the Rail/Pipeline Scenario.
Socioeconomics
Environmental Setting
Population/Housing
Construction and operations activities are not expected to have a significant effect on population and housing for this scenario. Because construction and operations job estimates have not yet been determined for this scenario, worker requirements for Prince Rupert, Lloydminster, and Epping are assumed to be minor..additional temporary housing could be needed in Prince Rupert… Prince Rupert only has about 740 hotel/motel rooms
Local Economic Activity
Tanker infrastructure and operations would be affected as ships transport crude oil from Prince Rupert through the Panama Canal to Texas ports near Houston.
Direct construction expenditures for facilities at Prince Rupert would be approximately $700 million, with approximately 1,400 annual construction jobs, based on the cost estimates of the proposed Enbridge Northern Gateway marine terminal in Kitimat
Despite the large population of First Nations people in the Prince Rupert area, Canada does not have a similar definition to minorities as the Keystone report applied under US law and so it notes “Impacts to minority and low-income populations during construction and would be similar to those described for the proposed [Keystone] Project and could possibly result in increased competition for medical or health services in underserved populations. Canada does not define HPSA and MUA/P, so it is unknown whether or not the minority populations in Prince Rupert or Lloydminster exist in a medically underserved area.
Tax Revenues and Property Values
It says construction of a new terminal Prince Rupert would generate provincial sales taxes, goods and services taxes, and hotel taxes. Construction of the tank and marine terminals at Prince Rupert…would involve large numbers of road trips by heavy trucks to transport construction materials and equipment to and from the sites. Construction in Prince Rupert could also potentially involve vessel deliveries of material. This traffic could cause congestion on major roadways, and would likely require temporary traffic management solutions such as police escorts for oversize vehicles.
Cultural Resources
Despite the rich heritage of First Nations in the Prince Rupert area, the Keystone alternative study reported;
No cultural resources studies have been conducted for the Prince Rupert area. Review of aerial photographs shows that a small portion of the area that could potentially be developed has already been disturbed by development, including port facilities, structures, and roads. This preliminary review shows that most of the area appears undeveloped and would have the potential for intact buried cultural resources.
The report notes that “Any ground disturbance, especially of previously undisturbed ground, could potentially directly impact cultural resources.”
It goes on to note that the potential to
include intact buried cultural resources would require evaluation through research and cultural resources surveys. If cultural resources were identified, follow-up studies could be required. In general terms, the archaeological potential of heavily disturbed areas, such as might be found in active rail yards or within developed transportation corridors, is normally lower than in undisturbed areas.
Archaeological potential is also contingent upon factors such as access to water, soil type, and topography, and would have to be evaluated for each area to be disturbed. Aboveground facilities have the potential to indirectly impact cultural resources from which they may be visible or audible. The potential for increased rail traffic to contribute to indirect impacts would require consideration.
Air and Noise
The report also summarizes the possible green house gas emissions for the rail and tanker project as whole from Prince Rupert to the Gulf Coast refineres and notes that overall
On an aggregate basis, criteria pollutant emissions, direct and indirect GHG emissions, and noise levels during the operation phase for this scenario would be significantly higher than that of the proposed [Keystone XL] Project mainly due to the increased regular operation of railcars, tankers, and new rail and marine terminals.
Air Quality
The rail cars and tankers transporting the crudes would consume large amounts of diesel fuel and fuel oil each day….The criteria pollutant emissions would
vary by transportation segment, particularly during marine-based transit. Oil tankers traveling from the Prince Rupert marine terminal through the Panama Canal to Houston/Port Arthur pass through several different operational zones, including reduced speed zones leading into and out of the ports, North American Emission Control Areas where the use of low-sulfur marine fuel is mandated, and offshore areas where the tankers travel at cruise speeds.
During the return trip, tankers are filled with seawater (ballast) to achieve buoyancy necessary for proper operation, which affects the transit speeds of the vessel. Furthermore, the tankers spend several days loading or unloading cargo at each marine terminal with auxiliary engines running (an activity called hoteling). The tanker emissions accounted for return trips (i.e., both loaded cargo going south and unloaded cargo going north).
In aggregate, the total operational emissions (tons) estimated over the life of the project (50 years) are several times greater than those associated with the combined construction and operation of the proposed Keyston XL Project
Greenhouse Gases
Direct emissions of GHGs would occur during the construction and operation of the Rail/Tanker Scenario. GHGs would be emitted during the construction phase from several sources or activities, such as clearing and open burning of vegetation during site preparation, operation of on-road vehicles transporting construction materials, and operation of construction equipment for the new pipeline, rail segments, multiple rail and marine terminals, and fuel storage tanks.
Due to limited activity data, GHG emissions from construction of the Rail/Tanker Scenario were not quantified; however, these emissions would occur over a short-term and temporary period, so construction GHG impacts are expected to be comparable to the proposed [Keystone XL] Project.
During operation of the railcars and tankers that comprise this scenario, GHGs would be emitted directly from the combustion of diesel fuel in railcars traveling over 4,800 miles (7,725 km) and fuel oil in marine tankers traveling over 13,600 miles (21,887 km) round-trip.
The Rail/Tanker Scenario would also result in indirect emissions of GHGs due to the operation of 16 new rail terminals, an expanded port, and potential pumping stations. The new rail terminal in Prince Rupert would be projected to require 5 MW of electric power to operate, possibly bring indirect GHG emissions
Noise
Noise would be generated during the construction and operation of the Rail/Tanker Scenario. Noise would be generated during the construction phase from the use of heavy construction equipment and vehicles for the new pipeline, rail segments, and multiple rail and marine terminals, and fuel storage tanks. Due to limited activity/design data, noise levels from the construction of this scenario were not quantified; however, this noise would occur over a short term and temporary period, so construction noise impacts are expected to be comparable to those
of the proposed Project. During operation of the railcars and tanker ships that comprise this scenario, noise would be generated from the locomotives, movement of freight cars and wheels making contact with the rails as the train passes, train horns, warning bells (crossing signals) at street crossings, and tanker engines during hoteling and maneuverings at the new rail and marine terminals in Prince Rupert.
(Noise from ocean going vessels which is a concern for coastal First Nations and environmental groups is covered later on impact on wildlife)
Climate Change Effects on the Scenario
Environmental Setting
The Keystone study looks at the affects of climate change, but concentrates largely on the Gulf Coast beause the most of the Rail/Tanker Scenario was outside of the boundaries of the study, but it does note that the sea levels are projected to rise due to glacial melting and thermal expansion of the water. The rate, total increase, and likelihood of the rise is in part dependent on how rapid the ice sheets warm and is a source of ongoing scientific uncertainty.
The United States Global Change Research Program (USGCRP) estimates that sea level rise could be between 3 to 4 feet by the end of the century.
Increasing sea level projected due to climate changes as described above shifts the impact of mean high tide, storm surge, and saltwater intrusion to occur further inland and this would negatively affect reliable operation of the port infrastrucure for tanker traffic. Mitigation of these climate effects could be addressed by making engineering and operational changes at the port.
Potential Risk and Safety
Environmental Setting
The Rail/Tanker Option would combine the risk inherent in both pipeline and oil tanker
transport. However, the risks and consequences for using oil tankers to transport the hazardous materials are potentially greater than the proposed Project. Overall, crude oil transportation via oil tankers has historically had a higher safety incident rate than pipelines for fire/explosion, injuries, and deaths.
Spills have been reported while the vessel is loading, unloading, bunkering, or engaged in other operations
The main causes of oil tanker spills are the following:
• Collisions: impact of the vessel with objects at sea, including other vessels (allision);
• Equipment failure: vessel system component fault or malfunction that originated the release of crude oil;
• Fires and explosions: combustion of the flammable cargo transported onboard;
• Groundings: running ashore of the vessel; and
• Hull failures: loss of mechanical integrity of the external shell of the vessel.
From 1970 to 2011, historical data shows that collisions and groundings were the maincauses of oil tanker spills worldwide.
Potential Impacts
Loading and unloading of the railcars at tank farms near seaports could allow spills to migrate and impact seawaters and shorelines.
However, the loading and unloading are generally carried out under supervision and would be addressed promptly by the operators, limiting the potential migration and impacts of the spill to the immediate area.
Once the tanker is loaded and at sea, the propagation and impacts of a spill could become significant. Oil tankers may carry up to 2,000,000 bbl of oil
A release of oil at sea would be influenced by wind, waves, and current. Depending on the volume of the release, the spreading of oil on the surface could impact many square miles of ocean and oil birds, fish, whales, and other mammals and could eventually impact shorelines. Oil would also mix with particulates in sea water and degrade. As this occurs some oil will begin to sink and either be retained in the water column (pelagic) or settle to the ocean floor (sessile).
Pelagic oil could be consumed by fish or oil fauna passing though the submerged oil. Sessile oil could mix with bottom sediment and potentially consumed by bottom feeding fauna. Spills in ports-of-call could affect receptors similar to an open ocean release but also could temporarily affect vessel traffic and close ports for cleanup activities.
The identification of key receptors along the rail route alternative was not available for this evaluation. Therefore a comparison to the proposed project was not completed.
Surface Water
The Lloydminster to Prince Rupert portion of this route would begin in the western plains at the Saskatchewan/British Columbia border and travel west through an area of high-relief mountains with large valleys, referred to as the Cordillera region. From a water resource perspective, the plains region of Canada is characterized by relatively large rivers with low gradients. The plains rivers drain the Rocky Mountains to the Arctic Ocean. The Cordillera region is largely composed of northwest-southwest trending mountain ranges that intercept large volumes of Pacific
moisture traveling from the west towards the east. River systems in this region are supplied by a combination of seasonal rainfall, permanent snowfields, and glaciers.
The following are larger rivers crossed by the existing rail lines between Lloydminster and Prince Rupert:
• North Saskatchewan River, Alberta
• Pembina River, Alberta
• McLeod River, Alberta
• Fraser River, British Columbia
• Nechako River, British Columbia
• Skeena River, British Columbia
Wetlands
Spills within wetlands would most likely be localized, unless they were to occur in open, flowing water conditions such as a river or in the ocean. A crude oil spill in a wetland could affect vegetation, soils, and hydrology. The magnitude of impact would depend on numerous factors including but not limited to the volume of spill, location of spill, wetland type (i.e., tidal versus wet meadow wetland), time of year, and spill response effectiveness. The construction of additional passing lanes to accommodate increased train traffic resulting from this scenario could
result in permanent impacts to wetlands if passing lanes were constructed where wetlands occur.
However, as there is some leeway regarding the exact location of the passing lanes, it is expected that wetlands would be avoided by design.
Fisheries
The Rail/Tanker Scenario railroad route would cross numerous major streams and rivers in Canada, many of which support anadromous fish species such as salmon.
Anadromous species are those that spawn and rear in freshwater but migrate to the ocean at a certain size and age. Pacific salmon are large anadromous fish that support valuable commercial and recreational fisheries. Commercial fisheries for salmon occur in marine water and most recreational fishing for salmon occurs in freshwater. Salmon eggs are vulnerable to the effects of fine sediment deposition because female salmon deposit their eggs in stream bed gravels.
Despite this vulnerability, the overland railway route is not expected to present any new impacts to salmon unless there is a spill into its habitat, although the risk of spills does increase under this scenario due to the increase in the number of trains that would use the route.
Potential new impacts under the Rail/Tanker Scenario on commercially or recreationally significant fisheries along the route would be minor because the railroads that would be used are already built and in operation. However, the risk of an oil spill or release of oil or other materials still exists. The tanker portion of this route scenario is also subject to oil spill risk.
Threatened and Endangered Species
The rail route would cross over the Rocky Mountain region of western Alberta, which is inhabited by species such as the woodland caribou (Rangifer tarandus) (a SARA threatened species) and grizzly bear (a SARA special concern species). This region of British Columbia is home to a number of SARA threatened/endangered species, including the peregrine falcon (Falco peregrinus anatum) (SARA threatened), salish sucker (Catostomus sp.) (SARA endangered), white sturgeon (Acipenser transmontanus) (SARA endangered), caribou (southern mountain population) (SARA threatened), northern goshawk (Accipiter gentilis laingi) (SARA threatened), and Haller’s apple moss (Bartramia halleriana) (SARA threatened).
A number of additional SARA special concern species inhabit the regions of Canada that would be traversed by the Rail/Tanker Scenario, including but not limited to those special concern species expected to occur in the Prince Rupert region, and discussed above (B.C. Conservation Centre 2012).
Northwest Coast Energy News Special report links
What the Keystone Report says about Kitimat and Northern Gateway
What the Keystone Report says about the Kinder Morgan pipeline to Vancouver.
What the Keystone Report says about CN rail carrying crude and bitumen to Prince Rupert.
The State Department Environmental Impact Study of the railway to Prince Rupert scenario.
State Department news release
State Department Index to Supplemental Environmental Impact Study on the Keystone XL pipeline